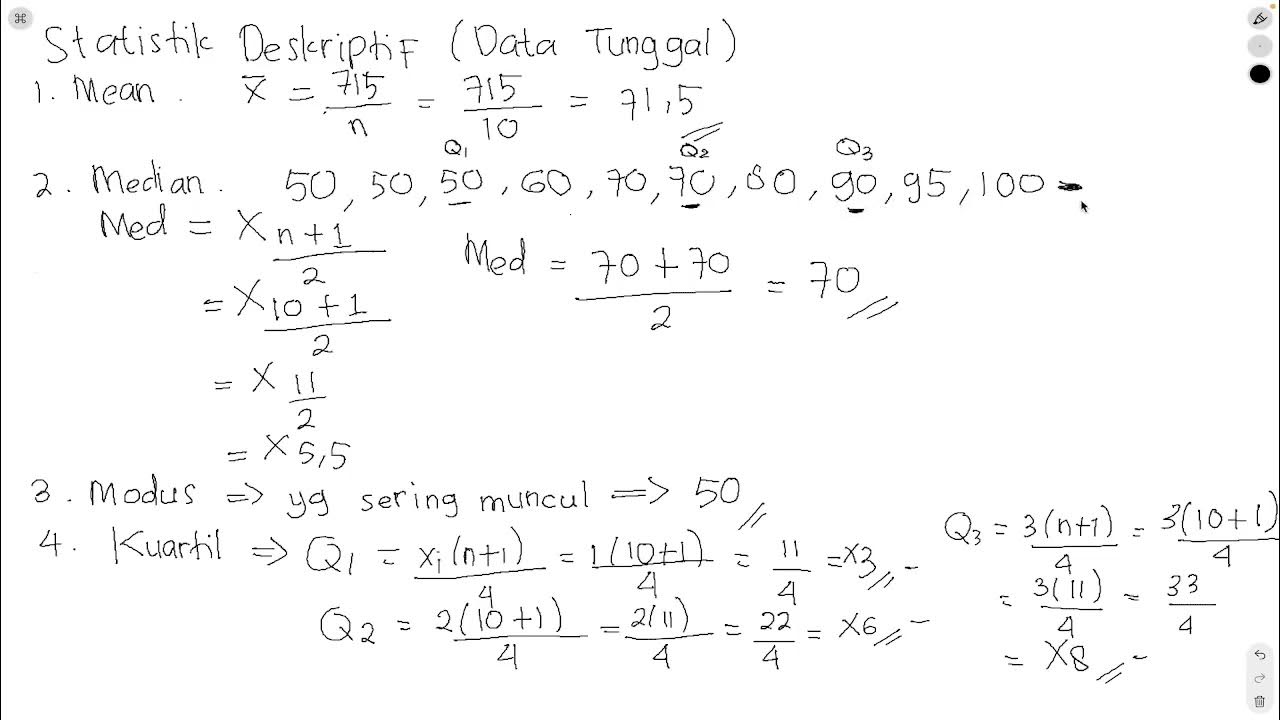Must know Visualization in Statistics | Descriptive Statistics | Ultimate Guide !! | Part 10
Summary
TLDRThe script discusses the significance of graphical representation in descriptive statistics, emphasizing its ability to visually convey data distribution, spread, and central tendency. It covers three main plots used in statistics: histograms, box plots, and scatter plots, along with bar and line charts. The explanation delves into how histograms display data distribution through bins, box plots represent the IQR range, and scatter plots illustrate the relationship between two variables. The script also touches on identifying outliers and the types of skewness in histograms, as well as the concept of modes in relation to histogram types.
Takeaways
- 📊 Graphical representation is crucial in descriptive statistics as it allows for visual data analysis, showing distribution, dispersion, and trends.
