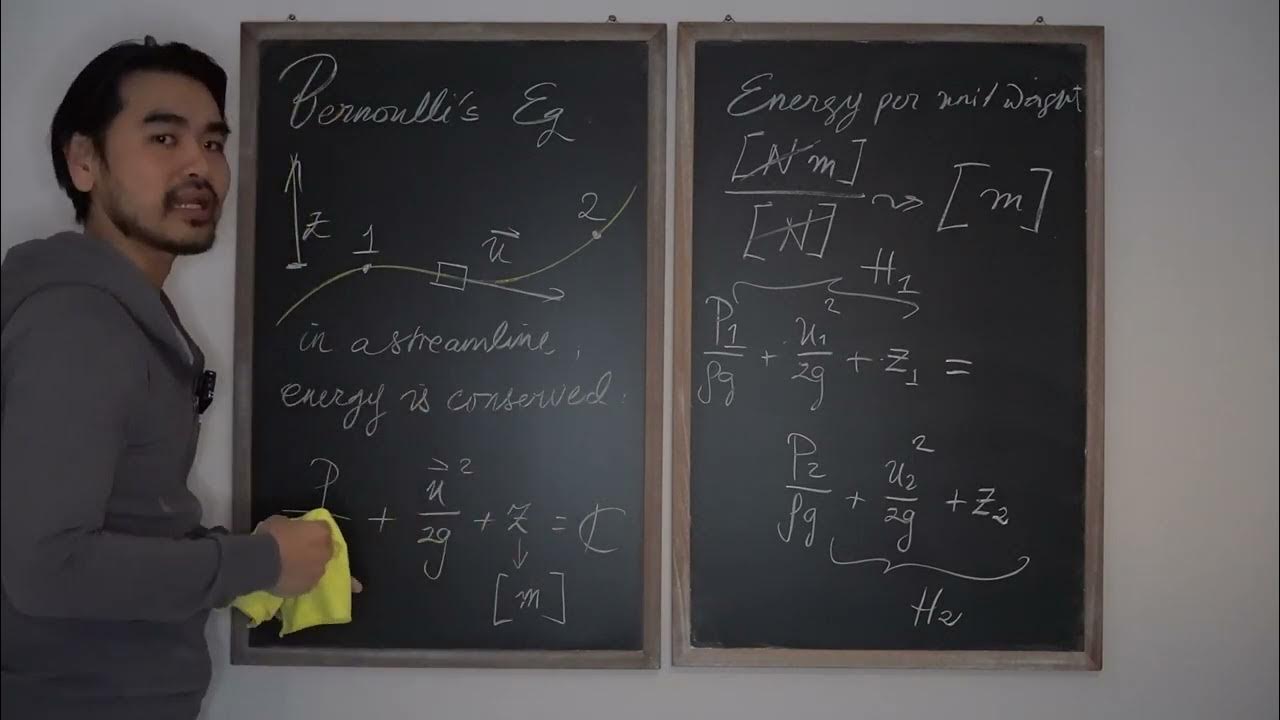How does Aircraft generates lift? Bernoulli's principle
Summary
TLDRThe script introduces Bernoulli's Principle, a fundamental concept in fluid dynamics, explaining how an increase in the speed of an ideal fluid results in a decrease in pressure. It uses the example of water flow from a pipe to illustrate static and dynamic pressure, and how changes in pipe diameter affect these pressures. The principle is then applied to explain how an airplane's wings generate lift, with the curvature of the wing surfaces affecting airspeed and pressure. The script aims to educate viewers on the principles of fluid dynamics and their practical applications, particularly in aeronautics.
Takeaways
- 📚 The Bernoulli's Principle is a fundamental concept in fluid dynamics, named after the scientist Bernoulli who proposed and proved this theory.
- 🌀 Ideal fluids, including liquids and gases, have constant properties such as density, temperature, and viscosity, which are essential for understanding Bernoulli's Principle.
- 💧 The principle states that in an ideal fluid, the total pressure at any point remains constant if the fluid is in an ideal condition, combining both static and dynamic pressure.
- 🔍 Static pressure is the force exerted perpendicular to a surface, like the wall of a pipe, and is always constant regardless of the fluid's flow.
- 🌪 Dynamic pressure arises from the fluid's flow and is directly related to the fluid's velocity; as the velocity increases, dynamic pressure increases, and vice versa.
