Direct Variation - Basic Introduction | Algebra
Summary
TLDRThis video provides an introduction to direct variation, explaining the relationship between two variables, typically x and y, through a linear equation y = kx, where k is the constant of variation. The presenter demonstrates how to calculate k and use it to solve problems involving direct variation. Practical examples are given, such as calculating values for specific x and y pairs, determining if y varies directly with x in tables, and applying direct variation to real-world scenarios, such as calculating walking distances based on time.
Takeaways
- 📊 Direct variation describes a linear relationship between two variables, X (independent) and Y (dependent).
- 🔢 The equation for direct variation is y = kx, where k is the constant of variation.
- ✏️ To find k, divide y by x (k = y/x).
- 📈 As x increases, y increases at a proportional rate in direct variation.
- 📝 Example 1: If y = 8 when x = 2, k = 4, and the equation is y = 4x. When x = 7, y = 28.
- 🧮 Example 2: If y = 9 when x = -4, k = -9/4, and the equation is y = (-9/4)x. When x = 11, y = -99/4 or -24.75.
- 🔍 To determine if y varies directly with x in a table, check if k (y/x) remains constant for all values.
- ✔️ If k is constant across all pairs in the table, y varies directly with x. If not, it doesn't.
- 🚶 Example 3: If Karen walks 2 miles in 25 minutes, she can walk 4.8 miles in one hour (60 minutes), using the equation y = (2/25)x.
- 🔗 Direct variation problems can also include inverse and joint variations.
Q & A
What is direct variation?
-Direct variation is a relationship between two variables where one variable increases proportionally with the other. It is represented by the equation y = kx, where k is the constant of variation.
How do you calculate the constant of variation (k)?
-The constant of variation (k) is calculated by dividing the dependent variable (y) by the independent variable (x), so k = y/x.
What is the equation for direct variation?
-The equation for direct variation is y = kx, where k is the constant of variation and x is the independent variable.
If y = 8 when x = 2, how do you find y when x = 7?
-First, calculate the constant of variation k = y/x = 8/2 = 4. Then use the equation y = kx to find y when x = 7. y = 4 * 7 = 28.
If y = 9 when x = -4, what is y when x = 11?
-First, calculate the constant of variation k = y/x = 9/(-4) = -9/4. Then use the equation y = (-9/4) * x. When x = 11, y = (-9/4) * 11 = -99/4 or -24.75.
How can you determine if y varies directly with x from a table of values?
-To determine if y varies directly with x, calculate the constant of variation (k = y/x) for each pair of values. If k is the same for all pairs, then y varies directly with x.
In the first table example, does y vary directly with x?
-Yes, y varies directly with x in the first table because the constant of variation k is the same (2) for all pairs of x and y values.
Why does y not vary directly with x in the second table example?
-Y does not vary directly with x in the second table because the constant of variation (k) changes for different pairs of x and y values.
What is the relationship between distance and time in Karen’s walking example?
-The distance Karen walks varies directly with the amount of time she spends walking. This means the distance is proportional to the time.
If Karen walks 2 miles in 25 minutes, how far can she walk in one hour?
-First, calculate the constant of variation k = 2/25. Then use the equation y = (2/25) * 60 (since 1 hour = 60 minutes). The result is y = 4.8 miles.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

Inverse Variation - Constant of Variation and Equation - Grade 9 Math Second Quarter
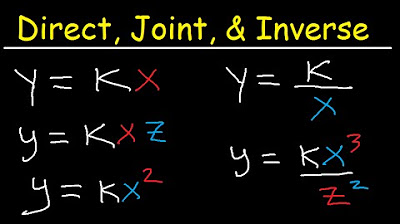
Direct Inverse and Joint Variation Word Problems
y=mx+b Ecuacíon de la recta, relación funcional
Direct and Inverse Proportion
Variación lineal: expresión algebraica, tabulación y gráfica.
Algebra - Proportional and Nonproportional Relationships
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
