Crystal Structure for Metallic Elements : BCC, FCC and HCP | Engineering Materials
Summary
TLDRThis educational session focuses on the crystal structures of metallic elements, specifically body-centered cubic (BCC), face-centered cubic (FCC), and hexagonal close-packed (HCP) arrangements. The lecture emphasizes the significance of crystal structure in determining the physical and mechanical properties of metals, including strength, ductility, and electrical conductivity. Key features of each structure are discussed: BCC has lower packing efficiency and is typically stronger but less ductile; FCC offers higher packing efficiency and ductility; HCP features efficient packing but less ductility compared to FCC. Examples of metals for each structure are provided, enhancing understanding of their properties.
Takeaways
- 😀 A crystal structure refers to the arrangement of atoms or ions in a crystalline material, which determines its physical and mechanical properties.
- 💪 The properties influenced by crystal structures include strength, ductility, and electrical conductivity.
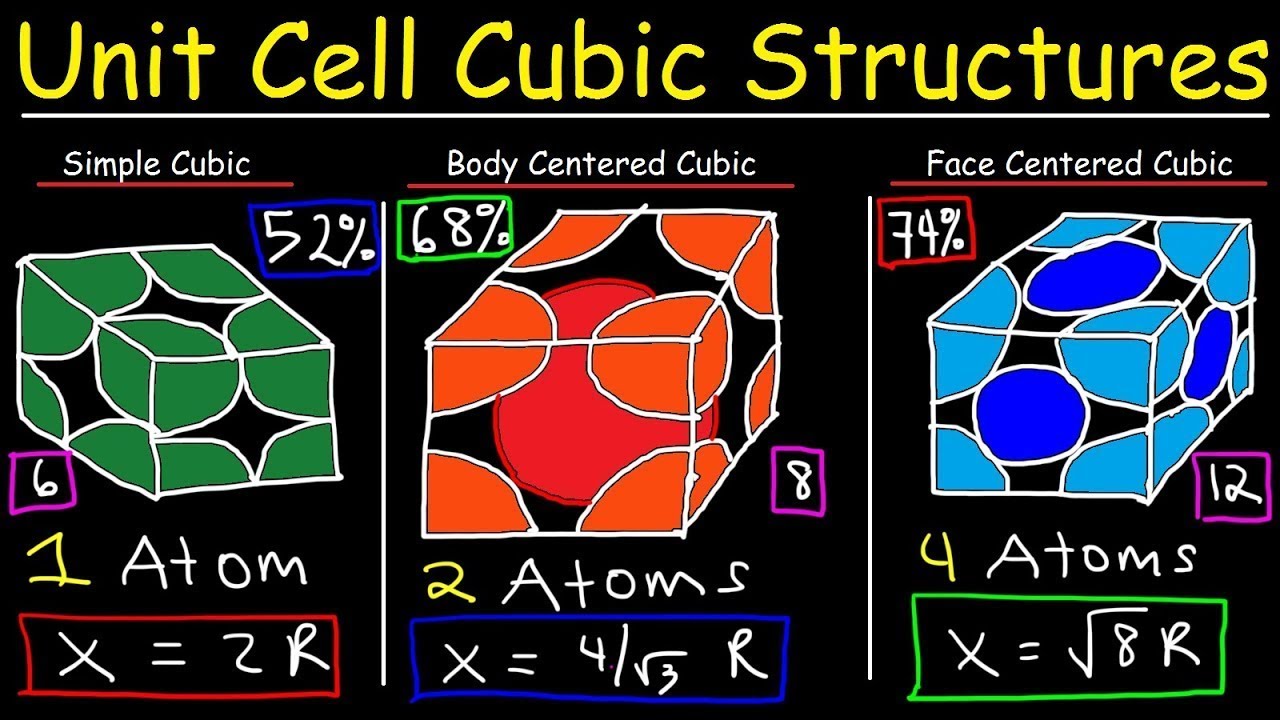
- 📦 The Body-Centered Cubic (BCC) structure has atoms arranged in a cube with one atom in the center and one at each corner, exemplified by iron (Fe).
- 🔗 In the BCC structure, each atom touches 8 neighbors and exhibits lower packing efficiency compared to FCC.
- ⚙️ BCC materials are typically stronger and less ductile than FCC materials and can undergo phase changes under certain conditions.
- 🧊 The Face-Centered Cubic (FCC) structure features atoms at each corner of the cube and one in the center of each face, with examples like aluminum (Al) and copper (Cu).
- 👥 Each atom in the FCC structure touches 12 neighbors, resulting in higher packing efficiency than BCC.
- 🔷 The Hexagonal Close-Packed (HCP) structure has atoms arranged in a close-packed hexagonal formation, with examples including titanium (Ti) and zinc (Zn).
- 🏗️ In the HCP structure, each atom also touches 12 neighbors but tends to be less ductile compared to FCC.
- 📈 Understanding different crystal structures is essential for predicting and manipulating the properties of metals in various applications.
Q & A
What is the primary focus of the lecture?
-The lecture focuses on the crystal structures of metallic elements, specifically Body-Centered Cubic (BCC), Face-Centered Cubic (FCC), and Hexagonal Close-Packed (HCP) structures.
What is a crystal structure?
-A crystal structure is the arrangement of atoms or ions in a crystalline material, which determines the material's physical and mechanical properties.
How do different crystal structures affect metallic properties?
-Different crystal structures lead to varying behaviors in materials, influencing properties like strength, ductility, and electrical conductivity.
Describe the BCC structure.
-In the BCC structure, atoms are arranged in a cubic lattice with one atom at the center and one at each corner. Each atom touches eight neighbors.
What is an example of a metal that exhibits a BCC structure?
-Iron (Fe) at room temperature is an example of a metal that exhibits a BCC structure.
What are the key properties of BCC metals?
-BCC metals are typically stronger but less ductile compared to FCC metals and can undergo phase changes under certain conditions.
Explain the FCC structure.
-In the FCC structure, atoms are arranged with one atom at each corner and one atom in the center of each face of the cube. Each atom touches twelve neighbors.
Can you provide examples of metals with FCC structures?
-Aluminum (Al) and Copper (Cu) are examples of metals that have FCC structures.
What is the packing efficiency comparison between BCC and FCC?
-FCC has a higher packing efficiency compared to BCC.
Describe the HCP structure.
-In the HCP structure, atoms are arranged in a close-packed structure with layers in a hexagonal arrangement. Each atom touches twelve neighbors.
What are some examples of metals with HCP structures?
-Titanium (Ti) and Zinc (Zn) are examples of metals that exhibit HCP structures.
How does the ductility of HCP compare to FCC?
-HCP metals generally exhibit less ductility compared to FCC metals, even though both have efficient packing.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

Materiais - Módulo 6 - Estrutura dos materiais (Parte 6)

Aula 10 – Estruturas Cristalinas Cúbicas de Face Centrada, Corpo Centrado e Hexagonal Compacta.

Lattice Structures Part 1

AMIE Exam Lectures- Materials Science & Engineering | BCC | FCC | HCP | Cubic System | 3.2
Unit Cell Chemistry Simple Cubic, Body Centered Cubic, Face Centered Cubic Crystal Lattice Structu

The Structure of Crystalline Solids
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
