Rangkaian Listrik Campuran (Mixed Electrical Circuits)
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, the host explains the concept of electrical circuits, focusing on series, parallel, and mixed circuits. The video begins with a comparison of series and parallel circuits, highlighting their differences and similarities, including how electrical flow behaves in each type. The host then introduces a mixed circuit, combining both series and parallel components, and explains how current flows through them, showing how different parts of the circuit behave when specific lights go out. The lesson concludes with a recap and invitation to follow future videos on similar topics.
Takeaways
- 😀 The video introduces the concept of mixed electrical circuits, focusing on series and parallel circuits.
- 😀 The series circuit involves lamps connected in a row, using fewer cables, but if one lamp goes out, all others will follow.
- 😀 In a series circuit, the brightness of the lamps is not the same.
- 😀 In contrast, a parallel circuit has lamps connected in branches, requiring more cables.
- 😀 In a parallel circuit, if one lamp goes out, the others remain on.
- 😀 The brightness of lamps in a parallel circuit is the same across all of them.
- 😀 Both series and parallel circuits share the feature of being closed circuits connected by electrical current.
- 😀 The lesson explains how to differentiate between series and parallel circuits using a Venn diagram.
- 😀 A mixed circuit is a combination of series and parallel circuits. For example, in the provided image, some lamps are arranged in series and others in parallel.
- 😀 If one lamp in a series section of a mixed circuit goes out, the lamps in that series will also go out, while lamps in parallel branches may continue to function.
- 😀 The video concludes by encouraging viewers to continue learning through future educational videos on the channel.
Q & A
What is the topic of the lesson in the video?
-The lesson is about mixed electrical circuits, focusing on series and parallel circuits.
What is the first concept discussed in the lesson?
-The first concept discussed is creating a Venn diagram comparing series and parallel electrical circuits.
How are the lightbulbs arranged in a series circuit?
-In a series circuit, the lightbulbs are arranged in a row, one after another.
What happens when one lightbulb goes out in a series circuit?
-If one lightbulb goes out in a series circuit, all the other bulbs will also go out because the circuit is broken.
What is the arrangement of lightbulbs in a parallel circuit?
-In a parallel circuit, the lightbulbs are connected in branches or separate paths.
What happens when one lightbulb goes out in a parallel circuit?
-If one lightbulb goes out in a parallel circuit, the other bulbs will remain on because the current can still flow through the other paths.
What is one key difference between series and parallel circuits?
-In a series circuit, the current passes through each component sequentially, while in a parallel circuit, the components are connected in separate branches allowing independent current flow.
What do series and parallel circuits have in common?
-Both series and parallel circuits are closed circuits, meaning the current flows through a continuous path.
What happens in a mixed circuit (series-parallel) when one lightbulb goes out?
-In a mixed circuit, if a lightbulb in the series section (e.g., L3) goes out, the others in that section (L4, L5) will also go out. However, lightbulbs in the parallel section (L1, L2) will still function because current can flow through other branches.
How does the current behave in a mixed electrical circuit?
-In a mixed circuit, the current flows through the series portion as one path, and through the parallel portion through multiple paths, ensuring that if one lightbulb in the parallel section goes out, the others remain unaffected.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

[NEW VERSION!] RANGKAIAN PARALEL DAN SERI PARALEL | Rangkaian Listik Arus Searah - Fisika Kelas 12
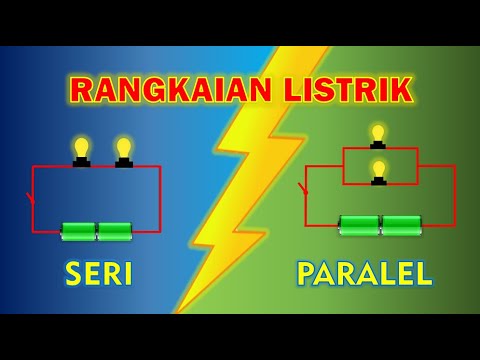
MEDIA PEMBELAJARAN RANGKAIAN LISTRIK SERI DAN PARALEL

PERSAMAAN DAN PERBEDAAN RANGKAIAN SERI DAN PARALEL

Resistive circuits in series
Hambatan Pengganti Rangkaian Seri, Paralel Dan Campuran

Listrik Dinamis-Rangkaian Listrik (Hukum Ohm) (Part 3)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)