Flame Photometry | Thermometric Sensors
Summary
TLDRFlame photometry is a technique for measuring thermal changes, particularly the emission of light from excited metal atoms in a flame. It involves the aspiration of metal compounds into a flame, where they dissociate into atoms, get excited, and emit light at specific wavelengths. The intensity of this light is proportional to the metal's concentration in the solution. The flame photometer uses a nebulizer, a burner, an optical system with a lens and filter, and a photodetector to convert the emitted light into an electrical signal. This method is widely used for qualitative and quantitative analysis of elements like sodium, potassium, and calcium in various samples, including biological fluids, plant material, water, soil extracts, cement, and glass.
Takeaways
- 🔍 Flame photometry is a thermometric sensor technique used for measuring thermal changes, such as temperature or flame emission, during the interaction between an analyte and a reagent.
- 🌡 The process involves the aspiration of compounds containing group two metals or alkali and alkaline earth metals into a flame, which leads to their dissociation into atoms.
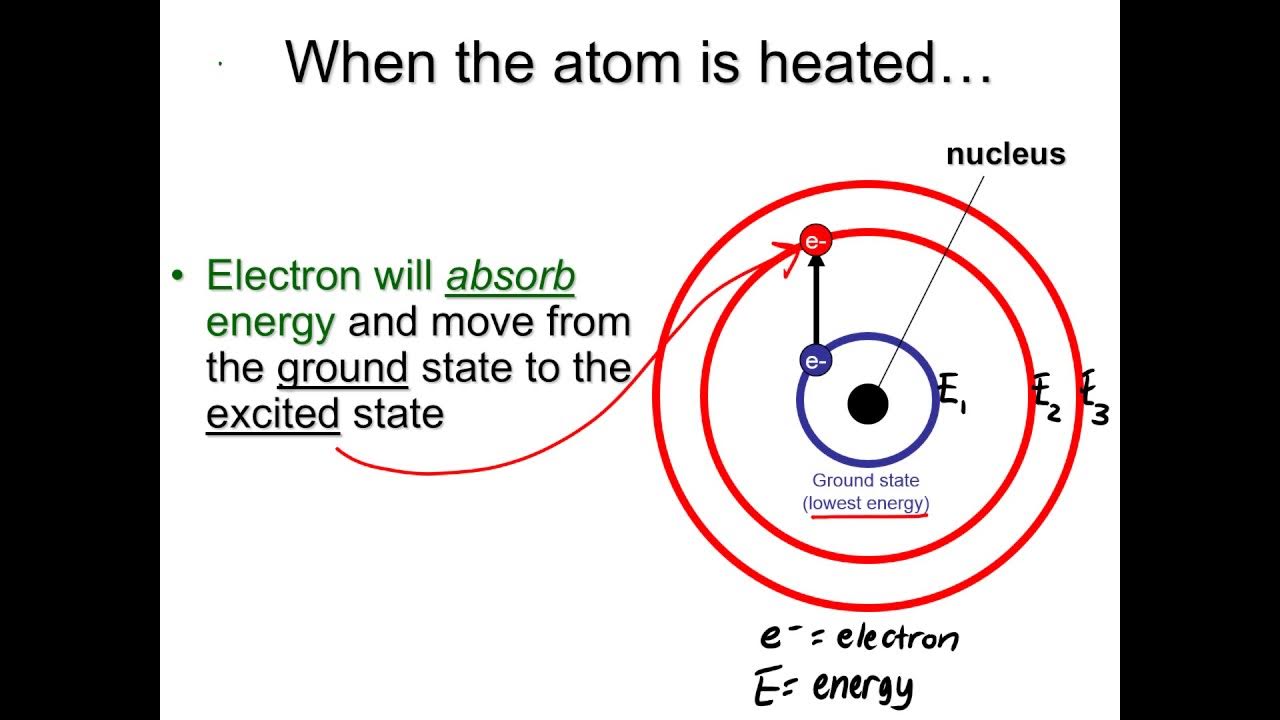
- 💧 When a solution is aspirated into the flame, the solvent evaporates, leaving the salt which then vaporizes and dissociates into gaseous atoms.
- 🔥 The metal atoms in the gaseous state absorb heat from the flame and become excited to a higher energy level, then return to their ground state by emitting light radiation.
- 📏 The intensity of the emitted light is proportional to the concentration of the solution and the number of atoms in the excited state.
- 🌈 Different metals emit light at different wavelengths, for example, sodium at 589 nanometers and potassium at 766 nanometers.
- 🔧 The detector response (E) is measured using the expression E = K * Alpha * C, where K is a constant, Alpha is the efficiency of atomic excitation, and C is the concentration of the solution.
