Lattice Structures Part 1
Summary
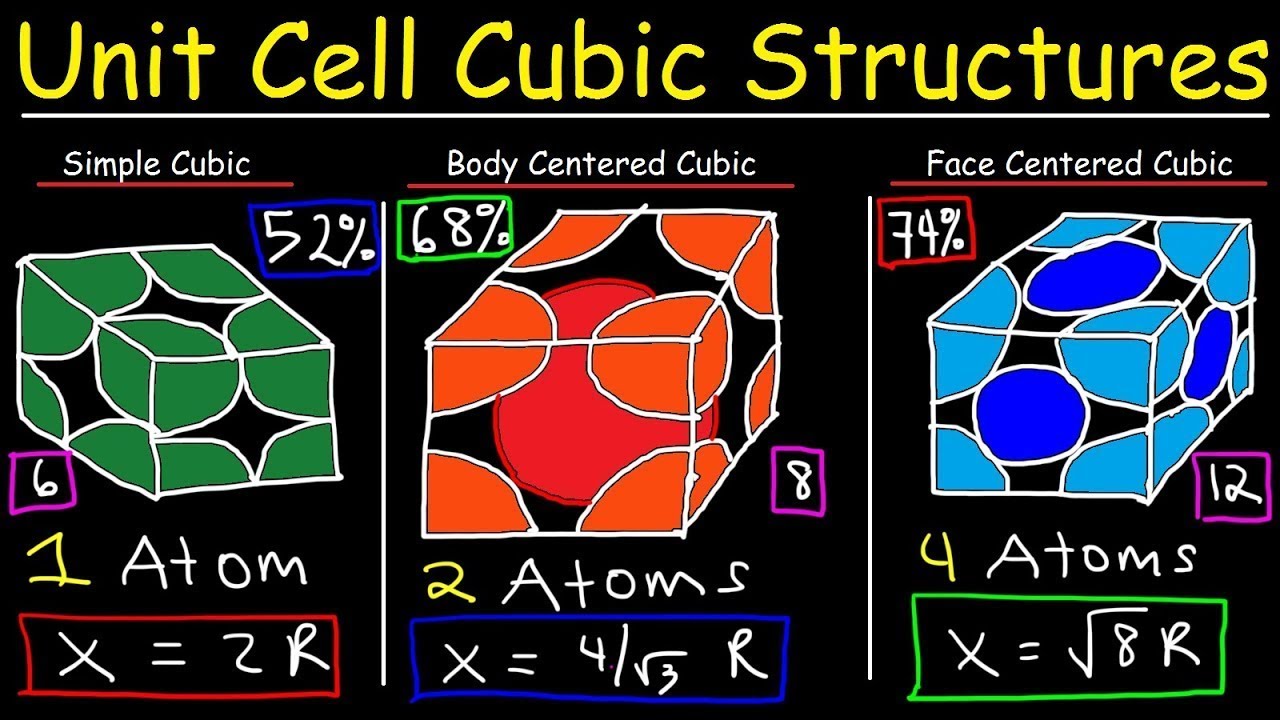
TLDRThe video explains common crystal lattices—simple cubic, body-centered cubic (BCC), face-centered cubic (FCC), and close-packed (hexagonal and cubic)—using ball-and-stick and space-filling models to show how atoms occupy and touch within unit cells. It compares atom counts per unit cell (1 for simple cubic, 2 for BCC, 4 for FCC), shows where atoms touch (edge, cube diagonal, side diagonal), and gives coordination numbers (6, 8, 12 respectively). Finally, it contrasts hexagonal close-packed and cubic close-packed stacking, noting that cubic close-packed is equivalent to the FCC structure. Clear visuals and color-coded layers illustrate packing and stacking differences.
Takeaways
- 📦 The simple cubic lattice has atoms at the eight corners of a cube, and they touch along the edges.
- 🧱 In a simple cubic unit cell, each corner atom contributes one eighth, resulting in one total atom per cell.
- 🔹 The body-centered cubic (BCC) lattice includes the eight corner atoms plus one atom in the center of the cube.
- 💠 BCC atoms touch along the cube diagonal, not the edges like in simple cubic structures.
- 🔢 The body-centered cubic unit cell contains the equivalent of two atoms inside the cell.
- 🔳 The face-centered cubic (FCC) lattice has eight corner atoms plus one on each of the six faces.
- 📐 FCC atoms touch along the face diagonal, making the structure more closely packed than simple cubic or BCC.
- 🧮 The face-centered cubic unit cell contains the equivalent of four atoms per cell.
- 🤝 Coordination number reflects how many atoms each atom touches; simple cubic is 6, BCC is 8, and FCC is 12.
- 🔷 Hexagonal close-packed (HCP) and cubic close-packed (CCP) structures are formed from close-packed layers with different stacking sequences.
- 🔁 CCP is identical to the face-centered cubic structure, sharing the same occupancy and coordination number.
Q & A
What is the structure of a simple cubic lattice?
-A simple cubic lattice consists of eight atoms located at the eight corners of a cube. The atoms touch along the edges of the cell, and in a space-filling model, the atoms are packed closely together.
How is the unit cell of a simple cubic lattice represented?
-In the unit cell of the simple cubic lattice, each of the eight atoms is considered to contribute 1/8th of an atom inside the cell, leading to the equivalent of one whole atom inside the unit cell.
What is the key difference between the simple cubic and body-centered cubic lattices?
-The body-centered cubic lattice has the same eight corner atoms as the simple cubic, but it also contains one atom at the center of the cell. This central atom causes the vertex atoms to no longer touch along the edges, but instead along the cube's diagonal.
