Perpindahan Kalor
Summary
TLDRThis educational video explains the different methods of heat transfer: conduction, convection, and radiation. Using practical examples such as cooking with a metal pot, ventilation in classrooms, and the function of a thermos, it demonstrates how heat moves through materials. The video highlights how metals conduct heat effectively, while non-metals like plastic and glass act as insulators. It also explores the role of air movement in convection and how heat from the sun reaches Earth via radiation. The thermos is presented as a practical application that prevents heat loss through all three methods.
Takeaways
- 😀 Heat transfer occurs when heat moves from a substance with a high temperature to one with a lower temperature.
- 😀 The presence of heat in an object can change its temperature, alter its state, and cause expansion.
- 😀 Expansion of objects due to heat will be discussed in a future video.
- 😀 Pots typically use handles made from insulating materials, such as plastic, to prevent heat transfer from the hot metal to your hands.
- 😀 Heat transfer by conduction happens when a material, like metal, effectively conducts heat, while insulators like plastic prevent heat transfer.
- 😀 Conduction is the transfer of heat through materials like metal, while insulators like plastic, rubber, and wood resist heat flow.
- 😀 In classrooms, ventilation is crucial to remove excess heat produced by students. Air flows from outside to inside and exits via ventilation openings.
- 😀 Convection is the transfer of heat through the movement of particles, such as air in a classroom or water in a pot.
- 😀 Convection in liquids and gases occurs when heated particles move to the top, carrying heat with them, as seen in boiling water.
- 😀 Heat from the sun reaches Earth through radiation, as space is a vacuum where conduction and convection cannot occur.
- 😀 A thermos is designed to retain heat by preventing heat transfer through conduction, convection, and radiation.
- 😀 The thermos uses insulating materials like glass and cork, a reflective inner surface, and a vacuum to minimize heat transfer and keep contents hot.
Q & A
What is the fundamental property of heat transfer discussed in the video?
-The fundamental property of heat transfer discussed is that heat moves from a substance with a higher temperature to a substance with a lower temperature.
What are the three main types of heat transfer explained in the video?
-The three main types of heat transfer explained are conduction, convection, and radiation.
How does heat transfer by conduction occur?
-Heat transfer by conduction occurs when heat flows through a medium, such as metal, which is a good conductor of heat. This happens as particles in the medium vibrate and pass on heat energy.
Why are the handles of cookware often made from materials like plastic?
-Cookware handles are often made from plastic because plastic is an insulator, which prevents heat from transferring from the metal pot to the handle, making it safer to touch.
What distinguishes conductors from insulators in heat transfer?
-Conductors are materials that allow heat to flow easily, such as metals like aluminum, while insulators are materials that resist the flow of heat, like plastic, rubber, or wood.
What role does convection play in heat transfer within a room?
-Convection involves the movement of heat through a fluid (such as air). In a room, warm air rises and cooler air replaces it, creating a cycle that helps distribute heat throughout the space.
How does convection work when heating water?
-In water, convection occurs when heated water at the bottom of the container rises to the top, while cooler water sinks. This creates a circular motion of water particles, transferring heat through the liquid.
Why can we feel the heat of the sun despite its distance from Earth?
-The heat from the sun reaches Earth through radiation, which can travel through the vacuum of space without the need for a medium or particles to transfer heat.
What is the main purpose of a thermos, and how does it prevent heat transfer?
-The main purpose of a thermos is to keep hot liquids hot or cold liquids cold. It prevents heat transfer through conduction, convection, and radiation by using insulating materials and a reflective inner surface.
How does the structure of a thermos reduce heat transfer by radiation?
-The thermos reduces heat transfer by radiation by having a shiny, reflective inner surface that reflects heat back into the liquid, preventing it from escaping.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
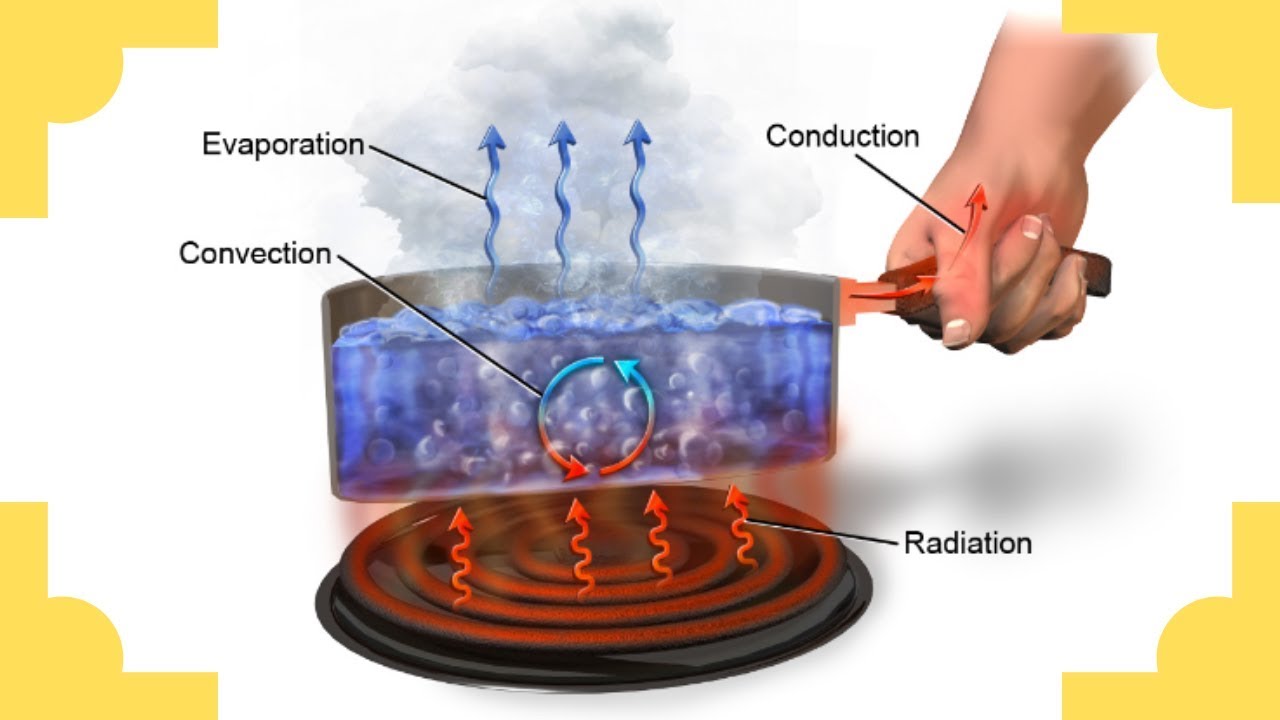
Conduction -Convection- Radiation-Heat Transfer

Heat Transfer - Conduction, Convection, and Radiation
Steam Boiler Operation on Ship Explained

Heat Transfer: Conduction, Convection, and Radiation

FISIKA KELAS XI | SUHU DAN KALOR (PART 5) - PERPINDAHAN KALOR Konduksi, Konveksi, dan Radiasi

CLASS 7 | FLOW OF HEAT | LIVING SCIENCE | HEAT | SUPRIYA RAI | NCERT CLASS 7 |CLASS 7 LIVING SCIENCE
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)