Matematika SMA - Relasi dan Fungsi (4) - Sifat-Sifat Fungsi, Fungsi Injektif Surjektif (A)
Summary
TLDRThis educational video script introduces the fundamental properties of functions, focusing on injective, surjective, and bijective functions. It explains the differences through examples and provides a clear method to determine if a function is injective, surjective, or bijective by examining the mapping of elements from the domain to the codomain. The script also includes exercises to test understanding, using sets A and B with various mappings to illustrate the concepts. The video concludes with an invitation to like, share, and subscribe for more educational content.
Takeaways
- 😀 The video provides an in-depth discussion about the properties of functions, specifically focusing on injective, surjective, and bijective functions.
- 📚 The presenter encourages viewers to subscribe to the channel and use the notification bell to stay updated with the latest videos on functions.
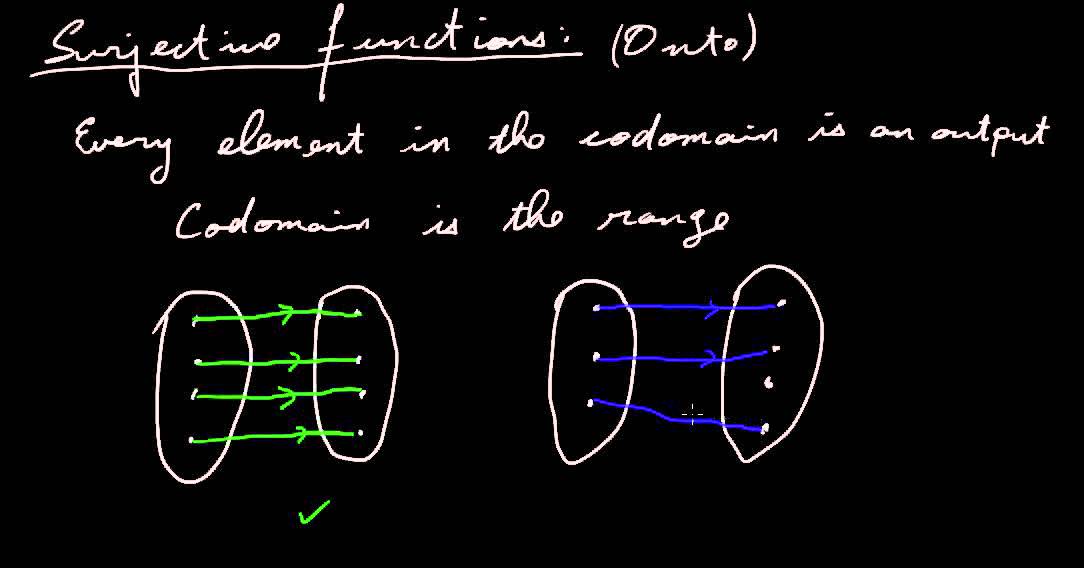
- 🔍 The difference between injective, surjective, and bijective functions is explained through their definitions: injective functions map each element of the domain to a unique element in the codomain, surjective functions cover every element in the codomain, and bijective functions are both injective and surjective.
- 📈 The script includes an example with sets A = {a, b, c, d} and B = {1, 2, 3, 4} to illustrate the concepts of injective, surjective, and bijective functions.
- 🤔 The video offers a step-by-step guide on how to check if a function is injective, surjective, or bijective by examining the mapping of elements between the domain and codomain.
- 🚫 It is demonstrated that the function f(x) = x^2 is not injective because different inputs can lead to the same output, violating the definition of an injective function.
- 📉 The function f(x) = x^2 is also shown not to be surjective because it cannot map to negative outputs, as the square of a real number is always non-negative.
- 💡 The linear function f(x) = 4x is proven to be injective by showing that different inputs result in different outputs, satisfying the injective condition.
- 🌐 The same linear function f(x) = 4x is also proven to be surjective, as every element in the codomain has a corresponding element in the domain.
- 🎯 The conclusion is drawn that f(x) = 4x is bijective because it meets both the injective and surjective criteria.
- 👍 The video ends with a reminder for viewers to like, share, and subscribe for more educational content, and to follow on Instagram for updates.
Q & A
What are the three types of functions discussed in the video script?
-The three types of functions discussed are injective (one-to-one), surjective (onto), and bijective (one-to-one and onto).
What is an injective function?
-An injective function is a function where every element of the codomain is paired with exactly one element from the domain.
How is a surjective function defined?
-A surjective function is one where every element of the codomain has at least one corresponding element in the domain.
What is a bijective function?
-A bijective function is one that is both injective and surjective, meaning every element in the domain is paired uniquely with an element in the codomain, and every element in the codomain is the image of some element in the domain.
How can you determine if a function is injective?
-To determine if a function is injective, check if different elements in the domain are mapped to different elements in the codomain, ensuring no two elements in the domain have the same image.
What is the criterion for a function to be surjective?
-A function is surjective if every element in the codomain is the image of at least one element in the domain, meaning the codomain is fully covered by the images of the domain elements.
How do you check if a function is bijective?
-A function is bijective if it is both injective and surjective. This means each element in the domain maps to a unique element in the codomain, and every element in the codomain has a pre-image in the domain.
What is the example function given in the script to illustrate a non-injective function?
-The example function given is f(x) = x^2, which is shown to be non-injective because different values of x (like 2 and -2) can result in the same output (f(2) = f(-2) = 4).
What is the example function provided to demonstrate a surjective function?
-The example function provided is f(x) = 4x, which is surjective because every element in the codomain has a corresponding element in the domain that maps to it.
How is the function f(x) = 4x proven to be injective in the script?
-The function f(x) = 4x is proven to be injective by showing that if x1 ≠ x2, then f(x1) ≠ f(x2), which is demonstrated by choosing specific values for x1 and x2 and showing their images are different.
Why is the function f(x) = x^2 not surjective?
-The function f(x) = x^2 is not surjective because there are elements in the codomain (negative numbers) that do not have a corresponding element in the domain that would map to them, as the square of a real number cannot be negative.
How is the bijectivity of the function f(x) = 4x established in the script?
-The bijectivity of f(x) = 4x is established by proving it is both injective (each domain element maps to a unique codomain element) and surjective (every codomain element has a pre-image in the domain).
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频
Injective Surjective Bijective Functions

FUNÇÃO INJETORA, SOBREJETORA E BIJETORA \Prof. Gis/

PERBEDAAN FUNGSI INJEKTIF, SURJEKTIF DAN BIJEKTIF LENGKAP DENGAN CONTOH SOAL

PEMBUKTIAN TRANSFORMASI | Geometri Transformasi #2

Fungsi #Part 13 // Jenis-jenis Fungsi // Fungsi Modulus // Fungsi Mutlak // Grafik, Domain , Range

Real Analysis | Set Theory | Set Theory Basic Definition & Examples
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
