How do resistors work? (Animated) | Basic Electronics
Summary
TLDRThis script delves into the ubiquity and versatility of resistors in electronics, highlighting their use in various applications like operational amplifiers and current limiters. It introduces different types of resistors, from the common axial lead to the tiny 0603 and the massive ones used in heavy machinery. The explanation covers the basics of resistors, including their symbols, physical appearances, and how to choose them based on resistance, power rating, tolerance, and thermal coefficient. The importance of Ohm's law for understanding their function in circuits is emphasized, along with their linear behavior and minimal impact on high-frequency designs.
Takeaways
- 💡 Resistors are the most common electronic components and are used in a wide range of applications like operational amplifiers, voltage dividers, and current limiters for LEDs.
- 🛠️ There are different resistor symbols: European and American, which are quite similar, making them easy to recognize on schematics.
- 📏 Resistors come in various shapes and sizes, from tiny surface-mount resistors to large chassis-mounted ones used in high-power applications.
- 🎨 The most stereotypical resistor is an axial lead quarter-watt through-hole resistor, typically identified by its color bands indicating resistance and tolerance.
- 🔍 Resistors have low parasitic inductance and capacitance, making them highly linear and easy to use in most circuits except for high-frequency applications.
- 🌊 Resistors work by resisting the flow of electrons, similar to how a smaller pipe restricts water flow in a hydraulic system.
- 📐 Ohm's law (V = IR) is fundamental in understanding resistor behavior, linking voltage, current, and resistance in a linear relationship.
- ⚠️ When choosing a resistor, consider its resistance, power rating, tolerance, and thermal coefficient to ensure it meets the circuit's requirements.
- 🔥 The power rating is crucial, as exceeding it can cause the resistor to overheat or fail, especially in high-power circuits.
- 📦 For most prototyping or hobby projects, standard resistors with typical tolerance and power ratings are sufficient, but more precise options are available for critical applications.
Q & A
What is the most common electronic component in the world according to the script?
-The resistor is considered the most common electronic component in the world.
What are some common uses of resistors in electronic circuits?
-Resistors are used in setting up operational amplifiers, creating feedback loops, voltage dividers, and as current limiters for LEDs, among other applications.
What are the two different resistor symbols mentioned in the script?
-The script mentions the European and the American (or more standard) resistor symbols.
What is an axial lead quarter watt through-hole resistor?
-It is a stereotypical resistor with color bands indicating resistance and tolerance, commonly used in electronics.
What is the significance of the color bands on a resistor?
-The color bands on a resistor indicate its resistance value and tolerance, which are crucial for its operation in a circuit.
What are some of the different sizes of resistors mentioned in the script?
-The script mentions 0603 resistors, which are tiny, and 0402 resistors, which are even smaller. It also talks about much larger resistors used in applications like elevator control boards.
Why are resistors considered easy to use in electronic circuits?
-Resistors are easy to use because they are highly linear, meaning the current changes linearly with voltage, and they have minimal parasitics that can usually be ignored unless working with RF circuits.
What is the basic principle of a resistor in terms of electron flow?
-A resistor slows the flow of electrons through a circuit, acting like a point where the 'pipe' gets smaller, thus reducing the current or water flow in the analogy provided.
How is the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance described in the script?
-The relationship is described using Ohm's law, which states that voltage (V) equals current (I) times resistance (R), or V = IR.
What are some factors to consider when choosing a resistor for a circuit?
-When choosing a resistor, one should consider its resistance value, power rating, tolerance, thermal coefficient, and inductance or capacitance if working with high-frequency circuits.
Why is it important to consider the power rating of a resistor?
-The power rating of a resistor is important because exceeding the rated power can cause the resistor to overheat and potentially fail, affecting the performance and safety of the circuit.
What is the role of the tolerance value in a resistor and why might someone choose a lower tolerance?
-The tolerance value indicates the acceptable variance in the resistance value from the nominal value. Choosing a lower tolerance is important for applications requiring higher precision, though it typically comes at a higher cost.
How does the thermal coefficient affect the performance of a resistor?
-The thermal coefficient affects the performance of a resistor by causing changes in resistance with temperature variations. This is important to consider in circuits that will operate in extreme temperature environments to ensure consistent performance.
What is the script's suggestion for hobbyists and prototypers regarding resistors?
-The script suggests that for most hobbyists and prototypers, standard resistors are sufficient for their projects, and they can start using smaller resistors for PCBs to make their circuits more compact as they advance in their skills.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