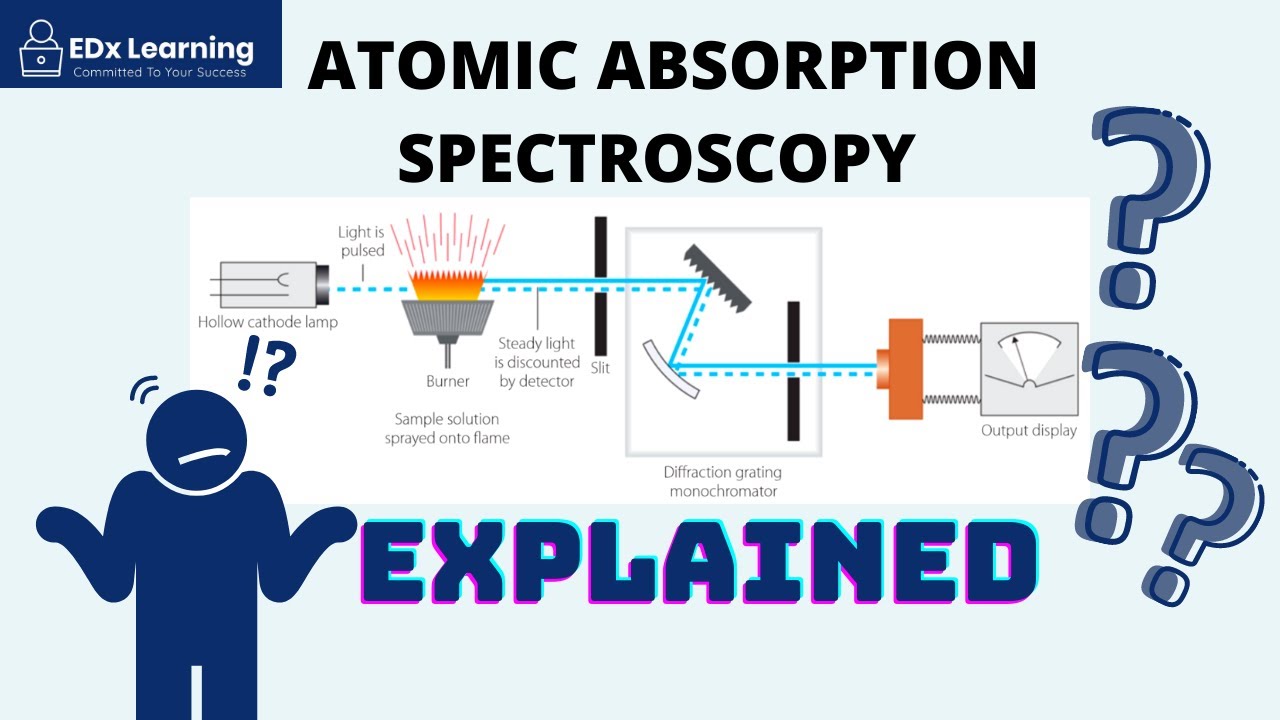
- 🧪 The flame photometer works by injecting the sample through a nebulizer, mixing it with fuel in a chamber, and then observing the flame emission after ignition.
- 🔭 The emitted radiation passes through a lens and filter to isolate the specific wavelength of interest, which is then detected and converted into an electrical signal by a photodetector.
- 🛠️ The optical system of a flame photometer includes a convex mirror and lens to focus the emitted light, a filter to isolate the wavelength, and a photodetector to convert light into an electrical signal.
- 🔬 Flame photometry is used for both qualitative and quantitative analysis of various materials in biological fluids, plant material, water samples, soil extracts, and even in cement and glasses for the determination of specific ions like sodium, potassium, and calcium.
Q & A
What is flame photometry?
-Flame photometry is a type of thermometric sensor used for measuring thermal changes, such as temperature changes or flame emission, during the interaction between an analyte and a reagent.
How are thermal changes in flame photometry converted into measurable signals?
-The thermal changes are converted into measurable electrical signals through the process of dissociation and excitation of atoms in the flame, which then emit light radiation.
What happens when a compound of group two metals or alkaline earth metals is aspirated into the flame?
-The compound dissociates into atoms, which then get vaporized into a gaseous state and further absorb heat from the flame, leading to the excitation of metal atoms.
How does the metal atom return to its ground state after excitation?
-The metal atom returns to its ground state by emitting energy in the form of light radiation.
Why is the intensity of emitted light radiation proportional to the concentration of the solution?
-The intensity of the emitted light radiation is proportional to the number of atoms in the excited state, which is related to the concentration of the solution fed to the flame.
What is the detector response 'e' in the context of flame photometry?
-The detector response 'e' is given by the expression e = K * Alpha * C, where K is a constant, Alpha is the efficiency of atomic excitation, and C is the concentration of the solution.
How does the emitted radiation differ for different metals?
-The emitted radiation differs for different metals due to the specific wavelengths at which each metal emits light, such as sodium at 589 nanometers and potassium at 766 nanometers.
What is the role of the nebulizer in flame photometry instrumentation?
-The nebulizer's role is to inject the sample into the flame photometer, creating a homogeneous solution that is sent into the flame at a balanced rate.
What is the function of the filter in the optical system of a flame photometer?
-The filter in the optical system allows only a particular wavelength of radiation to pass through, isolating the wavelength to be measured from the emitted radiations.
How does a photodetector contribute to flame photometry?
-The photodetector converts the emitted radiation into an electrical signal, which is then amplified and displayed, providing a measurement that is directly proportional to the intensity of the light.
What are some applications of flame photometry?
-Flame photometry is used for both qualitative and quantitative analysis, including the analysis of materials in biological fluids, plant material, determination of sodium, potassium, and calcium ions in water samples and soil extracts, and the determination of calcium ions in cement and glasses.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)