CLASS 7 | FLOW OF HEAT | LIVING SCIENCE | HEAT | SUPRIYA RAI | NCERT CLASS 7 |CLASS 7 LIVING SCIENCE
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, Supreeya Rai explains the principles of heat transfer through conduction, convection, and radiation, using relatable examples from everyday life. She demonstrates how heat moves through solids, liquids, and gases, highlighting the importance of temperature differences in conduction and the natural cycles in convection. The concept of radiation is also covered, showing how heat travels without a medium. The video is filled with practical applications, such as the behavior of cooking utensils, coastal breezes, and the impact of colors on heat absorption, helping viewers understand these scientific principles in real-world contexts.
Takeaways
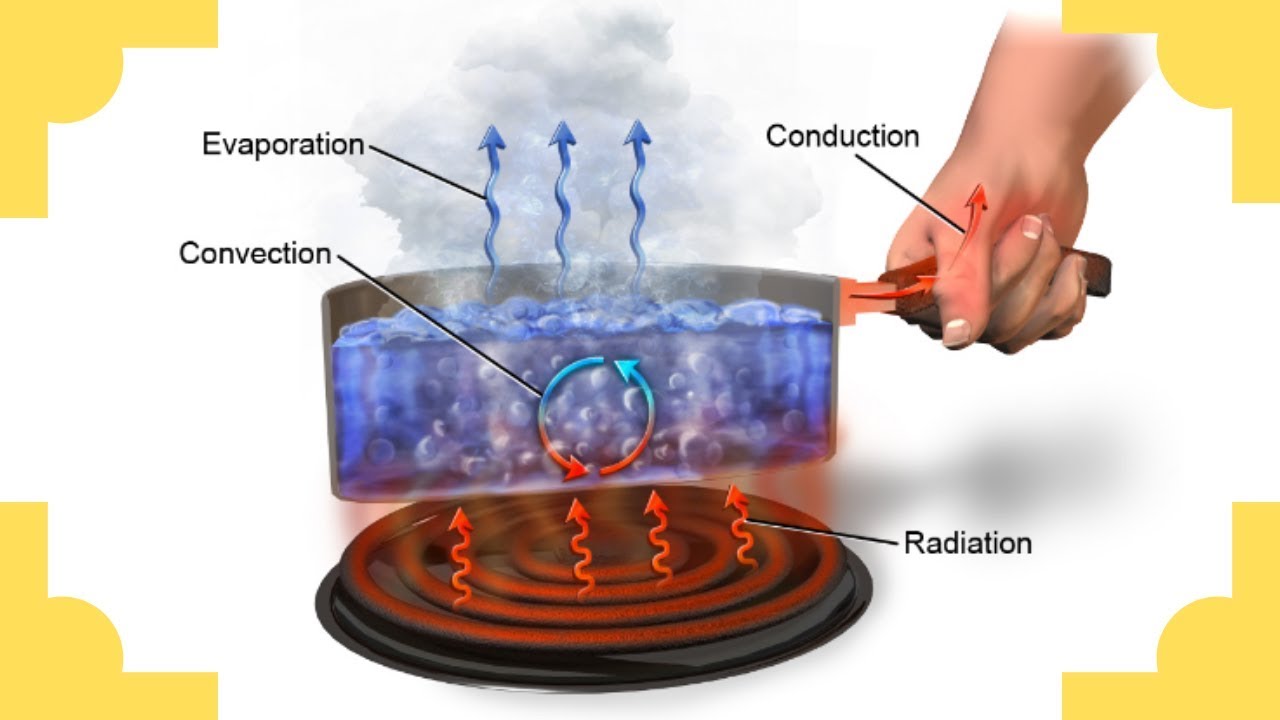
- 😀 Conduction occurs in solids, where heat is transferred through direct contact between molecules.
- 😀 In conduction, for heat transfer to occur, there must be a **temperature difference** between the objects and **contact** between molecules.
- 😀 Metals are **good conductors** of heat, whereas materials like plastic and wood are **insulators**.
- 😀 Convection primarily happens in liquids and gases, where heat transfer occurs due to the movement of molecules caused by temperature differences.
- 😀 In convection, warm air or water rises, and cool air or water moves in to take its place, creating a circulation pattern.
- 😀 Everyday examples of convection can be seen in coastal areas, where cool ocean air moves toward the land during the day and warm air moves out to the ocean at night.
- 😀 Radiation is the transfer of heat through electromagnetic waves and does not require any medium, unlike conduction or convection.
- 😀 Dark-colored objects absorb more heat compared to light-colored ones, which is why dark clothes are warmer in winter and cooler clothes are preferable in summer.
- 😀 Thermoses use all three modes of heat transfer (conduction, convection, and radiation) to keep the contents hot or cold for extended periods.
- 😀 Heat transfer in solids occurs by conduction, in liquids and gases by convection, and in space or a vacuum by radiation, without needing a medium.
- 😀 In practical applications, insulated materials like thermoses or coolers are designed to prevent heat transfer, keeping contents either hot or cold for a long time.
Q & A
What are the three modes of heat transfer discussed in the video?
-The three modes of heat transfer discussed are conduction, convection, and radiation.
How does conduction work in solids?
-In conduction, heat moves from the hotter part of a solid object to the cooler part through molecular vibrations. The molecules in solids are tightly packed and do not move, so heat transfer occurs through the transfer of energy between adjacent molecules.
Can you give an example of conduction from the video?
-An example of conduction from the video is when a metal spoon is heated by a candle. After some time, the heat moves along the spoon and is felt at the other end.
Why do heat transfers occur only between objects with different temperatures?
-Heat transfers occur only when there is a temperature difference between objects. Heat moves from the hot object (higher temperature) to the cooler one (lower temperature) until both reach thermal equilibrium.
What is convection and where does it mostly occur?
-Convection is the heat transfer process in liquids and gases, where heat is carried by the movement of molecules. This process mainly occurs in liquids and gases due to the ability of molecules to move and carry heat.
Can convection happen in solids? Why or why not?
-No, convection cannot happen in solids. This is because the particles in solids are tightly packed and cannot move freely to transfer heat. Convection requires fluidity, which solids lack.
How does convection affect the movement of air near coastal areas?
-In coastal areas, during the day, the land heats up faster than the ocean. This causes the warm air above the land to rise, and cooler air from the ocean rushes in to replace it, creating a cooling breeze. This cycle is reversed in the evening when the land cools faster than the ocean.
What is radiation and how does it differ from conduction and convection?
-Radiation is the transfer of heat through electromagnetic waves without the need for any medium. Unlike conduction and convection, radiation can occur even in a vacuum, such as the heat from the Sun reaching Earth.
What role does color play in heat absorption and emission, according to the video?
-Dark-colored objects absorb more heat compared to light-colored objects. In the winter, dark colors absorb heat from the surroundings, while light colors reflect it. This is why dark-colored clothes feel warmer in cold weather.
Why are thermos bottles designed with reflective materials?
-Thermos bottles are designed with reflective materials, such as silver, to reflect radiation and prevent heat from escaping or entering. This helps to keep the contents, like hot or cold water, at the desired temperature for longer periods.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)