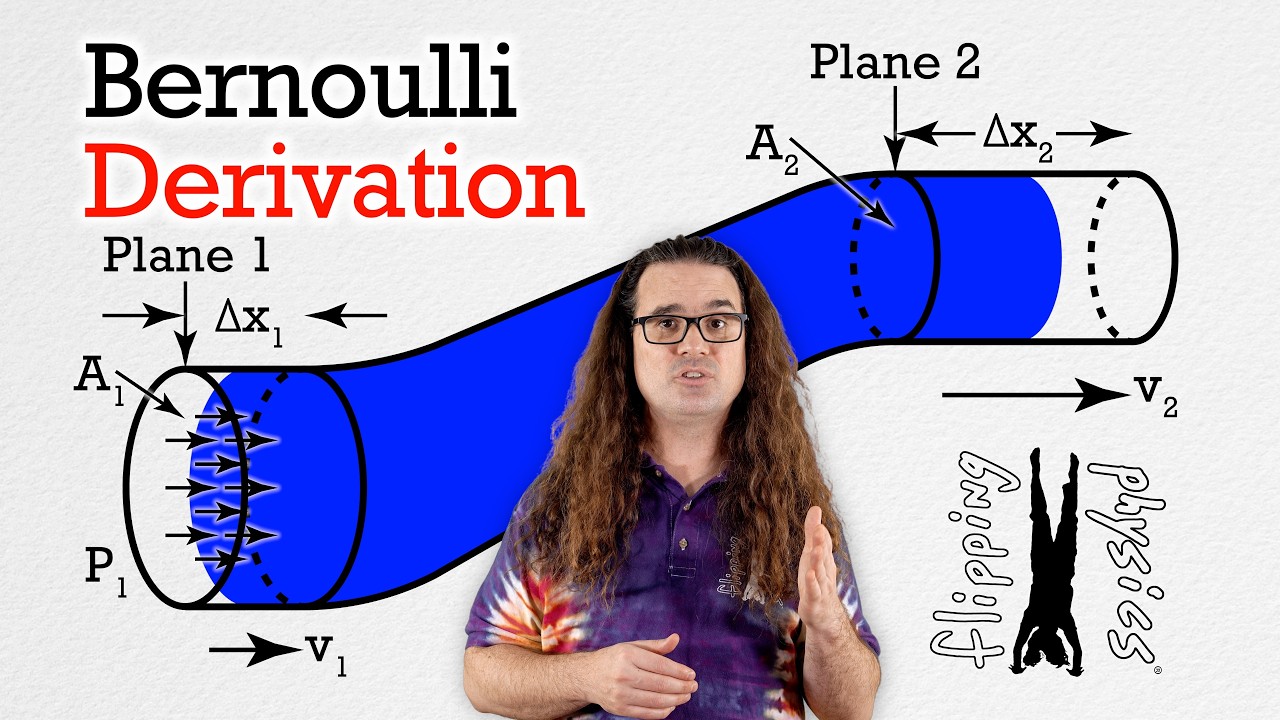
- 🚰 An example given in the script explains how increasing the flow rate (dynamic pressure) by constricting a pipe's opening results in a decrease in static pressure, causing water to travel a greater distance.
- ✈️ Bernoulli's Principle is applied in aerodynamics, particularly in the design of aircraft wings, where the shape of the wing influences the airflow and generates lift.
- 📉 The top surface of an aircraft wing is curved, causing the air to move faster and creating lower pressure, while the flat bottom surface results in slower air movement and higher pressure.
- 🛫 The difference in pressure between the top and bottom surfaces of the wing creates an upward force known as lift, which allows the aircraft to rise.
- 🔄 The principle of continuity in fluid dynamics, which states that the same amount of fluid will pass through different points in a pipe in the same amount of time, is used to explain the relationship between the speed and pressure of the fluid.
- 👍 The script emphasizes the importance of understanding both static and dynamic pressures as they are always in balance, and changes in one will affect the other, as demonstrated in various examples.
Q & A
What is the Bernoulli's Principle discussed in the script?
-Bernoulli's Principle states that in an ideal fluid flow, the sum of the static pressure, dynamic pressure, and potential energy remains constant along a streamline.
Who is Bernoulli in the context of the script?
-Bernoulli refers to Daniel Bernoulli, a scientist who proposed and proved the principle that is named after him, Bernoulli's Principle.
What are the two types of pressure mentioned in the script?
-The two types of pressure mentioned are static pressure and dynamic pressure.
How does the script explain the concept of static pressure?
-Static pressure is the force exerted by a fluid at right angles to a surface, like water pushing against the walls of a pipe.
What is dynamic pressure according to the script?
-Dynamic pressure is the pressure exerted by a fluid due to its velocity, causing the fluid to move through an opening with greater force.
How does the script illustrate the relationship between static and dynamic pressure?
-The script illustrates that if the dynamic pressure increases, the static pressure decreases, and vice versa, to maintain a constant total pressure in an ideal fluid flow.
What is an ideal fluid according to the script?
-An ideal fluid, as described in the script, is one where the temperature, density, and viscosity remain constant.
How does the script use the example of water in a pipe to explain Bernoulli's Principle?
-The script uses the example of water flowing out of a pipe to show how increasing the velocity of the water (dynamic pressure) results in a decrease in static pressure, causing the water to travel further.
What is the role of the shape of an airplane wing in relation to Bernoulli's Principle as explained in the script?
-The shape of an airplane wing, with a curved upper surface and a flatter lower surface, causes the air to move faster over the top, reducing static pressure and creating lift, while the slower air below creates higher static pressure.
How does the script describe the impact of lift on an airplane?
-The script describes lift as the force that causes an airplane to rise due to the difference in static pressure between the upper and lower surfaces of the wings, resulting from the shape of the wings and the speed of the air over them.
What is the script's suggestion for understanding the Bernoulli's Principle better?
-The script suggests using real-life examples such as water in a pipe and the shape of airplane wings to better understand the relationship between static and dynamic pressure in the context of Bernoulli's Principle.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)