Materiais - Módulo 6 - Estrutura dos materiais (Parte 6)
Summary
TLDRThis video explores three primary crystalline structures: body-centered cubic (BCC), face-centered cubic (FCC), and hexagonal close-packed (HCP). It details their atomic arrangements, coordination numbers, and the concept of atomic packing density. The BCC structure features two atoms per unit cell, while FCC is denser with four atoms, and HCP shares the same coordination number as FCC but differs in stacking sequence. The presentation emphasizes the significance of these structures in material science, illustrating how variations in atomic arrangement affect properties and behaviors.
Takeaways
- 😀 The three main crystalline structures discussed are Body-Centered Cubic (BCC), Face-Centered Cubic (FCC), and Hexagonal Close-Packed (HCP).
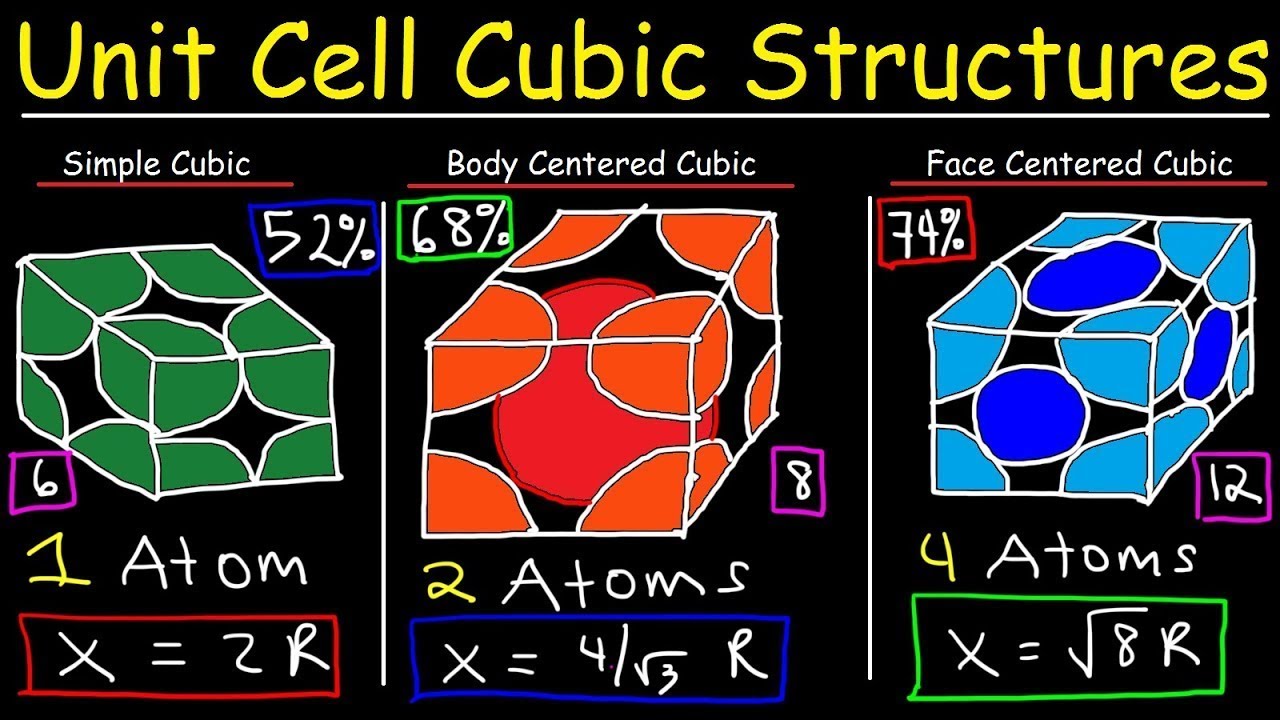
- 😀 The BCC structure has two atoms per unit cell: one at the center and eight at the corners, contributing to a coordination number of 8.
- 😀 FCC is denser than BCC, containing four atoms per unit cell, with a coordination number of 12, representing the maximum density for cubic structures.
- 😀 HCP also has a coordination number of 12, similar to FCC, but its atomic packing sequence differs, affecting atomic deformation.
- 😀 The concept of atomic planes is crucial, with FCC exhibiting planes of maximum atomic density, while BCC lacks such planes.
- 😀 Understanding crystal structures helps in predicting the properties of materials based on their atomic arrangement.
- 😀 The parameter 'a' describes the cell dimensions, and for cubic structures, one parameter is sufficient.
- 😀 Polymorphism in materials like iron shows that different crystalline structures can exist depending on temperature.
- 😀 In FCC, the densest planes are the {111} planes, while in BCC, the {110} planes are the densest.
- 😀 The arrangement and stacking sequence of atoms in structures like HCP and FCC have significant implications for material properties.
Q & A
What are the three main crystal structures discussed in the transcript?
-The three main crystal structures are Body-Centered Cubic (BCC), Face-Centered Cubic (FCC), and Hexagonal Close-Packed (HCP).
How many atoms are there in a unit cell of BCC?
-There are 2 atoms in a unit cell of Body-Centered Cubic (BCC).
What is the coordination number for FCC?
-The coordination number for Face-Centered Cubic (FCC) is 12.
What distinguishes FCC from BCC in terms of atomic density?
-FCC has a higher atomic density than BCC due to its arrangement allowing for planes of maximum atomic density.
What is the significance of the coordination number?
-The coordination number indicates how many atoms are in direct contact with a central atom, which helps understand the density and stability of the structure.
How are atoms arranged in the HCP structure?
-In Hexagonal Close-Packed (HCP), atoms are arranged in three layers with a specific stacking sequence, allowing for maximum packing density.
What type of atomic arrangement does the BCC structure lack?
-The BCC structure lacks planes of maximum atomic density.
What is the total number of atoms in a unit cell of FCC?
-There are 4 atoms in a unit cell of Face-Centered Cubic (FCC).
How does the stacking sequence differ between FCC and HCP?
-FCC has alternating layers that are misaligned, while HCP has a stacking sequence where every third layer is aligned with the first.
Why is understanding these crystal structures important in materials science?
-Understanding these crystal structures is crucial as they influence the material's properties, such as strength, density, and behavior under different conditions.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Aula 10 – Estruturas Cristalinas Cúbicas de Face Centrada, Corpo Centrado e Hexagonal Compacta.

Crystal Structure for Metallic Elements : BCC, FCC and HCP | Engineering Materials

Lattice Structures Part 1

The Structure of Crystalline Solids
Unit Cell Chemistry Simple Cubic, Body Centered Cubic, Face Centered Cubic Crystal Lattice Structu

AMIE Exam Lectures- Materials Science & Engineering | BCC | FCC | HCP | Cubic System | 3.2
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)