How Does The Internet Work? - BBC Click
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the evolution of the internet, tracing its origins back to 1969 with ARPANET, developed by the U.S. Defense Department to connect university computer systems. Over time, the internet grew into a vast global network, now spanning millions of kilometers of cables and impacting daily life through data transfer, social media, and video streaming. It highlights the technology behind the internet, including packet-switching, and addresses the challenge of distinguishing quality information in an age of echo chambers and misinformation. The video emphasizes the importance of understanding both the internet and the web in navigating modern digital landscapes.
Takeaways
- 😀 Every day, the world generates an enormous amount of data: 4 million hours of video on YouTube, 682 million tweets, and 67 million Instagram pictures.
- 😀 Over 4.4 billion people use the Internet, creating 2.5 exabytes (or 2.5 quintillion bytes) of data daily.
- 😀 Telehouse North, one of the Internet's critical hubs, houses computer systems, cables, and cooling equipment that support global data transmission.
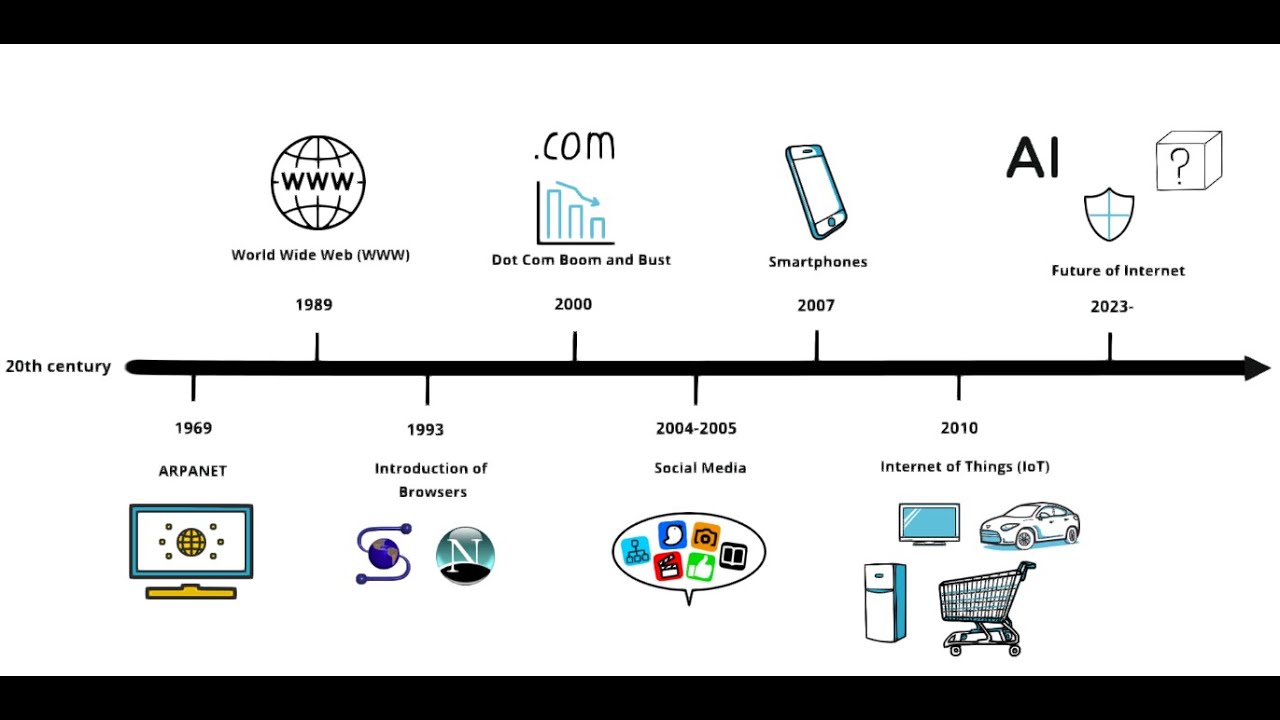
- 😀 The Internet's origins date back to 1969, when the U.S. Defense Department created ARPANET to connect university computer systems for research collaboration.
- 😀 The first message sent over ARPANET on October 29, 1969, was 'login,' but the system crashed before completing the word.
- 😀 ARPANET evolved into a global network, connecting millions of devices and growing into the Internet, a vast interconnected system of networks.
- 😀 The Internet relies on 1.2 million kilometers of submarine cables, some of which are as deep as Mount Everest is high, connecting servers globally.
- 😀 The Internet and the World Wide Web are distinct: the Web is how we access information, while the Internet is the infrastructure that makes global communication possible.
- 😀 When you watch a video online, your request splits into small data packets, which travel through various routes and reassemble at your device for smooth streaming.
- 😀 A key challenge today is distinguishing good quality information from misinformation, especially as the Internet has made it harder to engage in rational debates due to echo chambers.
Q & A
What is the significance of the 50th anniversary mentioned in the script?
-The 50th anniversary refers to the creation of ARPANET, the precursor to the modern Internet. It was launched in 1969 by the U.S. Defense Department to connect university computer systems for research purposes, marking the beginning of the Internet as we know it today.
What was ARPANET, and how did it evolve into the modern Internet?
-ARPANET was a packet-switched network developed by the U.S. Defense Department to connect universities for research sharing. It started with a few nodes and grew to become a global network, eventually evolving into the Internet, which now connects billions of devices worldwide.
What does the Internet consist of in terms of physical infrastructure?
-The Internet consists of over 1.2 million kilometers of submarine cables that connect server buildings. These cables also link smaller cables that connect individual computers. This vast network forms the backbone of the Internet's global connectivity.
How does the Internet differ from the World Wide Web?
-The Internet is the physical infrastructure that connects networks globally, while the World Wide Web is a system that organizes and accesses data such as web pages and documents on top of the Internet. The Web relies on the Internet to function.
What is the role of packet-switching in how the Internet functions?
-Packet-switching breaks data into small packets that travel through different routes to reach their destination. This approach ensures efficient data transfer and prevents delays caused by network congestion, allowing content, like videos, to be delivered smoothly.
What is the significance of Telly House North in the context of the Internet?
-Telly House North is one of the key buildings in London that serves as part of the Internet's backbone. It houses servers, cables, and cooling equipment essential for the smooth functioning of the Internet's data exchange between global networks.
Why does the script emphasize the challenge of distinguishing good information from bad on the Internet?
-The script highlights the issue of echo chambers and misinformation, where people are increasingly exposed only to information that aligns with their beliefs, making it harder to distinguish fact from opinion or fake news. This is a growing challenge in the digital age.
What does the script say about the quantity of data created daily on the Internet?
-The script mentions that every day, we collectively create around 2.5 exabytes (or 2.5 million terabytes) of data, including 4 million hours of video uploaded to YouTube, 682 million tweets, and 67 million Instagram pictures. This vast amount of data drives the Internet's activity.
How does the Internet's structure allow for the efficient delivery of content, such as videos?
-The Internet's structure uses packet-switching, where data is split into smaller packets and sent through various routes. This allows for faster and more efficient content delivery, as it avoids bottlenecks that would occur if the entire video were sent down a single route.
What role does the Internet play in modern research and development?
-The Internet is a vital tool for modern research and development, originally promoted by ARPANET to accelerate research in fields like artificial intelligence. It facilitates the sharing of knowledge, collaboration, and access to vast resources across the globe.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)