Heat Transfer – Conduction, Convection and Radiation
Summary
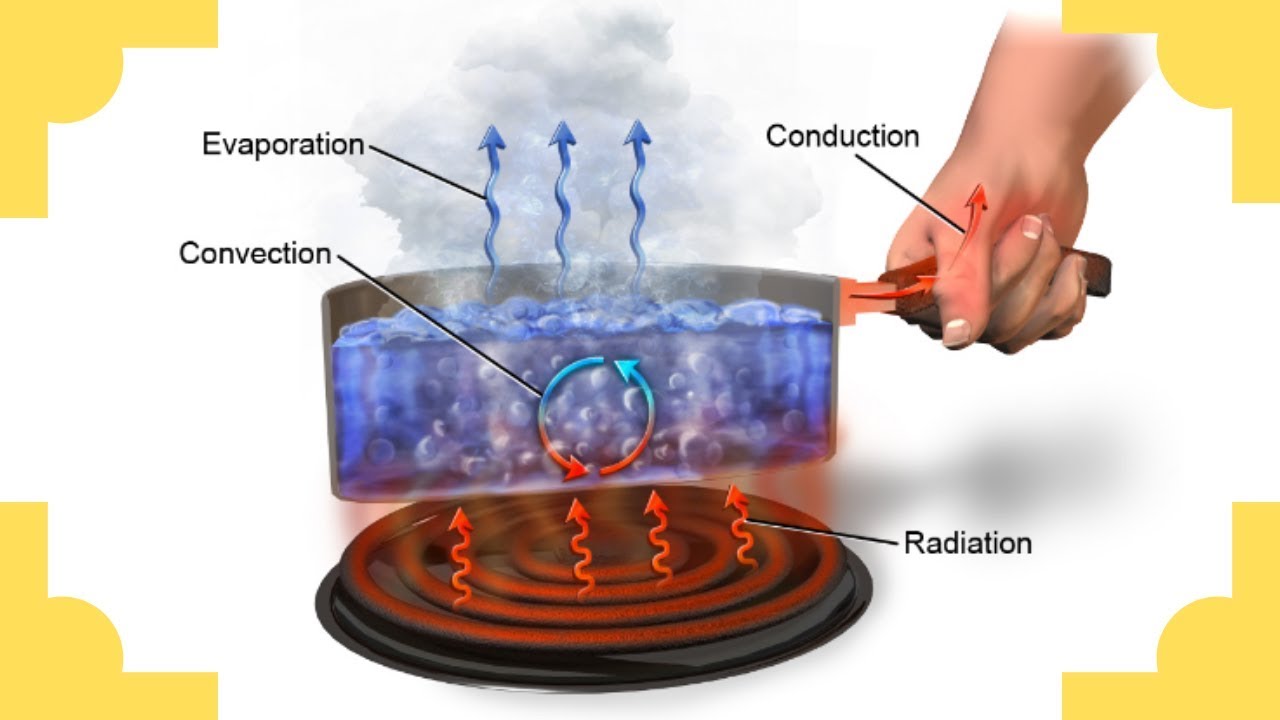
TLDRThe video explains the three main ways thermal energy transfers: conduction, convection, and radiation. Conduction occurs when heat moves through direct contact in solids, illustrated by a kettle heating water. Convection involves the movement of heat in liquids and gases, exemplified by hot air rising in a balloon and cold air circulating from an air conditioner. Radiation, distinct from the other methods, transfers heat through electromagnetic waves, as seen when warming by a fire. The video highlights these concepts using relatable examples, enhancing understanding of how thermal energy interacts in everyday situations.
Takeaways
- 🔥 Conduction is the transfer of heat through direct contact within solids.
- 💧 Butter melting on a frying pan is a classic example of conduction in action.
- 👅 When licking ice cream, heat transfers from your tongue to the ice cream, illustrating conduction.
- 🌬️ Convection describes the movement of heat in liquids and gases.
- 🎈 In hot air balloons, hot air rises and cooler air falls, creating convection currents.
- ❄️ Air conditioners use convection to circulate cold air and cool down rooms.
- ☀️ Radiation is the transfer of energy through electromagnetic waves, able to travel through empty space.
- 🔥 A person warming by a fireplace experiences both convection and radiation heat transfer.
- 🤲 The warmth felt near an electric heater is a direct example of radiation at work.
- 💧 When heating water in a kettle, conduction, convection, and radiation all play crucial roles.
Q & A
What are the three main ways thermal energy moves?
-Thermal energy moves through conduction, convection, and radiation.
How does conduction work?
-Conduction is the transfer of heat within solids, occurring when objects are in contact with each other.
Can you give an example of conduction?
-An example of conduction is a kettle on a stove where heat from the flame moves through the metal to warm the water inside.
What is convection and how does it function?
-Convection is the movement of heat in liquids and gases, involving the circulation of warmer and cooler air or fluid.
What happens in a hot air balloon during convection?
-In a hot air balloon, heated air rises, causing cooler air to fall, creating convection currents that distribute thermal energy.
How does an air conditioner utilize convection?
-An air conditioner blows out cold air, which circulates around the room and creates convection currents, transferring heat from warmer to cooler areas.
What is the process of radiation?
-Radiation is the transfer of energy through electromagnetic waves, which does not require any medium for heat transfer.
How does radiation differ from conduction and convection?
-Unlike conduction and convection, which require matter for heat transfer, radiation can occur through empty space.
Can you provide an example of radiation?
-An example of radiation is the warmth felt from a campfire or electric heater, which warms objects and people nearby without direct contact.
How do conduction, convection, and radiation occur when heating water in a kettle?
-In a kettle, conduction transfers heat from the metal to the water, convection circulates the heated water, and radiation allows heat to escape to the surroundings.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)