Come funziona internet?
Summary
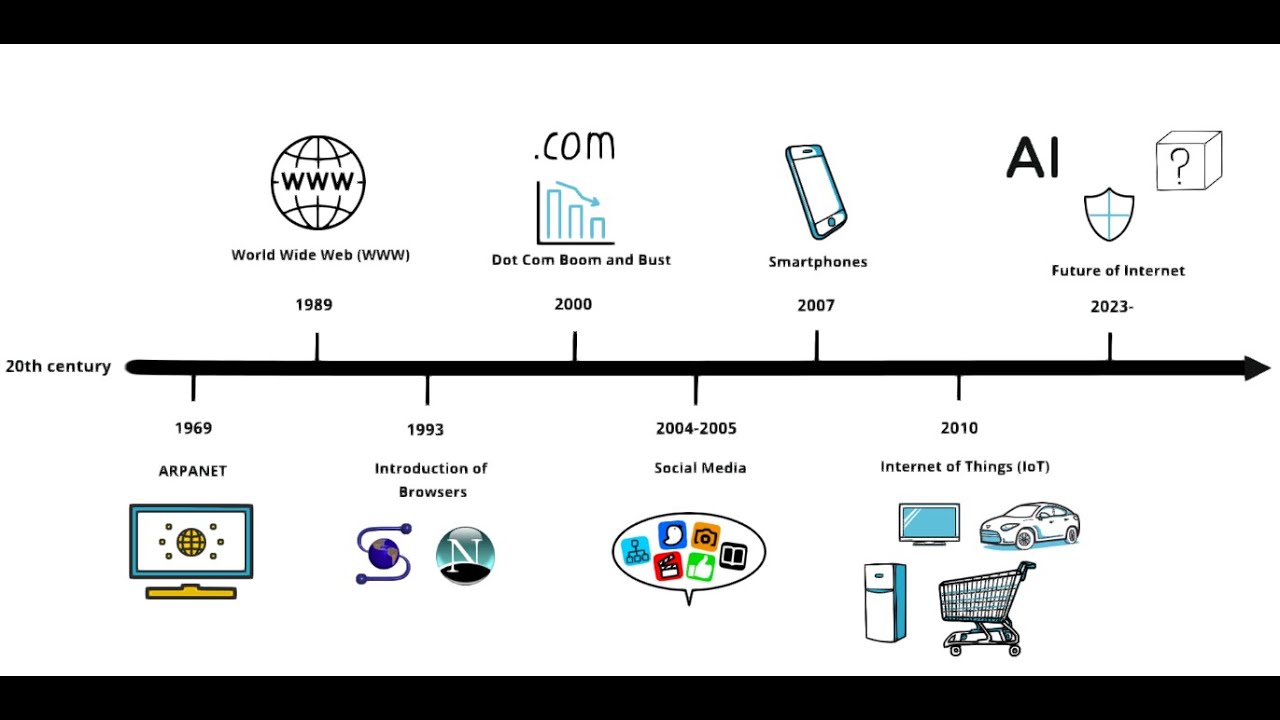
TLDRThe video script narrates the evolution of the internet from its early beginnings with ARPANET in 1969 to the invention of the World Wide Web by Tim Berners-Lee in 1989. It explains how data transmission has transformed communication globally, detailing the technical process of how data packets are sent and received across the internet, including the roles of modems, routers, and IP addresses in facilitating data exchange between devices.
Takeaways
- 🌐 The Internet allows global communication and information exchange through computers, which has revolutionized the way we communicate.
- 🔗最初,程序员只能在同一房间内的计算机之间通过直接连接的电缆发送数据,这种连接称为局域网(LAN)。
- 🚀 In 1969, the United States Department of Defense created ARPA (Advanced Research Projects Agency) to facilitate information exchange between computers across the country, leading to the creation of ARPANET.
- 🌍 1989年,英国物理学家Tim Berners-Lee在欧洲核子研究组织(CERN)工作时,提出了一个全球网络的想法,用于组织科学家之间的信息交流。
- 🌐 Berners-Lee在1991年8月6日公开了世界上第一个网站,这标志着万维网(World Wide Web)的诞生。
- 🔄 互联网是由许多计算机点组成的网络,这些点通过共同的规则交换数据,形成了我们今天所知的互联网。
- 📦 访问网站时,数据从我们的设备通过调制解调器(modem)传输,经过多个路由器(routers)和互联网服务提供商(ISPs),最终到达托管网站的服务器。
- 📨 数据在传输过程中被分割成数据包,每个数据包都包含目的地和组装指令的信息。
- 🔄 路由器通过添加自己的IP地址来帮助数据包找到通往目标计算机的路径。
- 🔄 当服务器返回信息时,它创建具有相同封装的数据包,这些数据包在返回途中通过每个路由器时逐渐解封装,直到到达我们的计算机。
- 🌐 互联网不仅仅是一个概念上的“云”,它实际上是地面下的光纤网络,这是数据传输的主要途径。
Q & A
What was the initial capability of computer programmers in terms of data transfer?
-Initially, computer programmers were able to send data from one computer to another in the same room using a cable that directly connected the two.
What is the term for the type of connection used by early computers within the same room?
-This type of connection is known as a Local Area Network (LAN).
What was the purpose of the Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA) created by the United States Department of Defense in 1969?
-ARPA aimed to enable the exchange of information between computers scattered across the United States by creating a network called ARPANET.
Who is credited with the invention of the World Wide Web, and in what year did this occur?
-English physicist Tim Berners-Lee is credited with the invention of the World Wide Web in 1989.
What was Tim Berners-Lee's profession when he developed the idea for the World Wide Web?
-Tim Berners-Lee was a technician at CERN when he developed the idea for the World Wide Web.
How did the World Wide Web initially function?
-The World Wide Web was initially designed as a mesh that allowed navigation through the various contents of the different research laboratories' computer archives, facilitating the organization of information exchanged by scientists within CERN.
What is the significance of August 6, 1991, in the history of the Internet?
-On August 6, 1991, Tim Berners-Lee made the first website in the world public, marking a significant milestone in the history of the Internet.
How does the Internet physically connect computers around the world?
-The Internet is a network of computers connected to each other, exchanging data through a series of common rules. It includes a hidden filament in the ground that corresponds to the main data transmission pathway.
What role does a modem play in connecting to the Internet?
-A modem allows digital signals to travel along telephone lines, facilitating the transmission of data from one device to an Internet Service Provider (ISP).
How do routers assist in directing data to the correct destination on the Internet?
-Routers help by dividing data into packets, which are then reassembled upon reaching their destination. They add their own IP address to the packet, which is added to each time it reaches a new router, until it reaches the server hosting the desired website.
What is the purpose of IP addresses in the context of the Internet?
-IP addresses are unique identifiers for devices on the Internet, allowing data to be correctly directed to and from the intended destinations, whether they are computers, servers, or other networked devices.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)