Virtualization Explained
Summary
TLDRKaleigh Bovey from IBM Cloud discusses the importance of virtualization in cloud computing. Virtualization involves creating virtual versions of resources like compute, storage, and servers using a hypervisor. Two types of hypervisors are explained: Type 1 (bare metal) and Type 2 (hosted), with Type 1 being more secure and efficient. Virtual Machines (VMs) are independent software-based computers that run on hypervisors, offering cost savings, agility, and reduced downtime. The video emphasizes virtualization's relevance to modern cloud strategies.
Takeaways
- 💡 **Virtualization Defined**: Virtualization is the creation of a software-based or virtual version of resources like compute, storage, networking, servers, or applications.
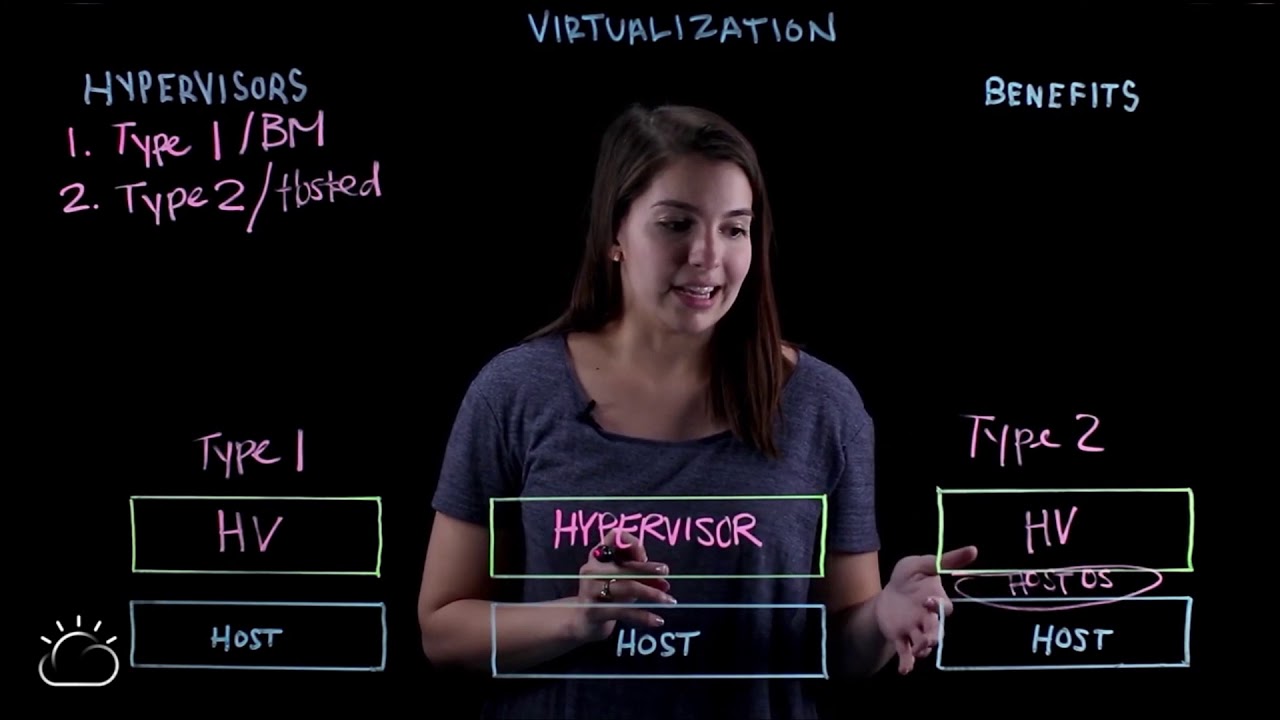
- 🛠️ **Role of Hypervisor**: A hypervisor is essential software that runs above the physical server, pooling and allocating resources to virtual environments.
- 🔑 **Type 1 Hypervisors**: Also known as bare metal hypervisors, these are installed directly on the physical server, offering security, lower latency, and are the most common in the market.
- 💻 **Type 2 Hypervisors**: Hosted hypervisors sit on a host OS layer between the server and hypervisor, used less frequently, and have higher latency.
- 🌐 **Building VMs**: Virtual Machines (VMs) are software-based computers that run independently, each with its own OS and applications, and can be managed by a hypervisor.
- 🔄 **VM Independence and Portability**: VMs can run different OSes and are portable, allowing for quick movement between hypervisors on different machines.
- 💰 **Cost Savings**: Virtualization enables running multiple environments on one piece of infrastructure, reducing physical server needs and associated costs.
- ⚡ **Agility and Speed**: Provisioning VMs is quicker than setting up new physical environments, offering faster deployment for development and testing.
- 🛡️ **Reduced Downtime**: The ability to move VMs between hypervisors ensures minimal downtime in case of server failure, providing a robust backup strategy.
- 🔍 **Relevance to Cloud Strategy**: Despite being decades old, virtualization remains critical for modern cloud computing strategies.
Q & A
What is virtualization?
-Virtualization is the process of creating a software-based or virtual version of something, such as compute, storage, networking, servers, or applications.
What role does a hypervisor play in virtualization?
-A hypervisor is a piece of software that runs above the physical server or host, pooling resources from the physical server and allocating them to virtual environments.
What are the two main types of hypervisors?
-The two main types of hypervisors are Type 1 (bare metal) and Type 2 (hosted) hypervisors.
What is a Type 1 hypervisor and why are they commonly used?
-A Type 1 hypervisor is installed directly on the physical server, also known as a bare metal hypervisor. They are commonly used because they are the most secure, lower latency, and are the most frequently seen in the market.
What are some examples of Type 1 hypervisors?
-Examples of Type 1 hypervisors include VMware ESXi, Microsoft Hyper-V, and the open-source KVM.
How does a Type 2 hypervisor differ from a Type 1 hypervisor?
-A Type 2 hypervisor, also known as a hosted hypervisor, has a layer of host OS between the physical server and the hypervisor, making it less secure and more latency-prone than Type 1 hypervisors.
What are some examples of Type 2 hypervisors?
-Examples of Type 2 hypervisors include Oracle VirtualBox and VMware Workstation.
What is a VM and how does it function?
-A VM (virtual machine) is a software-based computer that runs like a physical computer, complete with an operating system and applications, and is independent of other VMs.
What are the key benefits of virtualization in terms of cost savings?
-Virtualization allows for cost savings by reducing the physical infrastructure footprint, lowering maintenance costs, and reducing electricity usage, leading to a significant reduction in overall expenses.
How does virtualization contribute to agility and speed in IT operations?
-Virtualization contributes to agility and speed by simplifying and quickening the process of spinning up new virtual machines, which is much easier and faster than provisioning an entire new physical environment.
How does virtualization help in reducing downtime?
-Virtualization helps reduce downtime by allowing for the quick movement of VMs from one hypervisor to another in case of a host failure, ensuring business continuity and a robust backup plan.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)