AKM 1 - Bab 7. Kas & Rekonsiliasi Bank
Summary
TLDRThis video script provides a comprehensive overview of various cash management and accounting concepts, focusing on topics like cash equivalents, petty cash systems, and bank reconciliations. It explains the differences between liquid assets, restricted cash, and regular cash, as well as the importance of accurate record-keeping for financial transactions. Key elements such as bank overdrafts, imprest fund systems, and the reconciliation process for discrepancies between company books and bank statements are also covered. The content is tailored for those seeking to understand and manage company finances efficiently, with practical examples and journal entries.
Takeaways
- 😀 Cash is one of the most liquid assets for a company, allowing it to be used for various purposes like salaries, investments, and purchasing equipment.
- 😀 Cash equivalents, such as mutual funds (Reksadana pasar uang), are short-term investments that are easily convertible to cash within a year.
- 😀 Cash can be categorized into unrestricted cash (used for general purposes) and restricted cash (set aside for specific purposes like loan repayment or capital projects).
- 😀 A bank overdraft occurs when a company issues a check that exceeds its available bank balance, and the bank covers the shortfall, creating a liability.
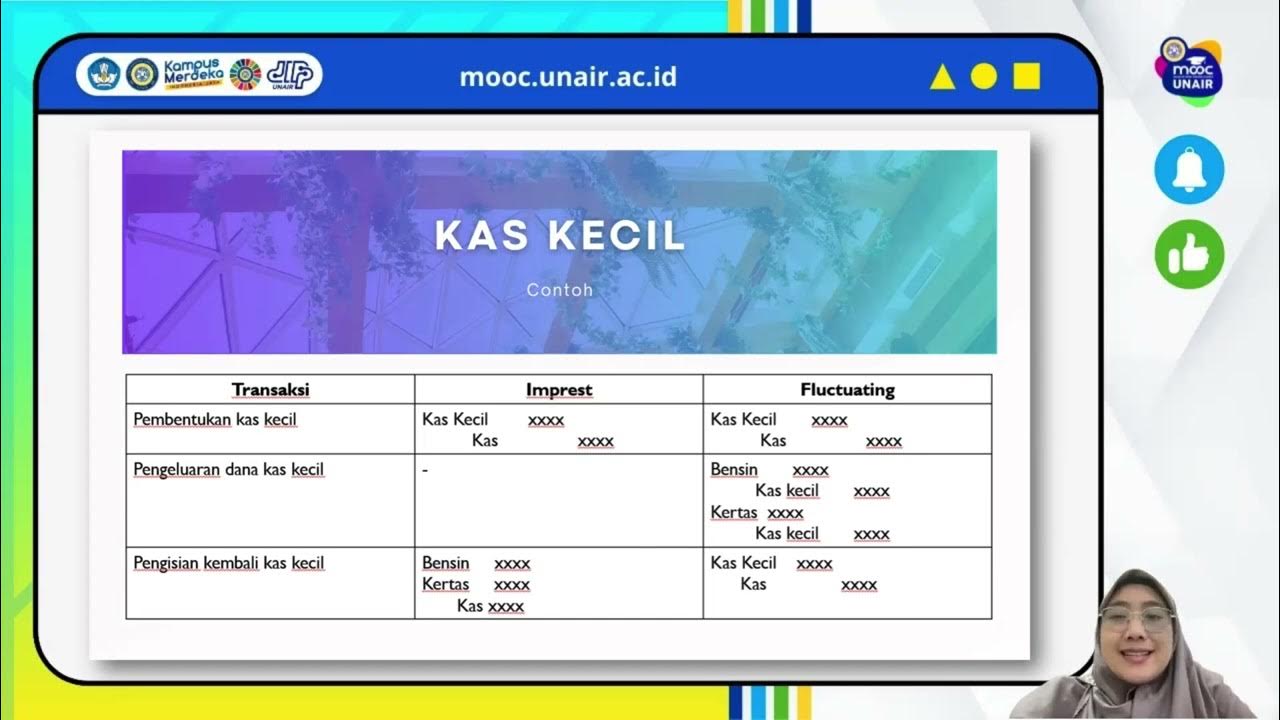
- 😀 The imprest fund system (petty cash) is used for managing small, everyday expenses like office supplies or parking fees, with the balance replenished when funds are low.
- 😀 Journal entries are necessary to track and replenish petty cash, ensuring that every small expense is properly accounted for in the company's financial records.
- 😀 Bank reconciliations are crucial for resolving discrepancies between the company's cash book and the bank statement, often caused by unrecorded deposits or outstanding checks.
- 😀 Adjustments during bank reconciliation include adding deposits in transit, subtracting outstanding checks, and accounting for bank errors or fees.
- 😀 Bank fees and errors should be recorded in the company’s books with appropriate journal entries, such as debiting the expense for bank charges and crediting cash.
- 😀 The purpose of bank reconciliation is to match the bank balance with the company's cash records, ensuring accuracy and consistency between the two sets of financial records.
- 😀 Common reconciliation items include deposits in transit, uncashed checks, bank service charges, and any errors either made by the bank or the company.
Q & A
What is the role of 'cash' in a company as described in the transcript?
-Cash is considered one of the most liquid assets in a company. It can be used for various purposes such as paying salaries, making investments, purchasing equipment, and more. Cash is recorded as a current asset in the financial statements unless it is restricted for specific uses, in which case it is classified as a non-current asset.
What does 'cash equivalents' refer to in the context of the transcript?
-'Cash equivalents' are short-term investments that are highly liquid and can be quickly converted into cash. These include instruments such as money market funds or short-term government bonds, which have maturities of less than one year.
