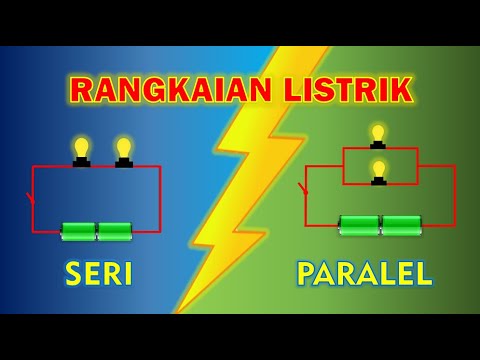
PERSAMAAN DAN PERBEDAAN RANGKAIAN SERI DAN PARALEL
Summary
TLDRThis educational video explains the differences between series and parallel circuits in electricity. It begins by defining open and closed circuits, demonstrating how each functions with lamps and batteries. The video then details the characteristics of series circuits, where components share a single pathway, causing brightness to decrease as more lamps are added. In contrast, parallel circuits allow multiple pathways, ensuring that if one lamp fails, the others remain lit. The lesson concludes with a demonstration of mixed circuits, highlighting practical applications for both series and parallel arrangements in home wiring and electrical installations.
Takeaways
- 😀 Understanding electrical circuits involves knowing the components connected to a voltage source for a specific function.
- 🔌 An open circuit means that the electrical flow is interrupted, preventing any devices from operating.
- 💡 A closed circuit allows current to flow, powering connected devices like light bulbs.
- ⚡ Series circuits connect components in a single path, meaning if one component fails, the entire circuit stops working.
- 🌟 In series circuits, adding more light bulbs decreases the overall brightness due to increased resistance.
- 🔄 Parallel circuits allow multiple paths for current to flow; if one bulb fails, others remain lit.
- ✨ Parallel circuits maintain brightness regardless of how many bulbs are added since each has its own pathway for current.
- 📈 Both series and parallel circuits require specific amounts of current and voltage, but their designs affect performance differently.
- 💵 Series circuits are generally cheaper and simpler to construct than parallel circuits, which require more components.
- 🔀 Mixed circuits can combine series and parallel components, allowing for flexible designs that optimize performance.
Q & A
What is the main topic of the lesson presented in the video?
-The main topic of the lesson is the difference between series and parallel electrical circuits.
What are the key components needed to create a simple electrical circuit?
-To create a simple electrical circuit, you need wires, batteries (as a power source), a switch, and lamps.
What defines an open circuit as described in the video?
-An open circuit is defined as one that is not connected, meaning electricity cannot flow through it, which is indicated by the lamps being off.
How does a closed circuit differ from an open circuit?
-A closed circuit allows electricity to flow, indicated by the lamps being lit when the switch is pressed.
What is the characteristic of a series circuit in terms of electrical flow?
-A series circuit has a single path for the electric current to flow, meaning if one lamp goes out, the others will also turn off.
What happens to the brightness of lamps in a series circuit when more lamps are added?
-In a series circuit, adding more lamps causes the brightness of each lamp to decrease because the total resistance increases.
What is the behavior of lamps in a parallel circuit when one lamp is removed?
-In a parallel circuit, if one lamp is removed, the others remain lit because they each have their own path for current.
What are the advantages of using parallel circuits in household wiring?
-Parallel circuits are advantageous because they provide multiple paths for current, ensuring that if one device fails, others can still operate.
What factors influence the resistance in an electrical circuit?
-Resistance in an electrical circuit is influenced by the length and cross-sectional area of the wires used; longer wires have greater resistance, and thinner wires have higher resistance.
Can circuits be mixed, and how is this demonstrated in the video?
-Yes, circuits can be mixed. The video demonstrates a mixed circuit with some lamps connected in series and others in parallel, showing how they interact.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

RANGKAIAN SERI DAN PARALEL
Series & Parallel Circuit, Electrical Safety Devices | Grade 8 Science DepEd MELC Quarter 1 Module 6
MEDIA PEMBELAJARAN RANGKAIAN LISTRIK SERI DAN PARALEL

Video Pembelajaran IPA Rangkaian Listrik Seri dan Paralel menggunakan KIT

Simulasi Rangkaian Seri dan Paralel

Series & Parallel Circuits
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)