[NEW VERSION!] RANGKAIAN PARALEL DAN SERI PARALEL | Rangkaian Listik Arus Searah - Fisika Kelas 12
Summary
TLDRThis educational video provides a detailed explanation of electrical circuits, focusing on series and parallel connections. The presenter breaks down key concepts like Ohm's law, Kirchhoff's laws, and the methods for calculating total resistance in both series and parallel circuits. Practical examples help viewers understand how to apply these principles to solve complex circuit problems, including mixed series-parallel circuits. By using clear notations and step-by-step approaches, the video equips learners with the tools needed to analyze and solve electrical circuit challenges efficiently.
Takeaways
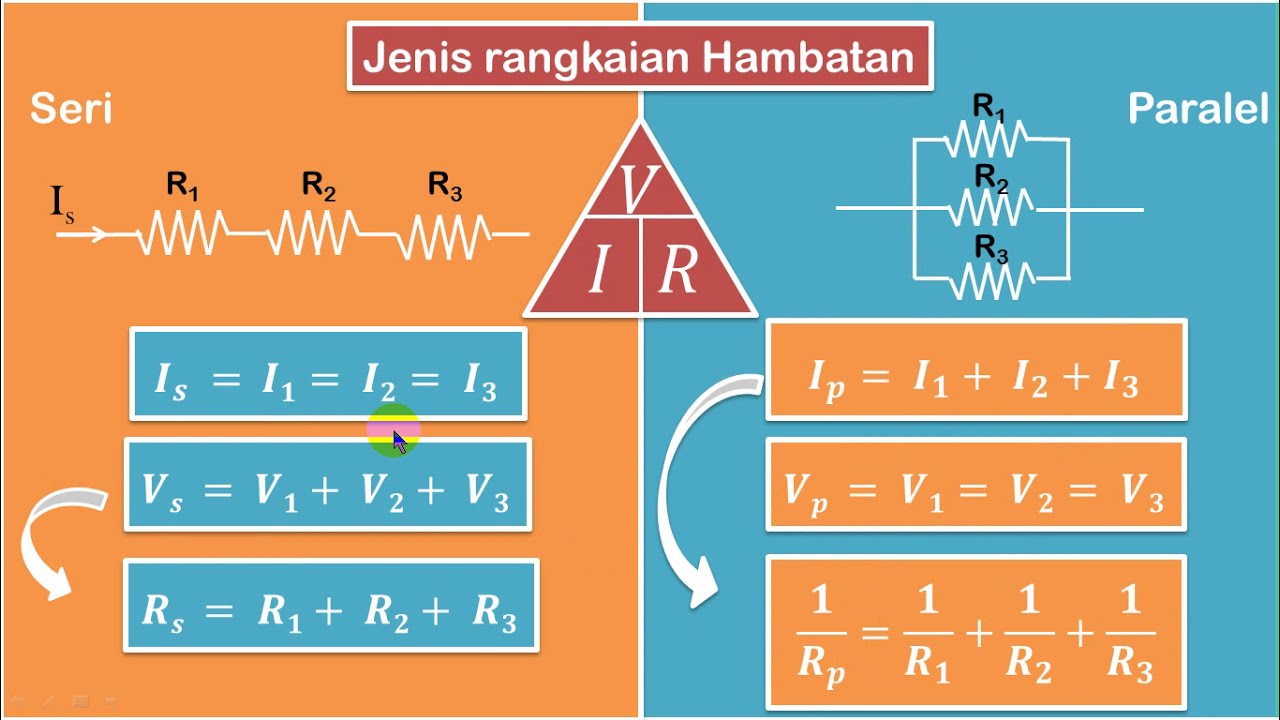
- 😀 **Series Circuit**: In a series circuit, the total resistance is the sum of individual resistances, and the current is the same through all components.
- 😀 **Parallel Circuit**: In a parallel circuit, the total resistance is calculated using the reciprocal sum of individual resistances, and the voltage is the same across all components.
- 😀 **Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL)**: The total current entering a junction is equal to the total current leaving the junction. This is critical for analyzing parallel circuits.
- 😀 **Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL)**: The sum of the voltages around any closed loop in a circuit is zero, which is particularly useful in series circuits.
