ETC1000 Topic 2b
Summary
TLDRThis instructional video script delves into the nuances of data analysis, emphasizing the importance of understanding and visualizing data effectively. It covers the generation of descriptive statistics in Excel, the creation of frequency distributions and histograms, and the use of box and whisker plots to illustrate data spread and central tendency. The presenter also discusses the significance of probability distributions, particularly the normal distribution, and how to calculate probabilities and identify corresponding data points using Excel functions. The script underscores the necessity of clear and accurate data visualization for effective communication.
Takeaways
- 📚 Watch the first video for Topic Two before this one for better understanding of the material.
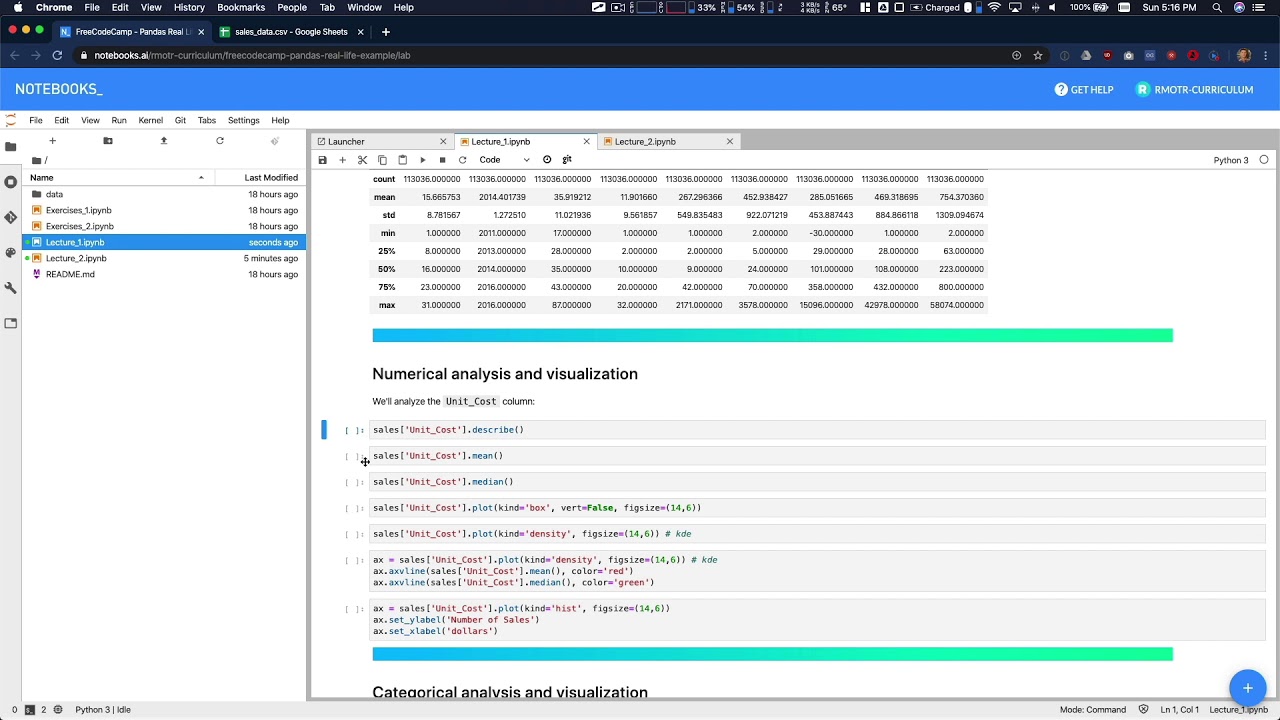
- 📈 Excel can generate various descriptive statistics like mean, median, mode, standard deviation, and range with a single step.
- 📊 Visualizations like histograms and box plots are crucial for effectively communicating data distribution and should be clear and well-presented.
- 📉 Numbers alone may not be enough; visualizations help provide a clearer picture of data distribution and are more memorable.
- 🗂 Creating a frequency distribution table helps in understanding the categorization and range of data, such as income levels.
- 📝 Customizing histogram appearance, including labels and bin ranges, is essential for accurate and effective data representation.
- 📉 Box and whisker plots are useful for visualizing quartiles and understanding the spread and central tendency of data.
- 📊 The choice of bin ranges in histograms can significantly affect the interpretation of data, as demonstrated with grade distributions.
- 🤔 Probability distributions, including the normal distribution, are foundational concepts for understanding how random data is distributed.
- 📝 The normal distribution is common in various fields because it represents data that is symmetrically distributed around the mean with probabilities decreasing as values move away from the mean.
- 🔢 Excel's norm.dist function can calculate probabilities for a normal distribution or find the x value for a given probability.
Q & A
What is the main focus of the second video in the series?
-The main focus of the second video is to complete the discussion on the second topic, which involves finishing off the rest of the material after introducing the concept of standardizing data and summarizing its characteristics using measures with quantitative data.
Why is it important to watch the first video before the second one?
-It is important to watch the first video before the second one because the second video continues from where the first left off, and concepts introduced in the first video are built upon in the second, ensuring that the content makes sense and is understood in the correct sequence.
What are some of the descriptive statistics measures discussed in the video?
-The descriptive statistics measures discussed in the video include mean, median, mode, standard deviation, variance, range, minimum, and maximum.
How can one obtain all the mentioned descriptive statistics in Excel with a single step?
-One can obtain all the mentioned descriptive statistics in Excel with a single step by using the 'Descriptive Statistics' tool, which provides all these measures at once, although it may not include all measures like quartiles and interquartile range.