Elektronika Dasar 004 Resistor 04 Universitas Jember

Electrical Engineering: Basic Concepts (7 of 7) Passive vs Active Elements

What is Electronics? || Electronics Terminology Course Preview
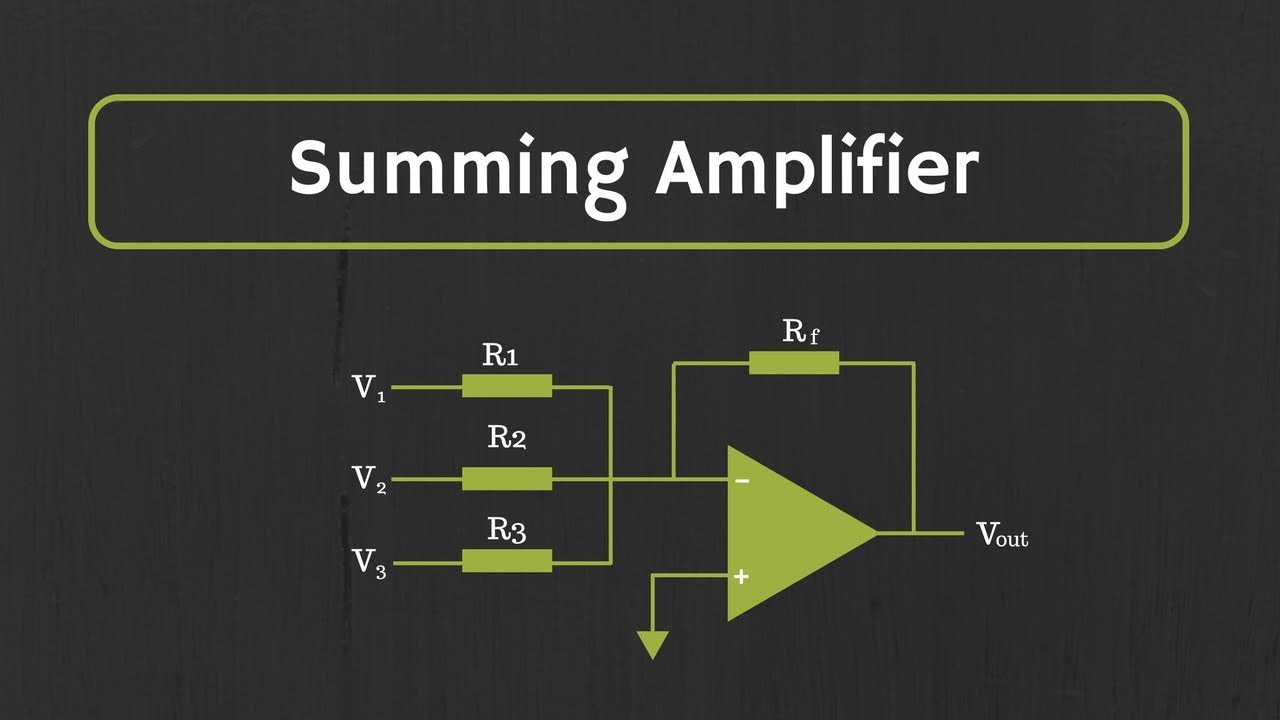
Op-Amp: Summing Amplifier (Inverting and Non-Inverting Summing Amplifiers)

Komponen Penunjang Single Board Controller | Sistem Komputer | Informatika XII
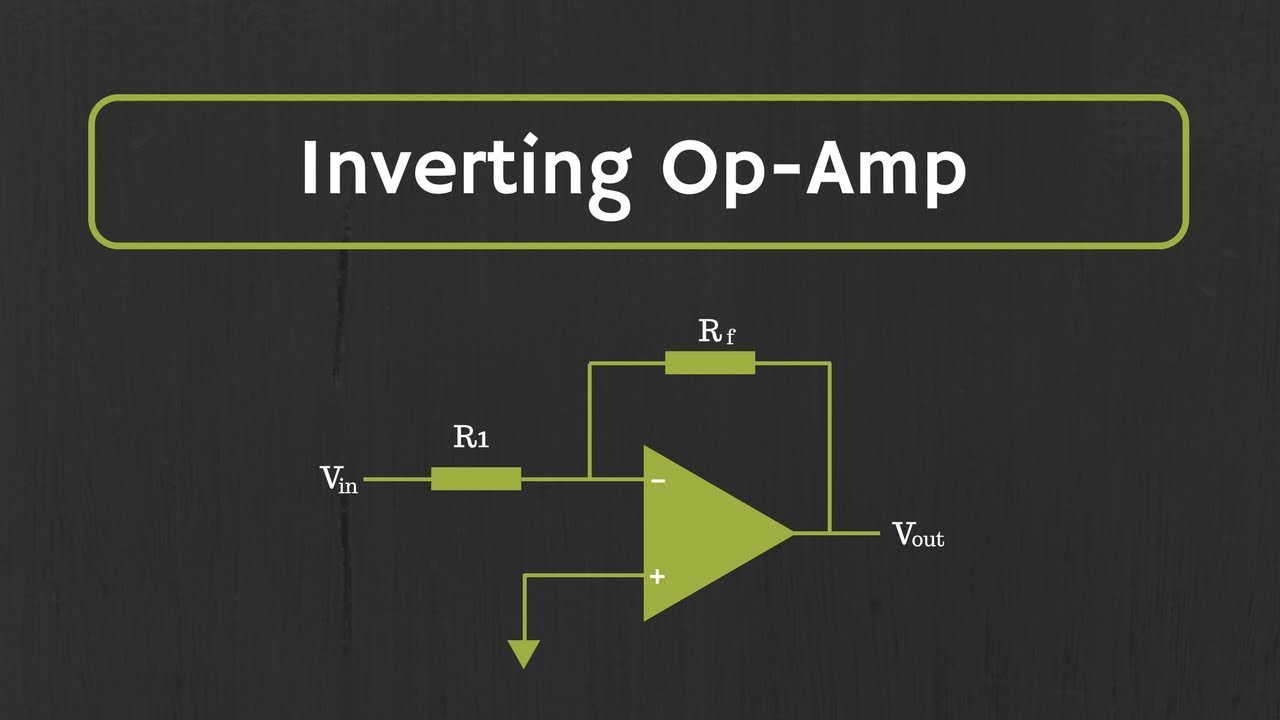
Operational Amplifier: Inverting Op Amp and The Concept of Virtual Ground in Op Amp
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
