Apa itu SEVEN WASTE (7 Pemborosan)
Summary
TLDRIn this lecture, Muhammad Suli, a professor at Universitas Islam Negeri Sultan Syarif Kasim Riau, discusses the concept of waste in manufacturing, focusing on seven common types: overproduction, corrections, unnecessary transport, excess inventory, overprocessing, motion waste, and waiting. He explains the importance of eliminating these wastes to reduce production costs and improve efficiency. The lecture emphasizes the value of identifying non-value-added activities and optimizing production processes through strategies like cross-training employees, automating tasks, and investing in better technology. This approach aims to improve productivity and boost profitability in manufacturing operations.
Takeaways
- 😀 The concept of 'Value-added' processes refers to activities that enhance a product's characteristics to meet customer requirements, such as cooking or cutting.
- 😀 'Non-value-added' activities are tasks that do not improve the product's value but are still necessary, like inspecting product dimensions or ensuring smoothness.
- 😀 'Waste' refers to activities that consume time, resources, and space without contributing to customer needs or adding value to the product.
- 😀 Reducing 'waste' in production processes aims to lower operational costs and increase production efficiency.
- 😀 Overproduction waste occurs when a company produces more than needed, leading to increased inventory costs and possible surplus of products.
- 😀 'Rework' waste happens when products are fixed or reprocessed, which uses extra resources like labor, materials, and energy without adding value.
- 😀 'Transportation' waste involves unnecessary movement of materials or products, which could be minimized by streamlining processes and combining operations.
- 😀 Excess inventory waste leads to higher storage costs, risks of damage, and decreased product quality, requiring efficient inventory management.
- 😀 'Processing' waste occurs when unnecessary processes are included in production that don't add value to the product, leading to wasted time and resources.
- 😀 'Motion' waste occurs when workers spend unnecessary time searching for tools, materials, or documents, which slows down the production process.
- 😀 'Waiting' waste happens when workers or materials are idle, such as when waiting for other tasks or equipment to be ready, which could be avoided by improving workflow.
Q & A
What is the main focus of the script?
-The script primarily focuses on explaining the concept of waste in manufacturing and the importance of eliminating these inefficiencies to improve production processes, reduce costs, and increase profitability.
What are 'fluid known pelet' and 'nonferro edit' in the context of the script?
-'Fluid known pelet' refers to value-adding activities that change the characteristics of a product according to customer requirements, such as cooking or cutting. 'Nonferro edit' refers to non-value-adding activities that are necessary for the current process but do not enhance the product itself, such as product inspections.
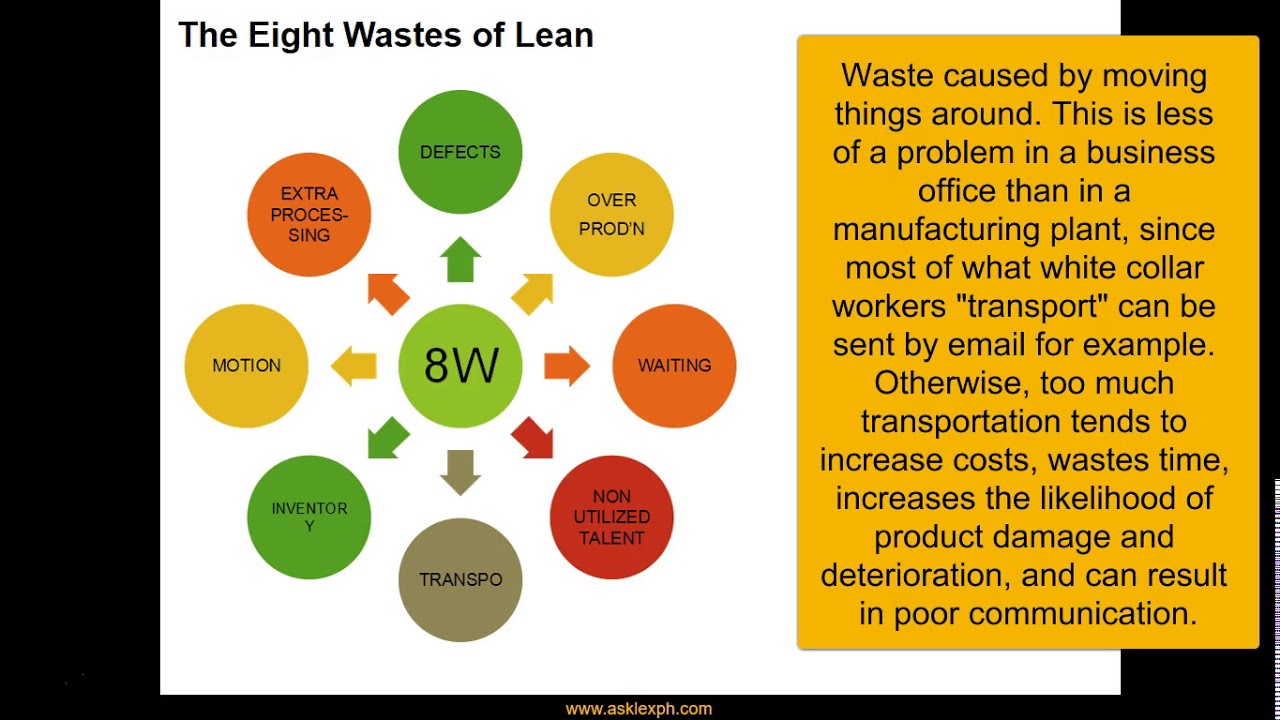
What are the seven types of waste (Wes) mentioned in the script?
-The seven types of waste discussed are: Overproduction, Rework (corrections), Unnecessary movement (transfer waste), Excess inventory, Excess processing, Unnecessary motion, and Waiting.
Why is overproduction considered waste in manufacturing?
-Overproduction is considered waste because it results in excessive inventory, leading to higher storage costs, potential product damage or obsolescence, and increased risk without adding value to the product.
How does rework contribute to waste in production?
-Rework involves fixing defects in products, requiring additional resources such as time, materials, and energy. This process does not add value to the product, making it an inefficient use of resources.
What is meant by 'unnecessary movement' or 'transfer waste' in manufacturing?
-Unnecessary movement, or transfer waste, refers to the excessive or unnecessary movement of materials or products between different stations or locations within the production process, which wastes time and energy without contributing to value.
What problems arise from excess inventory in manufacturing?
-Excess inventory can lead to problems such as increased storage costs, higher risk of product spoilage or damage, and the need for additional administrative effort to manage the excess stock.
What is excess processing, and why is it considered waste?
-Excess processing refers to performing unnecessary operations or procedures on a product, such as using machinery or handling materials in ways that do not align with customer demand. It wastes resources and time without adding value to the product.
How does unnecessary motion waste affect production?
-Unnecessary motion refers to workers or equipment spending time searching for materials, tools, or documents. This wastes time and reduces efficiency, as workers are not focused on productive tasks that add value to the product.
What is the impact of waiting in the production process?
-Waiting waste occurs when workers or machines are idle because they are waiting for materials, information, or other processes to be completed. This causes delays in the production line and reduces overall efficiency.
What steps can be taken to eliminate waste in manufacturing?
-Steps to eliminate waste include identifying and categorizing the types of waste, improving operational standards, conducting training for workers, implementing better machinery or automation, and optimizing inventory management to reduce excess stock.
How can eliminating waste improve company profitability?
-By eliminating waste, companies can reduce production costs, improve efficiency, and optimize resource usage, which leads to lower operating costs and higher profitability.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenant5.0 / 5 (0 votes)