Quickly Understand Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (AAS)
Summary
TLDRAtomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS) is a technique used to measure the concentration of specific elements in a sample by analyzing how light is absorbed by the atoms. The process involves using a hollow cathode lamp to emit light, which is absorbed by atomized particles of the sample in a flame. The absorbance is then calculated using Beer’s Law. AAS is widely used in fields such as food, water, clinical research, pharmaceuticals, and mining due to its efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and ability to analyze elements in solution.
Takeaways
- 😀 Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (AAS) is used to measure the concentration of specific elements in a sample.
- 💡 Spectroscopy is the study of how light interacts with matter, and in AAS, this principle is used to measure absorbance.
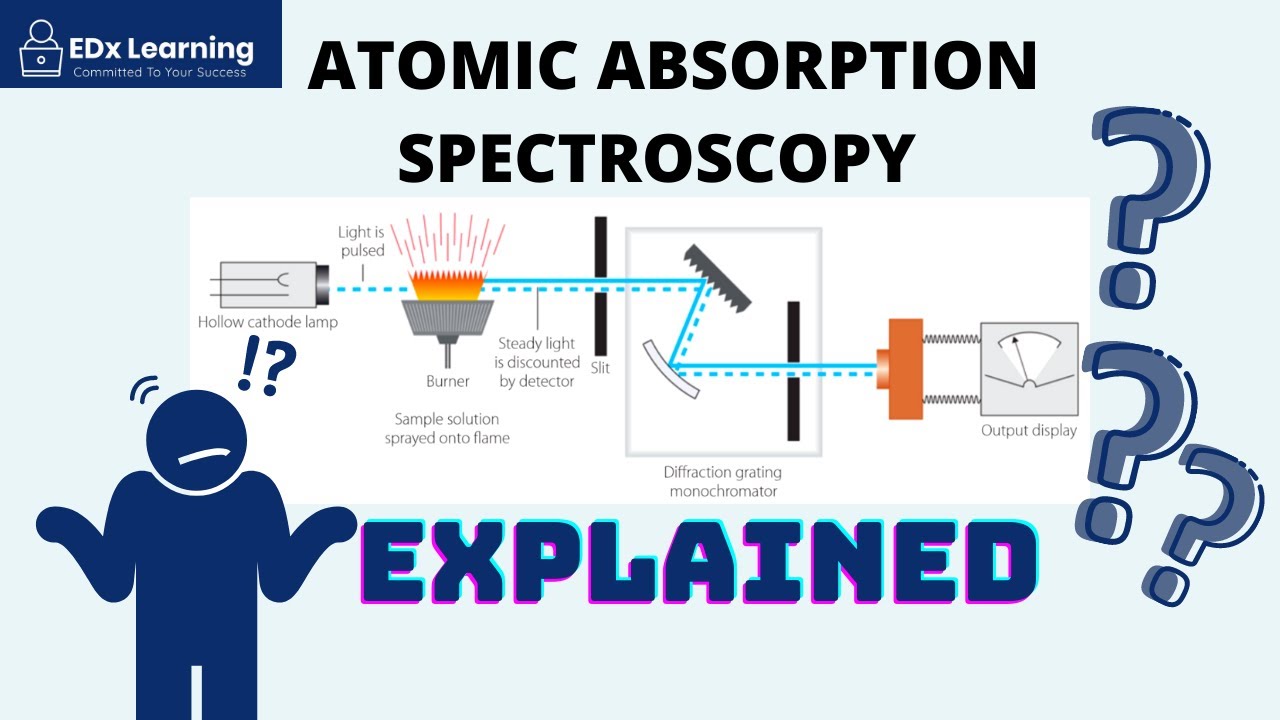
- 🔥 A hollow cathode lamp emits light specific to the element being analyzed to ensure accurate absorption readings.
- 🌬️ The sample is atomized in a flame with fuel and oxygen, which allows the atoms to interact with light.
- 🔬 The light absorbed by the atoms is measured to determine the element's concentration in the sample.
- 🎯 Beer’s Law is used to calculate absorbance, with the formula A = εbc, where 'A' is absorbance, 'ε' is molar absorptivity, 'b' is path length, and 'c' is concentration.
- 💻 Computer technology processes the signal, amplifying it through a photomultiplier and calculating the element concentration.
- ⚙️ AAS is a high-throughput, inexpensive technique suitable for various industries including food and beverage, water research, and pharmaceuticals.
- 💧 AAS is valuable in water and clinical research for detecting contaminants and analyzing trace elements.
- ⛏️ In mining, AAS helps determine the metal content of ores, such as precious metals like gold and silver.
- 📈 AAS is widely used for its accuracy, ease of use, and ability to handle a high volume of samples efficiently.
Q & A
What is atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS)?
-Atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS) is a technique used to measure the concentration of a specific element in a sample by analyzing the absorption of light at characteristic wavelengths.
How does atomic absorption spectroscopy work?
-AAS works by shining light through a sample that is atomized in a flame. The atoms of the element being measured absorb light at specific wavelengths. The intensity of the absorbed light is then measured and used to calculate the concentration of the element in the sample.
What is the role of the hollow cathode lamp in AAS?
-The hollow cathode lamp provides light at the characteristic absorption wavelengths of the element being analyzed. This ensures that only the relevant wavelengths interact with the sample.
Why is the sample atomized in a flame during AAS?
-Atomizing the sample in a flame is necessary because it breaks the sample into individual atoms, allowing them to absorb light at their specific wavelengths, which is crucial for accurate measurement.
What is the purpose of the monochromator in atomic absorption spectroscopy?
-The monochromator isolates a specific wavelength of light, ensuring that only the light corresponding to the element's absorption spectrum is measured. This simplifies the analysis.
How does the photomultiplier contribute to AAS?
-The photomultiplier amplifies the light signal after it passes through the sample, allowing for the detection of very small changes in light intensity, which are then used to calculate the absorbance.
What is Beer’s Law and how is it applied in AAS?
-Beer’s Law states that absorbance is directly proportional to the concentration of the absorbing element in the sample. In AAS, the absorbance (A) is calculated using the formula A = εbc, where ε is the molar absorptivity, b is the path length, and c is the concentration of the element.
What are some common applications of atomic absorption spectroscopy?
-AAS is used in food and beverage research, clinical research, pharmaceutical analysis, and mining operations. It helps analyze elements in solutions, determine trace elements in biological samples, and assess metal concentrations in ores.
Why is AAS considered a high throughput and inexpensive technique?
-AAS is considered high throughput because it allows for fast analysis of multiple samples. It is inexpensive because it uses relatively simple equipment and is efficient in terms of both cost and time.
What makes AAS particularly useful for analyzing metals in ores?
-AAS is particularly useful in mining because it can accurately measure the concentration of specific metals in ores, helping determine the purity of materials such as precious metals.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)