IPA FISIKA : Gas Ideal Hukum Charles, Hukum Gay Lussac dan Hukum Boyle (Simulasi)
Summary
TLDRThis video explains three fundamental gas laws: Charles' Law, Gay-Lussac's Law, and Boyle's Law. Charles' Law states that the volume of gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature at constant pressure. Gay-Lussac's Law describes how the pressure of gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature at constant volume. Boyle's Law reveals that the pressure of gas is inversely proportional to its volume at constant temperature. The video uses simulations and graphs to visually demonstrate the relationships between temperature, pressure, and volume, offering a clear and engaging overview of these gas laws.
Takeaways
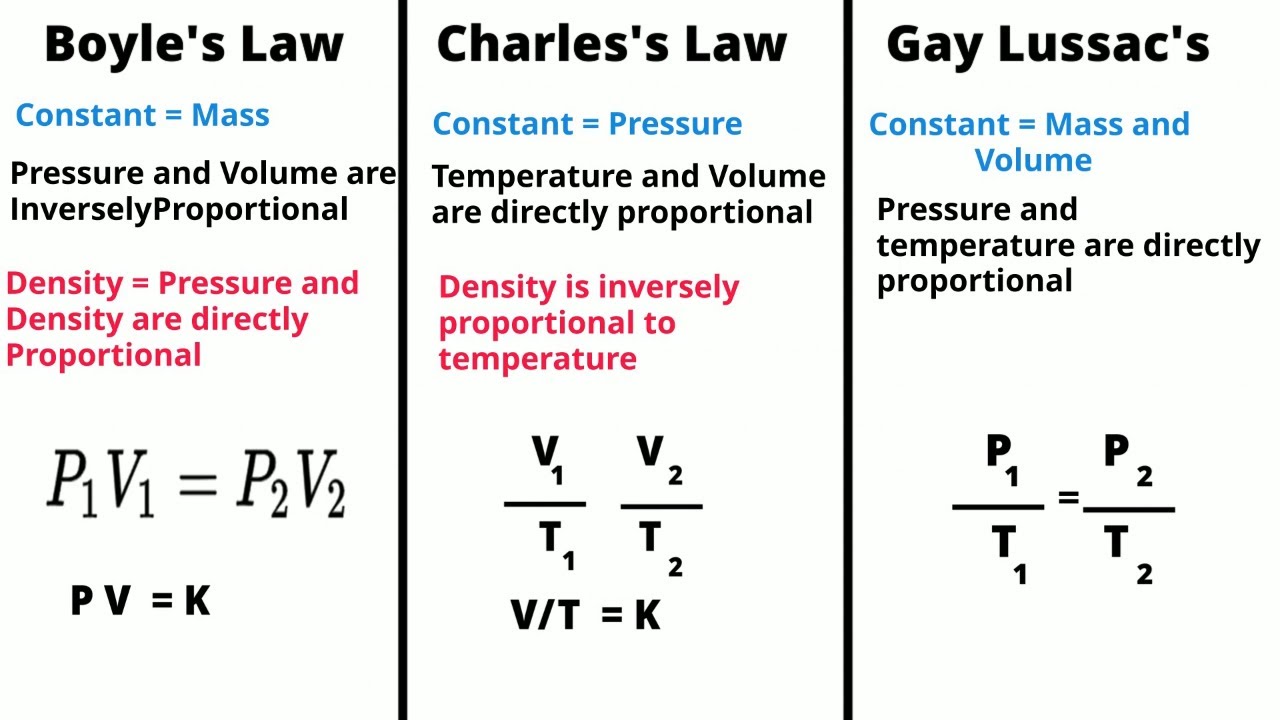
- 😀 Charles's Law states that at constant pressure, the volume of a gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature.
- 😀 When the temperature of a gas increases, its volume also increases, as described by Charles's Law.
- 😀 The graphical representation of Charles's Law shows an upward slope for volume vs. temperature at constant pressure.
- 😀 Gay-Lussac's Law states that at constant volume, the pressure of a gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature.
- 😀 As temperature increases, the pressure of the gas also increases, according to Gay-Lussac's Law.
- 😀 The graphical representation of Gay-Lussac's Law shows an upward slope for pressure vs. temperature at constant volume.
- 😀 Boyle's Law states that at constant temperature, the pressure of a gas is inversely proportional to its volume.
- 😀 When the volume of a gas decreases, its pressure increases, as stated by Boyle's Law.
- 😀 The graphical representation of Boyle's Law shows a downward slope for pressure vs. volume at constant temperature.
- 😀 All three gas laws (Charles's Law, Gay-Lussac's Law, and Boyle's Law) describe the behavior of gases in closed systems under various conditions of temperature, pressure, and volume.
Q & A
What does Charles' Law state?
-Charles' Law states that at constant pressure, the volume of a gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature. As the temperature increases, the volume increases as well.
How is Charles' Law mathematically expressed?
-Charles' Law is expressed as V ∝ T, where V is the volume of the gas and T is the absolute temperature in Kelvin, assuming constant pressure.
How does the volume of gas change according to Charles' Law when temperature changes?
-According to Charles' Law, when the temperature of the gas increases, the volume increases proportionally, and when the temperature decreases, the volume decreases as well, provided pressure remains constant.
What is Gay-Lussac's Law about?
-Gay-Lussac's Law states that at constant volume, the pressure of a gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature. If the temperature increases, the pressure also increases.
How is Gay-Lussac's Law mathematically represented?
-Gay-Lussac's Law is mathematically represented as P ∝ T, where P is the pressure of the gas and T is the absolute temperature, assuming constant volume.
How does the pressure of gas behave according to Gay-Lussac's Law when the temperature changes?
-According to Gay-Lussac's Law, when the temperature of the gas increases, the pressure increases as well, and when the temperature decreases, the pressure decreases, assuming the volume is held constant.
What does Boyle's Law state?
-Boyle's Law states that at constant temperature, the pressure of a gas is inversely proportional to its volume. When the volume decreases, the pressure increases, and vice versa.
How is Boyle's Law mathematically expressed?
-Boyle's Law is mathematically expressed as P ∝ 1/V, where P is the pressure of the gas and V is the volume, assuming constant temperature.
What happens to the pressure of gas when its volume is reduced according to Boyle's Law?
-According to Boyle's Law, when the volume of a gas is reduced, the pressure increases, assuming the temperature remains constant.
Why are the gas laws (Charles', Gay-Lussac's, and Boyle's) important in understanding gas behavior?
-These gas laws are essential for understanding how gases respond to changes in temperature, pressure, and volume. They help predict and explain the behavior of gases in a wide range of scientific and industrial applications, such as in thermodynamics and engineering.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)