What is Electronics? || Electronics Terminology Course Preview
Summary
TLDRThis video script delves into the fundamentals of electronics, explaining how electricity powers modern devices through circuits. It highlights the role of resistors in controlling electron flow and voltage, and distinguishes between alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC). The script also covers electrical power measured in Watts and the various applications of electronics in consumer, portable, automotive, avionics, industrial, and medical devices, showcasing their integral role in our daily lives.
Takeaways
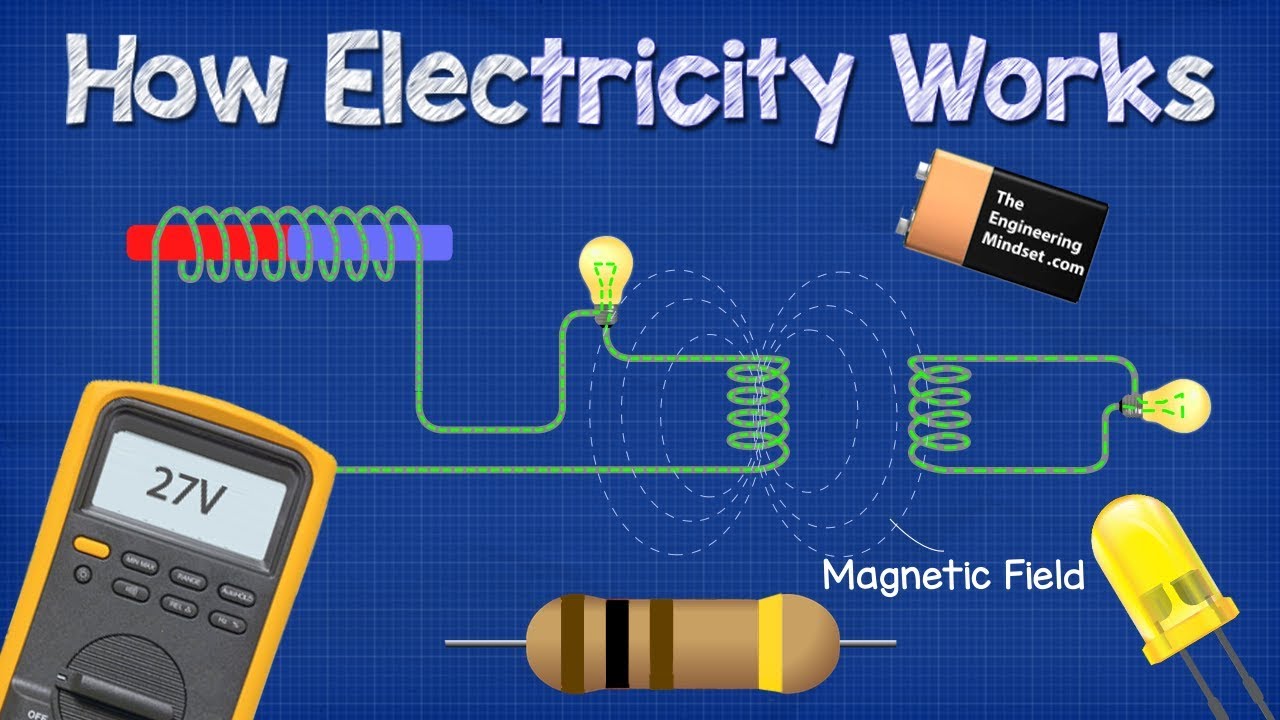
- 🔌 Electricity is a form of energy that powers most modern devices and flows through closed loops called circuits.
- 📚 The study of electron flow in devices and circuits is known as Electronics.
- 🛠️ Electronic components like resistors, inductors, transistors, capacitors, and switches control the flow of electrons.
- 🚦 Resistors are key for understanding voltage and current by restricting electron flow to provide required voltage.
- 🔋 Voltage is the potential difference in charge between two points in a circuit, necessary for electron movement and current production.
- 🔁 Electric current can be Alternating Current (AC) or Direct Current (DC), with AC reversing direction and DC maintaining a constant direction.