- 😀 **Ohm's Law**: Voltage (V) = Current (I) × Resistance (R). This relationship is fundamental for solving electrical circuit problems.
- 😀 **Notations Matter**: When analyzing circuits, make sure to use correct notations for voltage, current, and resistance to avoid confusion during problem-solving.
- 😀 **Voltage in Parallel Circuits**: In parallel circuits, the voltage across all components is the same, unlike in series circuits where voltage is divided.
- 😀 **Current Distribution in Parallel Circuits**: In parallel circuits, the total current is divided among the branches, and each branch will carry a current based on its resistance.
- 😀 **Solving Mixed Circuits**: For circuits with both series and parallel components, first simplify parallel parts to an equivalent resistance, then proceed with the series components.
- 😀 **Step-by-Step Problem Solving**: To calculate total resistance, current, and voltage in a circuit, break the problem into smaller steps, such as solving for parallel sections before series sections.
Q & A
What is Kirchhoff's First Law (KCL) and how is it applied in parallel circuits?
-Kirchhoff's First Law states that the total current entering a junction is equal to the total current leaving the junction. In parallel circuits, this law is used to analyze how current splits between different branches. Each branch will have its own current, and the sum of the currents in all branches will equal the total current from the power source.
How does Ohm's Law apply to both series and parallel circuits?
-Ohm's Law (V = I * R) is essential in both series and parallel circuits. In series circuits, the same current flows through all resistors, and the total voltage is the sum of the individual voltages across each resistor. In parallel circuits, the voltage across each resistor is the same, and the total current is the sum of the currents through each branch.
What is the difference between series and parallel circuits in terms of voltage and current?
-In series circuits, the current is the same through all components, but the voltage divides across the resistors. In parallel circuits, the voltage is the same across each branch, but the current divides based on the resistance of each branch.
How do you calculate total resistance in a parallel circuit?
-In a parallel circuit, the total resistance (R_total) is found by taking the reciprocal of the sum of the reciprocals of the individual resistances. The formula is 1/R_total = 1/R1 + 1/R2 + ... for all resistors in parallel.
What is the importance of labeling components in a circuit diagram?
-Labeling components in a circuit diagram is crucial to avoid confusion and ensure that each element, such as resistance, voltage, and current, is correctly identified and calculated. Proper labeling helps in applying Ohm's Law and Kirchhoff's Laws accurately.
What does it mean for resistors to be in series, and how is their total resistance calculated?
-When resistors are in series, the current flows through each resistor in sequence. The total resistance (R_total) is simply the sum of the individual resistances: R_total = R1 + R2 + ... for all resistors in series.
In a mixed circuit with series and parallel resistors, how do you solve for the total resistance?
-In a mixed circuit, you first solve for the equivalent resistance of the parallel sections by using the parallel resistance formula. Then, treat the resulting equivalent resistance as a single resistor in series with the other resistors. Add up the resistances for the final total resistance.
Why is it important to use the correct notation for current and voltage in circuit analysis?
-Using correct notation for current (I) and voltage (V) ensures that the calculations are consistent with the laws of electricity. Incorrect notation can lead to confusion, especially when applying Kirchhoff's Laws and Ohm's Law, potentially resulting in wrong answers.
How do you determine the voltage across each resistor in a parallel circuit?
-In a parallel circuit, the voltage across each resistor is the same and equal to the voltage of the power source. This is because all resistors are connected across the same two points in the circuit.
What is the method for calculating the total current in a parallel circuit?
-To calculate the total current in a parallel circuit, you first find the total resistance using the parallel formula. Then, use Ohm's Law (I = V/R) with the total resistance to find the total current. The total current is the sum of the currents in each parallel branch.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Listrik Dinamis-Rangkaian Listrik (Hukum Ohm) (Part 3)

Video Pembelajaran IPA Rangkaian Listrik Seri dan Paralel menggunakan KIT
Rangkaian Listrik Campuran (Mixed Electrical Circuits)
Hambatan Pengganti Rangkaian Seri, Paralel Dan Campuran
IPA Kelas 9 : Listrik Dinamis 3 (Rangkaian Hambatan Seri dan Paralel)

Petunjuk Praktikum Membuat Rangkaian Listrik dan Pengukuran dengan Basicmeter
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)