What is a frequency distribution and why is it useful?
-A frequency distribution is a table that shows the number of data points that fall within certain ranges or categories. It is useful because it provides a detailed view of the data, showing how many observations fall into each defined range, which helps in understanding the distribution of the data.
How does the video script emphasize the importance of visualization in data analysis?
-The script emphasizes the importance of visualization by stating that visualizations can be more memorable and clearer than numbers alone. It also mentions that the presentation of data through graphs can be misleading if not done properly, highlighting the need for careful and accurate visualization to communicate the data effectively.
What is a histogram and how does it help in understanding data distribution?
-A histogram is a graphical representation of the distribution of data. It groups data into intervals, or 'bins', and shows the frequency of observations within each bin. It helps in understanding the data distribution by visually showing the concentration of data points, the spread, and any patterns or outliers.
What is a box and whisker plot and how does it represent data?
-A box and whisker plot is a standardized way of displaying the distribution of data based on a five-number summary: minimum, first quartile (Q1), median, third quartile (Q3), and maximum. It provides a clear visual representation of the spread and skewness of the data, including potential outliers.
Why is the normal distribution important in statistics and what does it represent?
-The normal distribution is important in statistics because it is a symmetrical bell-shaped curve that represents the distribution of many real-world phenomena. It is widely used in statistical inference and hypothesis testing due to its properties and the central limit theorem, which states that the sum of independent and identically distributed variables will be approximately normally distributed regardless of the original distribution.
How can Excel be used to calculate probabilities associated with a normal distribution?
-Excel can be used to calculate probabilities associated with a normal distribution using the NORM.DIST function, which calculates the cumulative probability for a specified value in a normal distribution with a given mean and standard deviation. The function can also be used in reverse to find the value (x) that corresponds to a given probability.
What is the significance of standard deviation in the context of the normal distribution?
-In the context of the normal distribution, the standard deviation indicates the spread of the data around the mean. A smaller standard deviation means the data points are closer to the mean, while a larger standard deviation indicates a greater spread. It is also used to define the ranges within which a certain percentage of data falls, such as within one or two standard deviations from the mean.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Qualitative and Quantitative Research

Social Network Analysis Menggunakan Gephi

Bioinformatics - File Formats Part-3 | SAM vs BAM | HANDS ON | NGS | LINUX | BEGINNER |
Data Analysis Example A - Data Analysis with Python

Cara menentukan histogram dan poligon data kelompok

Iterations using combination of filtering conditions
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)