- 🔁.1 AC's frequency, measured in hertz, is the number of times it reverses direction per second.
- 🔁.2 DC has a frequency of 0 Hertz, as it does not reverse direction.
- ⚡ Electrical power, measured in Watts, describes the amount of electrical energy consumed by a component in one hour.
- 🤖 Electronic components can be assembled in various configurations for different applications, from consumer to industrial electronics.
- 🏠 Consumer electronics are commonly found in homes and include devices like computers, printers, TVs, and electronic appliances.
- 📱 Portable electronics, also known as handheld electronics, are battery-operated devices like smartphones, tablets, and smartwatches.
- 🚗 Automotive electronics are systems used in cars, including those in the engine and braking systems.
- ✈️ Avionics are the electronic systems on aircrafts, including navigation, communication, and weather radar systems.
- 🏭 Industrial electronics are used in systems like CNC machines, programmable logic controllers, and robotics.
- 🩺 Medical electronics are found in devices such as MRI scanning machines, blood sugar monitors, and pulse oximeters.
Q & A
What is electricity and why is it important for modern devices?
-Electricity is a form of energy that powers most modern devices. It is crucial because it enables the operation of various electronic devices and systems through the flow of electrons.
What is a circuit and how does it relate to the flow of electrons?
-A circuit is a closed loop through which the flow of electrons, or electric current, runs. It is essential for the functioning of electronic devices as it provides a path for electrons to move and generate power.
What are the roles of electronic components like resistors, inductors, transistors, capacitors, and switches in controlling the flow of electrons?
-These components control and regulate the flow of electrons in circuits. Resistors restrict the flow to provide the required voltage, inductors store energy in a magnetic field, transistors act as switches or amplifiers, capacitors store energy and release it when needed, and switches control the opening and closing of the circuit.
Why are resistors important in understanding voltage and current?
-Resistors are important because they help in controlling the voltage and current in a circuit. By restricting the flow of electrons, resistors ensure that devices receive the necessary voltage to operate correctly.
What is the difference between voltage and electric current?
-Voltage is the potential difference in charge between two points within a circuit, necessary for the movement of electrons. Electric current is the flow of electrons through a circuit, which can be produced by this voltage.
What are the two types of electric current and how do they differ?
-The two types of electric current are Alternating Current (AC) and Direct Current (DC). AC reverses its direction many times at regular intervals, while DC flows in a single direction without reversing.
How is frequency related to Alternating Current (AC) and what is its unit of measurement?
-Frequency in AC refers to the number of times the current direction reverses per second. It is measured in hertz (Hz).
What is the frequency of AC and DC in hertz, and what does it indicate?
-The frequency of AC is typically 50 or 60 hertz, indicating the number of times it reverses direction per second. The frequency of DC is 0 hertz, as it does not reverse direction.
How is electrical power defined and what unit is it measured in?
-Electrical power is the amount of electrical energy consumed by a component when in use for one hour. It is expressed in watts (W).
What are consumer electronics and what are some common examples?
-Consumer electronics are electronic equipment commonly found in homes. Examples include desktop computers, printers, scanners, TVs, monitors, and various electronic appliances.
What is the difference between portable electronics and other types of electronics?
-Portable electronics, also known as handheld electronics, are battery-operated devices that do not need to be plugged in. Examples include smartphones, tablets, laptops, smartwatches, calculators, handheld game consoles, and personal digital assistants.
What are avionics and what role do they play in aircrafts?
-Avionics are the electronic systems used on aircrafts. They include navigation, communication, weather radar, and fuel systems, playing a crucial role in the operation and safety of flights.
What is the role of industrial electronics in manufacturing and automation?
-Industrial electronics are systems used in computer numerical control or CNC machines, programmable logic controllers, and robotics. They are essential for automation, precision manufacturing, and efficient industrial processes.
What are medical electronics and how are they used in healthcare?
-Medical electronics are found in medical devices such as MRI scanning machines, blood sugar monitors, and pulse oximeters. They are used for diagnosis, monitoring, and treatment in healthcare.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)