AMIE Exam Lectures- Materials Science & Engineering | BCC | FCC | HCP | Cubic System | 3.2
Summary
TLDRIn this lecture on Material Science and Engineering, the focus is on understanding different cubic crystal structures, specifically Body Centered Cubic (BCC), Face Centered Cubic (FCC), and Hexagonal systems. The video covers the number of atoms in each unit cell, their coordination numbers, and packing fractions, with a detailed explanation of how atoms are arranged in these structures. Examples of metals with each structure are also discussed, including Iron, Copper, and Magnesium. The lecture aims to help viewers grasp the complexities of crystal systems and their significance in materials science.
Takeaways
- 😀 The lecture focuses on understanding different types of crystal systems, particularly the Body-Centered Cubic (BCC), Face-Centered Cubic (FCC), and Hexagonal systems.
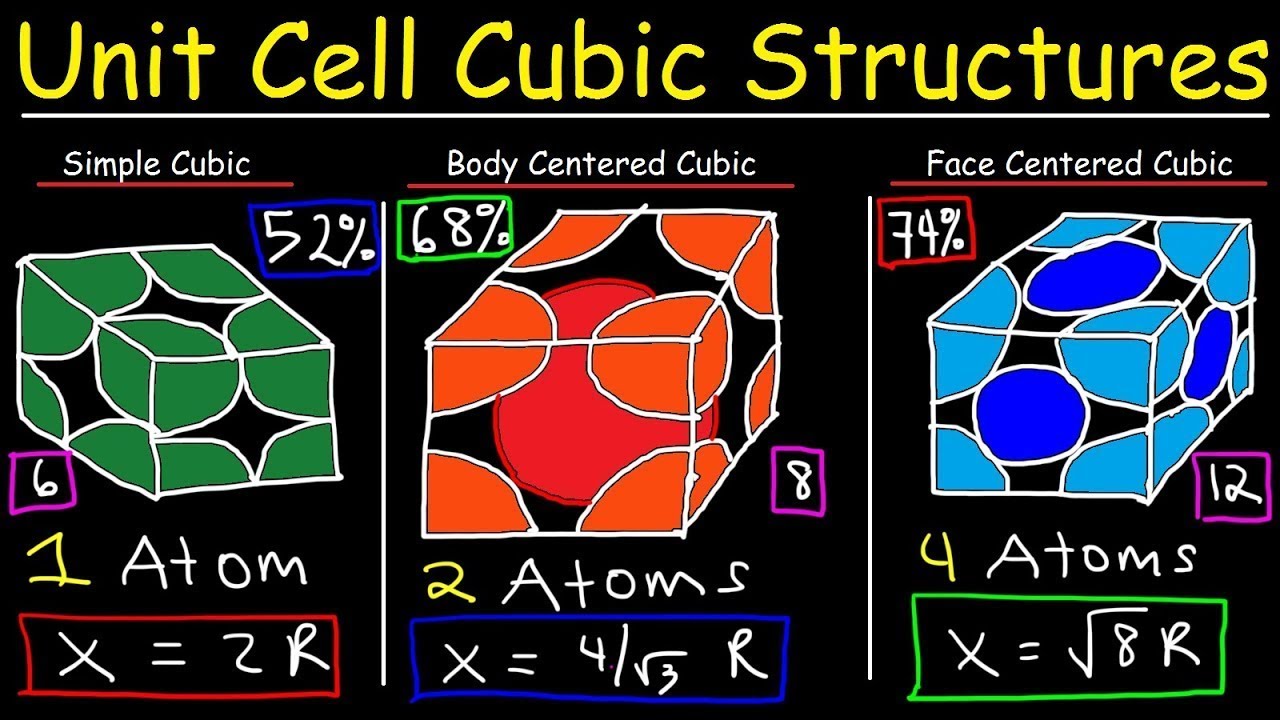
- 😀 BCC is a cubic system where atoms are located at the eight corners and one atom at the center of the unit cell, contributing two atoms per unit cell.
- 😀 The coordination number for BCC is 8, meaning each atom is surrounded by 8 nearest neighbor atoms.
- 😀 The percentage packing in BCC is about 68%, indicating 32% void space in the unit cell.
- 😀 Examples of elements with a BCC structure include iron, tungsten, molybdenum, and potassium.
- 😀 FCC is also a cubic system, with atoms at the corners and at the center of each face of the cube, contributing four atoms per unit cell.
- 😀 The coordination number for FCC is 12, meaning each atom is surrounded by 12 nearest neighbor atoms.
- 😀 The packing fraction for FCC is about 74%, meaning it has a higher packing efficiency than BCC by approximately 6%.
- 😀 Elements such as copper, aluminum, nickel, and silver exhibit FCC structures.
- 😀 The FCC structure can also be represented as an ABC-ABC stacking sequence, where three distinct layers repeat, leading to high packing efficiency.
- 😀 The Hexagonal system, similar to FCC, also achieves high packing efficiency with a coordination number of 12, but the stacking sequence differs as it follows an AB-AB pattern.
Q & A
What are the main types of lattice systems discussed in the lecture?
-The lecture discusses three main types of lattice systems: Body-Centered Cubic (BCC), Face-Centered Cubic (FCC), and Hexagonal Close-Packed (HCP).
What is a unit cell in a crystal structure?
-A unit cell is the smallest repeating unit that can be replicated in three dimensions to form the entire crystal structure. It defines the geometry and the arrangement of atoms in the crystal.
