The Secrets Behind how the Internet Works
Summary
TLDRThis ColdFusion video delves into the origins and evolution of the Internet, starting from ARPANET in 1969 to the modern-day World Wide Web. It explores the physical infrastructure, including undersea cables, and the organizations like ICANN that govern it. The video also discusses the Internet's impact on society, the challenges of misinformation and echo chambers, and the potential future with 5G and the implications of Article 13 on content sharing.
Takeaways
- 🌐 The Internet began in 1969 with ARPANET, funded by the US Defense Department's Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA), which aimed to connect computers across universities.
- 🌟 Sir Tim Berners-Lee invented the World Wide Web at CERN, creating a way to access information via the Internet, distinct from the Internet's infrastructure.
- 🌍 The modern Internet is a vast network of interconnected points, with approximately 420 undersea cables spanning over 1.1 million kilometers as of 2017.
- 🚧 The process of laying undersea Internet cables involves ships pulling cables across oceans, with sea plows creating trenches for the cables to be buried by natural ocean currents.
- 🛠️ Despite the physical vulnerability of undersea cables, the Internet's robustness is ensured by multiple routes, making it nearly impossible to disrupt entirely by severing a single cable.
- 🌐 The Internet is decentralized, with no single government or entity owning it, but governments can regulate access through laws affecting Internet Service Providers (ISPs).
- 🔑 In 2016, the US government transferred the ownership of the Internet's domain name database to ICANN, promoting a more community-driven approach to Internet governance.
- 🔒 ICANN manages the Domain Name System (DNS), ensuring that web addresses correctly resolve to their intended destinations, and performs ceremonies to renew the DNS's security.
- 🚀 The Internet's future includes advancements like 5G, which promises significant increases in speed, although concerns about its safety and health effects have been raised.
- 📉 The European Union's Article 13, a controversial copyright law, has sparked debates on its potential impact on content sharing and the livelihood of small independent creators.
Q & A
What was the initial purpose of ARPANET, the precursor to the modern Internet?
-ARPANET, funded by the US Defense Department's Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA), was initially developed to connect computers across a few universities for communication and research purposes.
Who is credited with the invention of the World Wide Web, and what was his primary motivation?
-Sir Tim Berners-Lee is credited with inventing the World Wide Web. His primary motivation was to address the incompatibility of different networks and systems at CERN, creating a uniform and usable system for accessing information via the Internet.
How does the Internet infrastructure physically connect different countries?
-The Internet infrastructure physically connects different countries through a network of approximately 420 undersea cables spanning over 1.1 million kilometers as of 2017, which are laid by ships and buried by ocean currents on the sea floor.