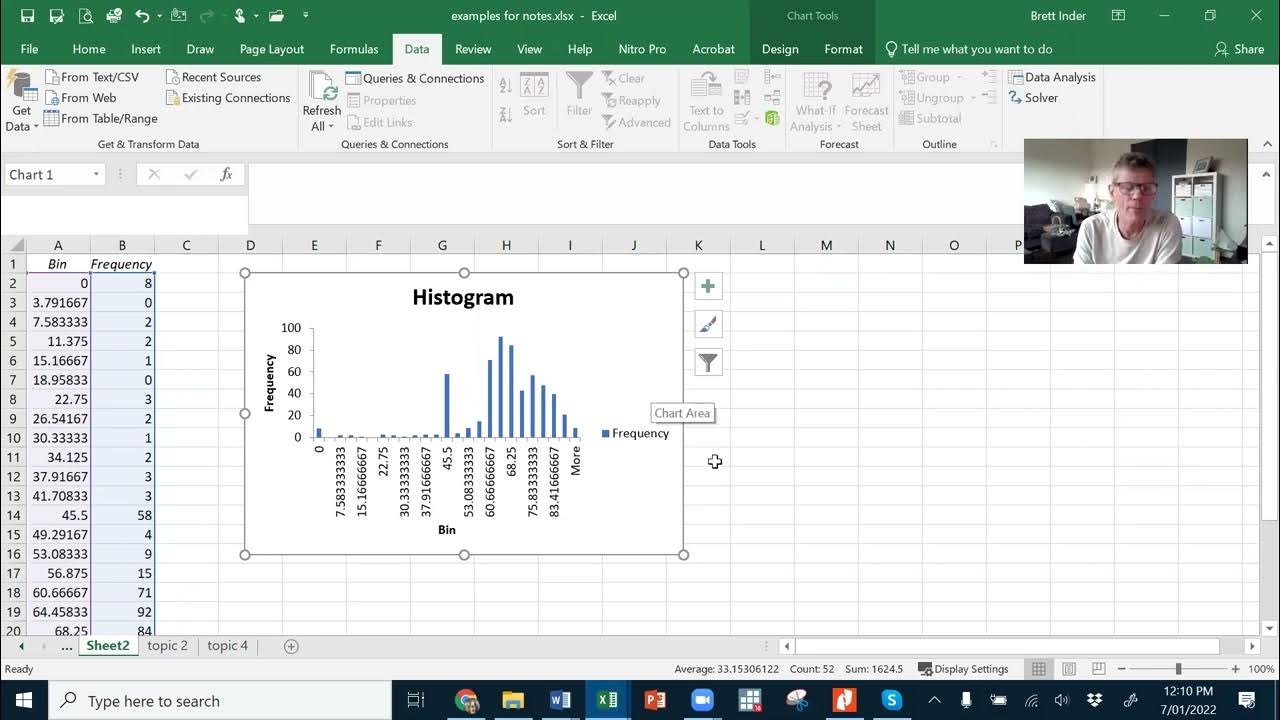
- 📈 Histograms are a primary tool in graphical representation, displaying the distribution of data through bins, which can be adjusted to show different distributions.
- 📉 Box plots are useful for showing the spread of data, identifying outliers, and providing a quick summary of key statistics like median, quartiles, and range.
- 🔍 Scatter plots are essential for visualizing relationships between two variables, helping to identify patterns, trends, and correlations.
- 📊 Histograms can reveal the shape of data distribution, such as whether it's skewed left or right, and can identify outliers and the central tendency of the data.
- 📊 Types of histograms include symmetric, right-skewed, and left-skewed, each indicating different characteristics of the data distribution.
- 📊 Based on the number of modes, histograms can be classified into unimodal, bimodal, and multimodal, each revealing different aspects of the data set.
- 📊 Box plots not only show the IQR range but also help in identifying outliers by calculating values beyond 1.5 times the IQR from the quartiles.
- 📊 Scatter plots are enhanced by adding a regression line, which can indicate the strength and direction of the relationship between variables.
- 🚫 Outliers can significantly affect data analysis processes, and understanding how to identify and handle them is crucial for accurate statistical analysis.
Q & A
What is the importance of graphical representation in descriptive statistics?
-Graphical representation is crucial in descriptive statistics as it allows for visual interpretation of data, making it easier to understand the spread, dispersion, distribution, frequency, and central tendency of the data.
What are the three main types of plots used in graphical representation for statistics?
-The three main types of plots used in graphical representation for statistics are histograms, box plots, and scatter plots.
How does a histogram help in understanding the distribution of data?
-A histogram divides data into intervals (bins) and shows the frequency of data points within these intervals. It helps visualize the distribution, spread, and shape of the data.
What do the bins in a histogram represent?
-Bins in a histogram represent the intervals into which the data is divided. They indicate the range of values within the data set.
What is the difference between a bar chart and a histogram?
-A bar chart represents categorical data, showing the count or quantity of data within categories, while a histogram displays the distribution of continuous data by dividing it into bins.
How can you identify outliers using a histogram?
-Outliers in a histogram are represented by bars that are significantly separated from the rest of the data. They indicate values that are unusually high or low compared to the rest of the data.
What is the significance of the shape of a histogram?
-The shape of a histogram can indicate the type of distribution the data follows, such as normal, right-skewed, or left-skewed distributions.
What are the three types of skewed histograms?
-The three types of skewed histograms are symmetric, right-skewed, and left-skewed. Symmetric histograms have a balanced distribution around the center, while right-skewed histograms have a longer tail on the right side, and left-skewed histograms have a longer tail on the left side.
How can you determine the center of a distribution using a histogram?
-The center of a distribution in a histogram can be determined by looking at the mean, median, and mode. These values are typically located around the center of the distribution.
What is a box plot and what does it represent?
-A box plot is a graphical representation that displays the interquartile range (IQR) of a data set. It shows the median, first quartile (Q1), and third quartile (Q3), as well as any outliers beyond the IQR.
How are the upper and lower whiskers of a box plot calculated?
-The upper whisker is calculated by subtracting 1.5 times the IQR from the third quartile (Q3), and the lower whisker is calculated by subtracting 1.5 times the IQR from the first quartile (Q1).
What is the purpose of a scatter plot in statistical analysis?
-A scatter plot is used to visualize the relationship between two variables. It helps identify patterns, trends, and the direction of the relationship, such as positive, negative, or no correlation.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahora5.0 / 5 (0 votes)