How are the atoms arranged in a Body-Centered Cubic (BCC) system?
-In a BCC system, there are eight atoms at the corners of the unit cell, with one atom at the center of the unit cell. The corner atoms are shared by eight neighboring unit cells.
What is the effective number of atoms per unit cell in a Body-Centered Cubic (BCC) system?
-In a BCC system, the effective number of atoms per unit cell is 2. The eight corner atoms contribute 1/8th of an atom each, and the center atom contributes one full atom.
What is the coordination number in a Body-Centered Cubic (BCC) system?
-The coordination number in a BCC system is 8, which means each atom is surrounded by 8 nearest neighbor atoms.
What is the packing fraction in a Body-Centered Cubic (BCC) system?
-The packing fraction in a BCC system is 68%, meaning that 68% of the volume of the unit cell is occupied by atoms, with the remaining 32% being void space.
How is the coordination number of a Face-Centered Cubic (FCC) system different from that of a BCC system?
-The coordination number in an FCC system is 12, which means each atom is surrounded by 12 nearest neighbor atoms, compared to 8 in the BCC system.
What is the packing fraction in a Face-Centered Cubic (FCC) system?
-The packing fraction in an FCC system is approximately 74%, meaning 74% of the volume of the unit cell is occupied by atoms.
What is the significance of the ABC ABC stacking in a Face-Centered Cubic (FCC) system?
-The ABC ABC stacking refers to the arrangement of layers in the FCC system, where each layer is stacked in a specific order to maximize packing density. This results in a coordination number of 12 and a packing fraction of 74%.
What is the difference between the stacking sequence in FCC and HCP systems?
-The stacking sequence in the FCC system follows the ABC ABC pattern, while the HCP system follows an AB AB pattern. Despite this difference in stacking, both systems have the same packing fraction of 74%.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Crystal Structure for Metallic Elements : BCC, FCC and HCP | Engineering Materials

Aula 10 – Estruturas Cristalinas Cúbicas de Face Centrada, Corpo Centrado e Hexagonal Compacta.

Lattice Structures Part 1

Materiais - Módulo 6 - Estrutura dos materiais (Parte 6)
Unit Cell Chemistry Simple Cubic, Body Centered Cubic, Face Centered Cubic Crystal Lattice Structu

The Structure of Crystalline Solids
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)