How does the coordination number of the body-centered cubic lattice compare to the simple cubic lattice?
-In the body-centered cubic lattice, the coordination number is eight, as each body atom touches eight vertex atoms. In contrast, the simple cubic lattice has a coordination number of six, as each corner atom touches three others along the edges of the cell.
What is the arrangement of atoms in a face-centered cubic lattice?
-The face-centered cubic lattice contains eight corner atoms and six face atoms, with the face atoms positioned at the centers of the cell's faces. In a space-filling model, the atoms touch along the side diagonals of the cell.
How is the coordination number of a face-centered cubic lattice calculated?
-In a face-centered cubic lattice, each face atom touches four corner atoms within the same plane and is surrounded by eight other face atoms, giving it a coordination number of 12. Similarly, each corner atom also has a coordination number of 12.
What distinguishes close-packed structures from the cubic lattices discussed?
-Close-packed structures consist of layers of atoms stacked in a way that each atom is surrounded by six others. The two types of close-packed structures are hexagonal close-packed (hcp) and cubic close-packed (ccp), with the key difference being in how the layers are stacked.
What is the arrangement of atoms in the hexagonal close-packed (hcp) structure?
-In the hexagonal close-packed structure, the atoms are arranged in layers where every other layer is identical, forming a repeating ABAB stacking pattern.
What is the stacking pattern in the cubic close-packed (ccp) structure, and how does it compare to the face-centered cubic structure?
-The cubic close-packed structure has a stacking pattern where every third layer is identical, forming an ABCABC sequence. This arrangement is structurally identical to the face-centered cubic (fcc) structure, so they share the same occupancy and coordination number.
How does the coordination number differ in various lattice structures?
-The coordination number varies by structure: for the simple cubic lattice, it's 6; for the body-centered cubic lattice, it's 8; for the face-centered cubic and close-packed structures, it's 12. The coordination number represents how many atoms surround a given atom within the lattice.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Aula 10 – Estruturas Cristalinas Cúbicas de Face Centrada, Corpo Centrado e Hexagonal Compacta.
Unit Cell Chemistry Simple Cubic, Body Centered Cubic, Face Centered Cubic Crystal Lattice Structu

Materiais - Módulo 6 - Estrutura dos materiais (Parte 6)

The Structure of Crystalline Solids

AMIE Exam Lectures- Materials Science & Engineering | BCC | FCC | HCP | Cubic System | 3.2

Crystal Structure for Metallic Elements : BCC, FCC and HCP | Engineering Materials
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)