How are restricted and unrestricted cash treated differently in accounting?
-Restricted cash is cash that has been set aside for a specific purpose and cannot be used for general business operations. It is classified as a non-current asset. Unrestricted cash, on the other hand, is available for general use and is classified as a current asset.
What is an overdraft facility in banking, and how does it relate to company cash management?
-An overdraft facility allows a company to withdraw more money than it has in its bank account, up to an agreed limit. The company incurs a liability when using the overdraft. As soon as money is deposited into the account, the overdraft is paid off, and the balance becomes positive again.
What is the purpose of the 'Imprest Fund System' or petty cash system?
-The Imprest Fund System is used for managing small, day-to-day expenses within a company. It involves setting up a petty cash fund that is replenished as expenses are incurred, such as paying for small office supplies or transportation costs.
How is petty cash replenished in the Imprest Fund System?
-When petty cash is used for expenses, the fund is replenished by recording a journal entry. For example, if $173 is spent, the company adds that amount back to the petty cash fund by transferring money from the main bank account to restore the balance.
What is 'bank reconciliation' and why is it important?
-Bank reconciliation is the process of comparing the company's cash book (or records) with the bank statement to identify discrepancies. This process ensures that the cash balances match and accounts for items like deposits in transit, outstanding checks, and errors made by either the company or the bank.
What are some common reasons for differences between the company’s cash records and the bank’s records?
-Common reasons for discrepancies include deposits that are recorded by the company but not yet by the bank (deposits in transit), checks written by the company but not yet cashed by the recipient (outstanding checks), and errors made by the company or the bank.
What is the treatment of 'outstanding checks' in a bank reconciliation?
-Outstanding checks are checks that have been written and deducted from the company's cash records but have not yet been cashed by the payee. These need to be subtracted from the bank’s cash balance during reconciliation, as they reduce the available bank balance.
How should a bank error be corrected during reconciliation?
-If an error is found on the bank’s side, such as an incorrect transaction or a misposted amount, the bank statement should be adjusted to reflect the correct balance. Any corrections to the company's records should also be made to ensure consistency between the two accounts.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
Kas & Setara Kas | MOOC | Materi Akuntansi Perpajakan Seri 2

ALUR PENGELOLAAN KAS KECIL PADA PERUSAHAAN

AKUNTANSI KEUANGAN MENENGAH - Bagian 2

Auditing the CASH account - tests of controls and substantive testing

[MEET 10-1] AKUNTANSI SEKTOR PUBLIK - AKUNTANSI ASET & KEWAJIBAN

Akuntansi Keuangan - Dana Kas Kecil Definisi, fungsi dan tujuan
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)