What are some of the challenges faced by undersea Internet cables?
-Undersea Internet cables face challenges such as vulnerability to damage from ship anchors, natural disasters, and uneven sea floor conditions that can leave them exposed. Repairs are constantly carried out to address severed cables.
How does the Internet remain functional even if one cable is cut?
-The Internet remains functional even if one cable is cut due to its decentralized nature and the presence of multiple redundant routes for data traffic, making it nearly impossible to disable the Internet by severing a single cable.
Who owns the Internet, and how is it governed?
-The Internet is decentralized, meaning no single government or body owns or controls it. However, governments can regulate access through laws affecting ISPs. Organizations like ICANN manage critical aspects like the DNS, ensuring the Internet's safe and open operation.
What is the role of ICANN in the governance of the Internet?
-ICANN, the Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers, is responsible for managing the domain name system (DNS), ensuring that web addresses correctly resolve to their intended destinations and maintaining the security and stability of the Internet.
What is the significance of the 'key ceremony' mentioned in the script?
-The 'key ceremony' is a secure process where a group of trusted community members renew and insure the DNS system for the next three months. It involves the use of a master key controlled by seven smart cards, emphasizing the importance of security and redundancy in Internet governance.
How has the Internet impacted society, both positively and negatively?
-The Internet has positively impacted society by providing a platform for creators, artists, and journalists, and enabling rapid information sharing. Negatively, it has contributed to misinformation, echo chambers, and changes in societal structure, as discussed in the video 'The Death of Facebook'.
What are some of the anticipated developments in the future of the Internet?
-The future of the Internet includes advancements such as 5G technology, which promises at least a tenfold increase in speed, and the potential impact of regulations like Article 13 on content sharing and creation.
What is Article 13, and why has it been a point of controversy?
-Article 13 is a controversial copyright law approved by the European Union, which has raised concerns about its potential to impact content sharing and the livelihood of small independent creators on the Internet.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
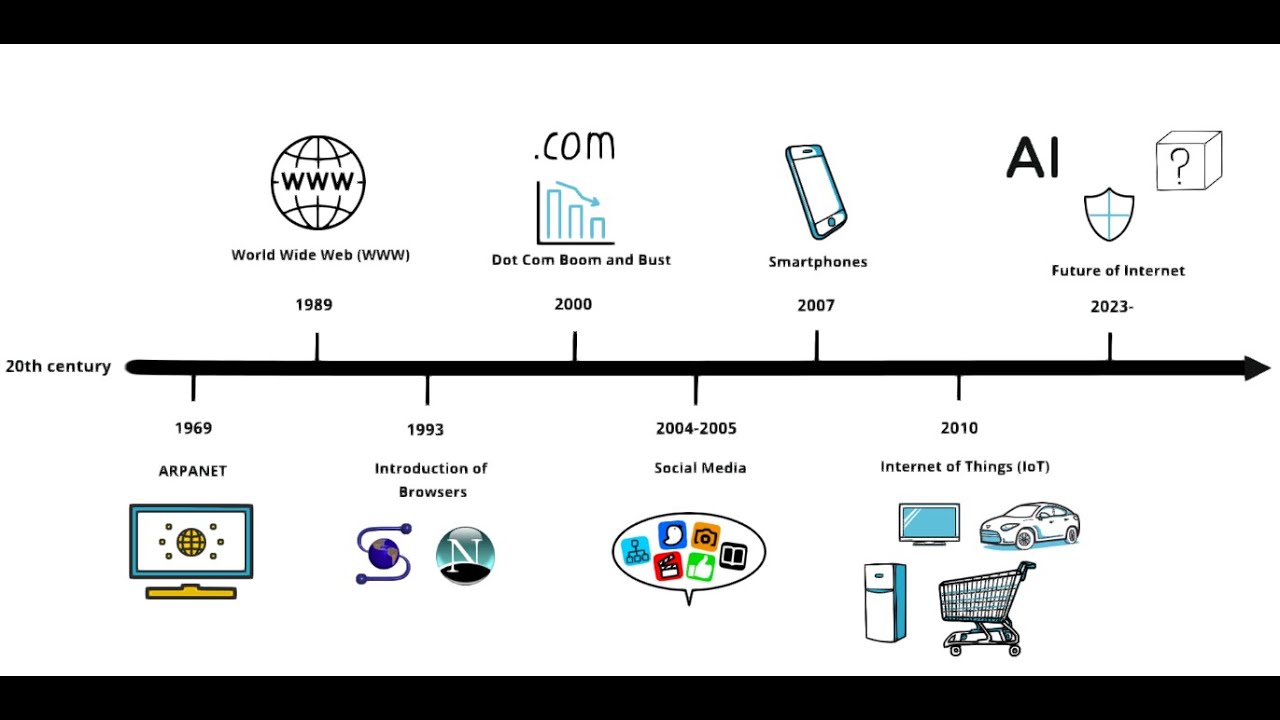
The History of the Internet: A Timeline
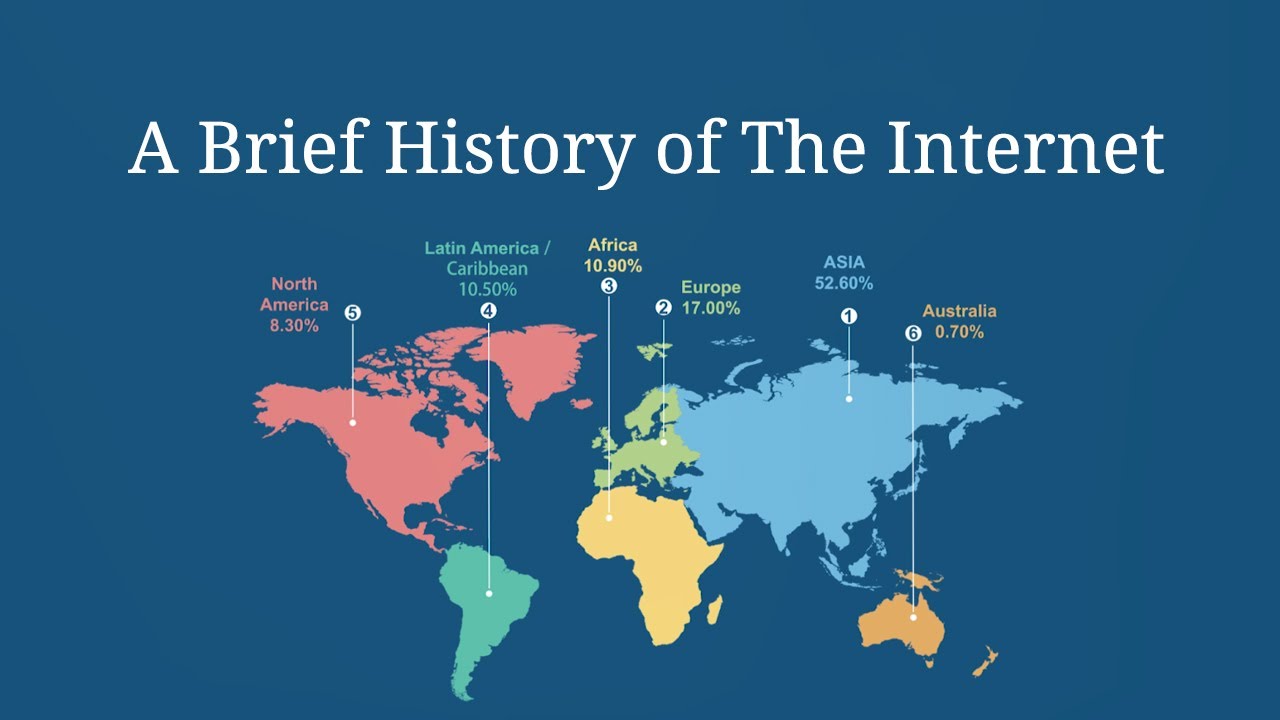
A Brief History of the Internet

Internet history | Web Technology | Lec-1 | Bhanu Priya

Como surgiu a INTERNET? Uma das tecnologias que mais utilizamos em nosso dia a dia! | Fala Cientista

Come funziona internet?
History of the Internet - How was the Internet Invented Short Documentary Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)