Kas kecil Metode Imprest dan Fluktuasi
Summary
TLDRIn this video, Ibu Lia Nurliawati explains the concept of Petty Cash (Kas Kecil) in accounting, highlighting the differences between 'Kas Besar' (Cash in Bank) and 'Kas Kecil'. She covers two methods for managing Petty Cash: the Imprest System, which maintains a fixed fund and replenishes it based on expenditures, and the Fluctuating System, where every expense is recorded and the balance fluctuates. The video includes practical examples and journal entries for both methods, helping viewers understand how to properly manage and record small operational expenses in a company.
Takeaways
- 😀 Petty cash (Kas Kecil) is used for small operational expenses that are impractical to pay via check, such as postage or utility bills.
- 😀 Cash in Bank (Kas Besar) is used for larger operational expenditures, such as vehicle purchases, land, and employee salaries.
- 😀 There are two methods for managing petty cash: the Imprest method and the Fluctuation method.
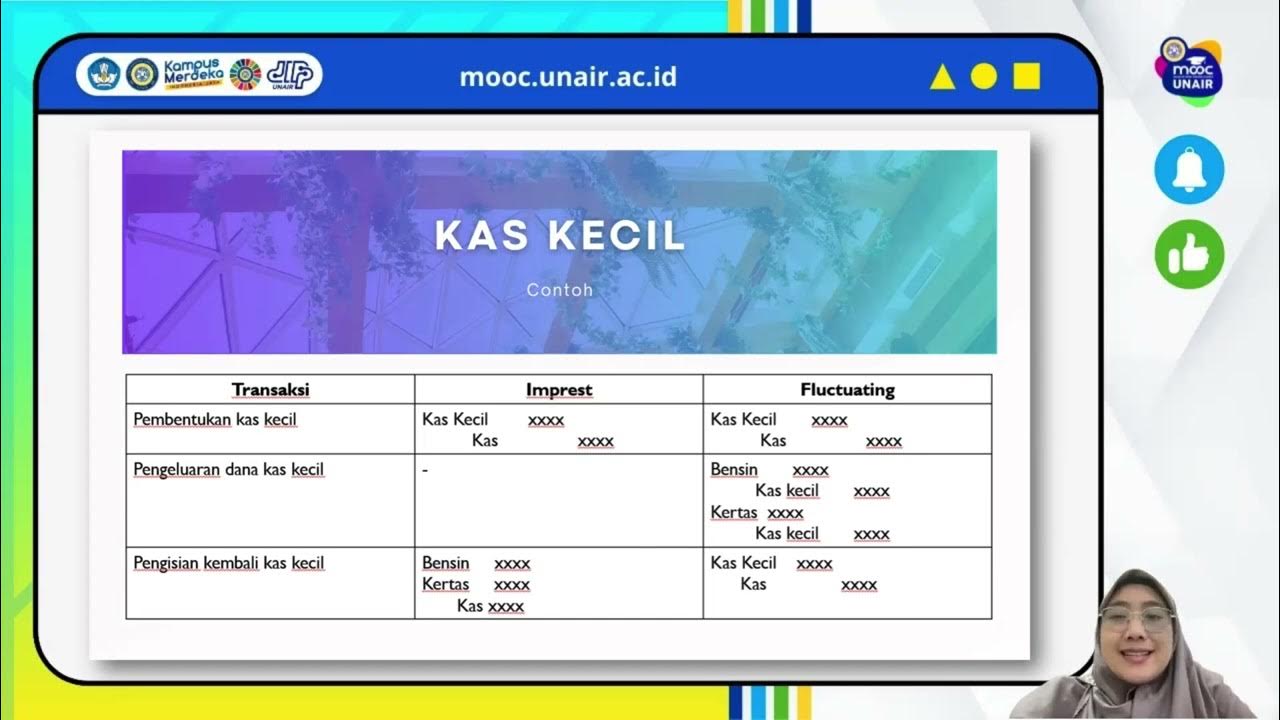
- 😀 The Imprest method maintains a fixed petty cash amount, and the fund is replenished to the original level after expenditures.
- 😀 The Fluctuation method allows the petty cash fund to vary, with journal entries recorded for each expense.
- 😀 Under the Imprest method, no journal entry is made for each small expenditure; only the replenishment is recorded.
- 😀 Under the Fluctuation method, every small expenditure is recorded in the journal, affecting both expense accounts and petty cash.
- 😀 The Imprest method ensures that the petty cash balance always remains the same, regardless of the amount spent.
- 😀 When excess petty cash is returned to the main cash fund, the amount of petty cash is reduced accordingly.
- 😀 Accurate journal entries must be made to ensure that both the debit and credit sides balance for each transaction.
Q & A
What is petty cash in accounting?
-Petty cash is a small amount of money set aside for minor operational expenses within a company that are too small to justify payments by check. These expenses include things like stamps, office supplies, and utility bills.
What are the two main types of cash mentioned in the script?
-The two main types of cash mentioned are 'kas besar' (large cash), which is used for larger operational expenditures, and 'kas kecil' (petty cash), which is used for smaller, everyday expenses.
What is the purpose of the imprest method in managing petty cash?
-The imprest method involves maintaining a fixed amount of petty cash. The balance remains constant, and when cash is spent, it is replenished to the original amount based on the expenditures recorded.
How does the fluctuation method differ from the imprest method?
-The fluctuation method does not maintain a fixed amount of petty cash. Instead, the petty cash balance changes according to the actual expenditures, and there is no set amount to be replenished.
What are some examples of expenses covered by petty cash?
-Examples of petty cash expenses include the purchase of stamps, postage, utility bills (like electricity, water, or phone), minor repairs, and office supplies.
How is petty cash recorded in the imprest method when it is initially set up?
-When petty cash is set up, the journal entry in the imprest method records an increase in petty cash and a corresponding decrease in the main cash account.
What happens when petty cash is replenished under the imprest method?
-When petty cash is replenished under the imprest method, the expenditures are recorded, and the main cash account is decreased by the total amount spent, bringing the petty cash balance back to its fixed amount.
What is the procedure for handling petty cash in the fluctuation method when expenses are made?
-In the fluctuation method, every expense is recorded with a journal entry that reflects the nature of the expense (e.g., office supplies, utilities), and the petty cash balance is adjusted according to the actual expenditures.
How is petty cash handled when it is considered too large in the fluctuation method?
-If the petty cash balance is deemed too large, the excess amount is returned to the main cash account. This is done by decreasing the petty cash balance and increasing the main cash account.
What does the script explain about the journal entries for petty cash expenditures in both methods?
-The script explains that in the imprest method, there are no journal entries for petty cash expenditures, only for replenishing the fund. In the fluctuation method, every petty cash expenditure is recorded as a journal entry with corresponding debits and credits for each expense.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة

Bagaimana Cara Input Kas Masuk & Keluar di IPOS Laundry?? Cek Caranya di Sini! #laundry #tutorial
Kas & Setara Kas | MOOC | Materi Akuntansi Perpajakan Seri 2

AKM 1 - Bab 7. Kas & Rekonsiliasi Bank

ALUR PENGELOLAAN KAS KECIL PADA PERUSAHAAN

KAS KECIL METODE IMPREST DAN FLUKTUASI || Kas Kecil Sistem Dana Tetap dan Sistem Dana Tidak Tetap

Akuntansi Keuangan - Dana Kas Kecil Definisi, fungsi dan tujuan
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
