The Sci Guys: Science at Home - SE2 - EP9: Boyle's Law of Ideal Gases
Summary
TLDRIn this educational episode, hosts Ryan and Mark demonstrate Boyle's Law, which states that pressure and volume are inversely proportional for a fixed amount of gas at constant temperature. Through a hands-on experiment using a syringe and a water balloon, they show how increasing pressure causes the balloon to shrink, and decreasing pressure causes it to expand. The experiment visually illustrates the relationship between pressure and volume in gases, providing a clear, engaging explanation of this fundamental gas law. Viewers are encouraged to try the experiment themselves and share their results.
Takeaways
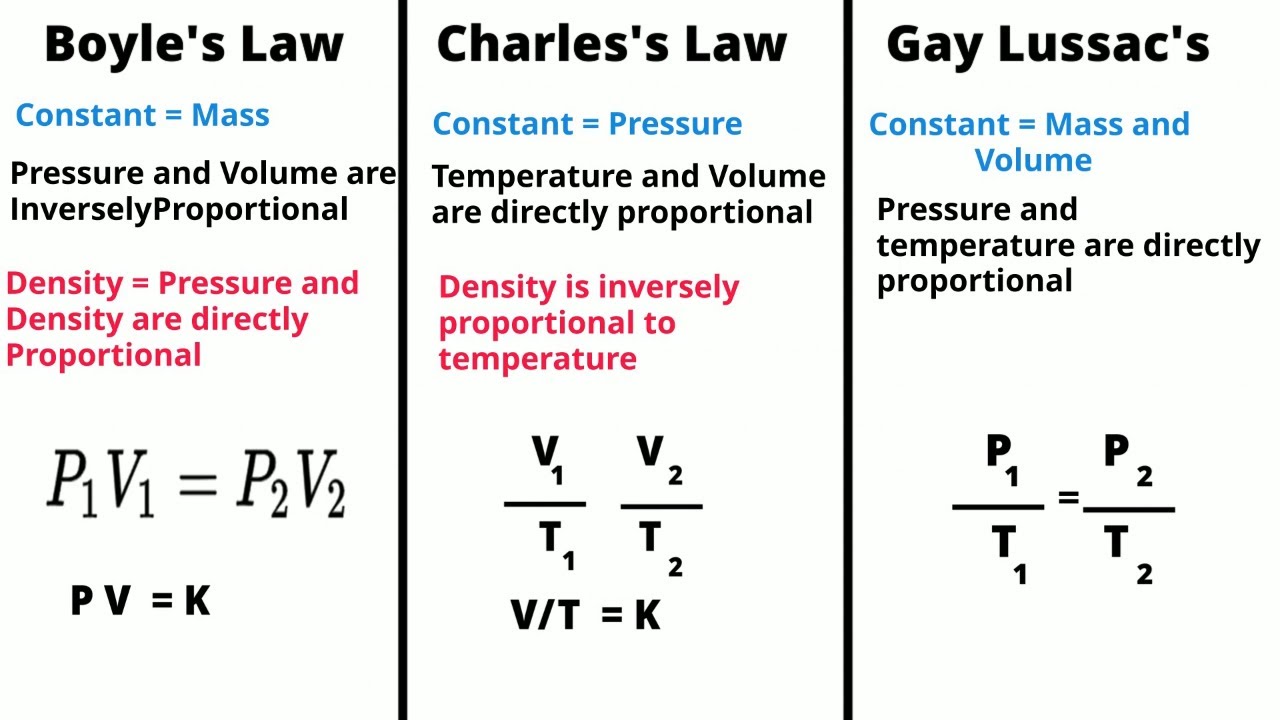
- 😀 Boyle's Law states that in a closed system, pressure and volume of a gas are inversely proportional, meaning as pressure increases, volume decreases, and vice versa.
- 😀 The experiment demonstrates Boyle’s Law using a syringe and a water balloon, providing a hands-on way to visualize the relationship between pressure and volume.
- 😀 The necessary materials for the experiment include a large syringe, water balloons, and optional safety equipment like eye protection and a lab coat.
- 😀 In the first part of the experiment, pressing the plunger down on the syringe increases pressure, causing the balloon to shrink as the volume decreases.
- 😀 In the second part of the experiment, pulling the plunger upwards reduces pressure, causing the balloon to expand as the volume increases.
- 😀 The experiment shows how gas molecules are forced closer together (increasing pressure) or spread further apart (decreasing pressure) as volume changes.
- 😀 Boyle’s Law applies to ideal gases, which are theoretical gases composed of randomly moving, non-interacting particles.
- 😀 Ideal gases follow the laws of gas behavior, such as Boyle’s Law, under normal conditions like those used in the experiment.
- 😀 The key takeaway from the experiment is that pressure and volume are inversely proportional—when one increases, the other decreases.
- 😀 The video encourages viewers to try the experiment at home, share their results, and engage with the show on social media, making sure to ask for parental permission before sharing photos or videos.
Q & A
What is Boyle's Law?
-Boyle's Law states that, in a closed system at constant temperature, the pressure and volume of a gas are inversely proportional. This means that when the pressure increases, the volume decreases, and when the pressure decreases, the volume increases.
What equipment is required for the Boyle's Law experiment?
-The equipment required includes a large syringe, a small water balloon, eye protection, and a lab coat or apron for safety.
How does the water balloon demonstrate Boyle's Law in this experiment?
-The water balloon acts as the gas inside the syringe. By changing the pressure inside the syringe (by pushing or pulling the plunger), the volume of the balloon changes, which demonstrates the inverse relationship between pressure and volume.
Why do we use a syringe for this experiment?
-A syringe is used because it allows us to control and manipulate the volume and pressure of the air inside the closed system. The plunger can move up and down, either compressing or expanding the volume of the gas.
What happens to the balloon when pressure is applied by pushing the plunger down?
-When the plunger is pressed down, the volume of the air inside the syringe decreases, which increases the pressure. As a result, the balloon shrinks in size as the air molecules are forced closer together.
What happens to the balloon when the pressure is released by pulling the plunger up?
-When the plunger is pulled up, the volume of the syringe increases, reducing the pressure. As a result, the balloon expands as the air molecules move further apart due to the decreased pressure.
Why is it important to keep the system closed in this experiment?
-Keeping the system closed ensures that the mass of the gas inside the syringe remains constant. This allows us to manipulate pressure and volume without any external factors like air entering or leaving the system.
What is an ideal gas?
-An ideal gas is a theoretical gas composed of particles that are in random motion and do not interact with each other. Under normal conditions, many gases like oxygen and carbon dioxide behave like ideal gases and follow the laws of ideal gases such as Boyle's Law.
Why is it important to wear eye protection during the experiment?
-While the experiment involves no hazardous materials, wearing eye protection is a safety precaution in case of any accidental pressure buildup or if the syringe or balloon were to break.
What other gases, besides air, can behave like an ideal gas?
-In addition to air, gases like hydrogen, nitrogen, and even some heavier gases like carbon dioxide can behave like an ideal gas under typical conditions, following laws like Boyle's Law.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahora5.0 / 5 (0 votes)