3 1 2 Virtualization and Virtual Machines explained
Summary
TLDRIn this IBM cloud team video, Kaylee Bovie explains virtualization as creating a software-based virtual version of resources like compute, storage, and networking. She covers the role of hypervisors, distinguishing between Type 1 (bare-metal) and Type 2 (hosted), highlighting their significance in cloud computing. Bovie emphasizes virtual machines' independence, portability, and the benefits of virtualization, such as cost savings, agility, and reduced downtime.
Takeaways
- 🌐 **Virtualization Defined**: Virtualization is the process of creating a software-based virtual version of compute, storage, networking servers, or applications.
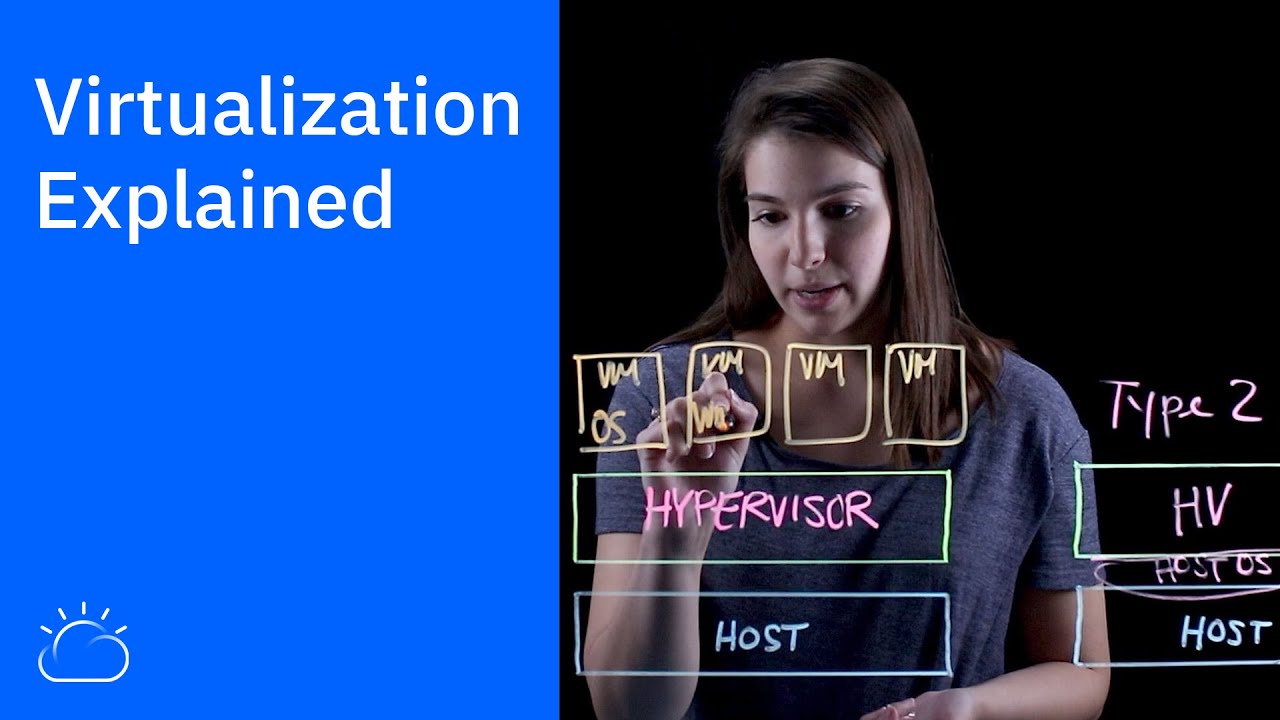
- 🛠️ **Role of Hypervisor**: A hypervisor is essential software that runs above the physical server to allocate resources to virtual environments.
- 💻 **Type 1 Hypervisor**: Type 1 hypervisors, also known as bare-metal, are installed directly on the physical server and are more secure and lower latency.
- 🌟 **Examples of Type 1**: VMware ESXi, Microsoft Hyper-V, and KVM are examples of Type 1 hypervisors.
- 📚 **Type 2 Hypervisor**: Type 2 hypervisors, or hosted hypervisors, sit on top of a host OS and are less frequent with higher latency.
- 🔄 **Virtual Machines (VMs)**: VMs are software-based computers that run like physical computers with their own OS and applications.
- 🔄 **Independence of VMs**: VMs are independent and can run different operating systems, providing flexibility.
- 🔄 **Portability of VMs**: VMs can be moved from one hypervisor to another quickly, enhancing portability.
- 💰 **Cost Savings**: Virtualization allows for cost savings by reducing the need for physical infrastructure, thus lowering maintenance and electricity costs.
- ⚡ **Agility and Speed**: Virtualization enables quick provisioning of new environments, increasing agility.
- 🛡️ **Reduced Downtime**: Virtualization helps in reducing downtime by easily moving VMs to another hypervisor in case of host failure.
Q & A
What is virtualization?
-Virtualization is the process of creating a software-based virtual version of something like compute, storage, networking servers, or applications.
What role does a hypervisor play in virtualization?
-A hypervisor is a piece of software that runs above the physical server or host and manages the allocation of resources from the physical server to virtual environments.
What are the two main types of hypervisors?
-The two main types of hypervisors are Type 1 (bare-metal) and Type 2 (hosted).
What is a Type 1 hypervisor and why is it considered more secure?
-A Type 1 hypervisor is installed directly on the physical server and is also known as a bare-metal hypervisor. It is considered more secure because it has direct access to the hardware, which lowers latency and is more frequently used in the market.
What are some examples of Type 1 hypervisors?
-Examples of Type 1 hypervisors include VMware ESXi, Microsoft Hyper-V, and the open-source KVM.
How does a Type 2 hypervisor differ from a Type 1 hypervisor?
-A Type 2 hypervisor has a layer of host OS between the physical server and the hypervisor, making it a hosted hypervisor. It is less frequent, used mostly for end-user virtualization, and has higher latency compared to Type 1.
What are some examples of Type 2 hypervisors?
-Examples of Type 2 hypervisors include Oracle VirtualBox and VMware Workstation.
What is a virtual machine (VM)?
-A virtual machine is a software-based computer that runs like a physical computer, complete with an operating system and applications, and is independent from other VMs.
How does virtualization enable multiple operating systems to run on the same physical server?
-Virtualization allows multiple VMs to run on a single physical server, each with its own operating system, because they are independent of one another.
What are the key benefits of virtualization?
-Key benefits of virtualization include cost savings through reduced physical infrastructure, increased agility and speed in provisioning new environments, and reduced downtime due to the ability to quickly move VMs to another hypervisor in case of host failure.
How does virtualization contribute to cloud computing?
-Virtualization and VMs are central to cloud computing as they provide flexibility, portability, and the ability to scale resources up or down as needed.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenant5.0 / 5 (0 votes)