Mecánica de fluidos primera parte
Summary
TLDRThis script offers an insightful overview of fluid mechanics, distinguishing between fluid statics and dynamics. It delves into concepts like density, specific gravity, and pressure, emphasizing their significance in engineering and science. The script explains Torricelli's experiment, illustrating how atmospheric pressure is measured. It also introduces Pascal's principle, highlighting its applications in hydraulic systems, and discusses Archimedes' principle, explaining buoyancy. The educational content is designed to engage viewers with its comprehensive explanation of fundamental fluid mechanics concepts and their practical applications.
Takeaways
- 💧 Fluid Mechanics studies fluids at rest and in motion, including liquids, gases, and plasmas.
- 🔍 Fluid Statics focuses on fluids at rest, using principles from Newton's laws of motion and conservation laws.
- 🌊 Fluid Dynamics examines fluids in motion, utilizing simplified models and known principles like Newton's laws and conservation of mass and energy.
- 📏 Density is a key parameter of fluids, defined as a material's intrinsic property related to how atoms are structured within it.
- 📉 The density of a homogeneous material like ice or iron is uniform throughout, represented by the Greek letter 'rho'.
- 📚 Common substances' densities are listed, such as air at 20 degrees Celsius (1.20 kg/m³), ethanol (0.81 kg/m³), ice (0.92 kg/m³), pure water (1.00 kg/m³), and seawater (1.03 kg/m³).
- 🧭 Specific gravity is the ratio of a material's density to that of water at 4 degrees Celsius, a dimensionless number.
- 📐 Pressure in a fluid is crucial, with applications in engineering and sciences; fluids can only exert normal force, not shear stress.
- 🌡 The weight of a fluid column can be calculated using its density, base area, height, and gravity, resulting in pressure exerted on a surface.
- 🌍 Atmospheric pressure results from gases in the Earth's atmosphere, with Torricelli's experiment pioneering the measurement of atmospheric pressure using mercury columns.
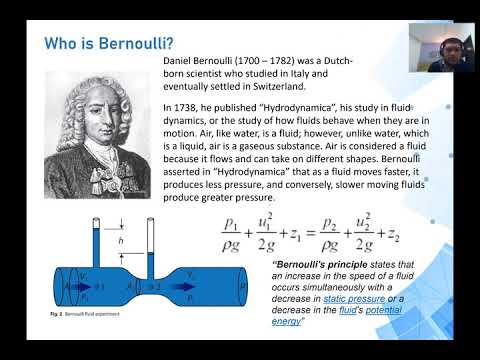
- 🚗 Pascal's Principle is fundamental to hydraulic systems, allowing force multiplication with minimal effort, impacting modern life, including car hydraulic systems.
Q & A
What is fluid mechanics?
-Fluid mechanics is the study of fluids, which can be liquids, gases, or plasmas. It examines the behavior of these substances at rest and in motion.
What are the two main branches of fluid mechanics?
-The two main branches of fluid mechanics are fluid statics, which studies fluids at rest, and fluid dynamics, which studies fluids in motion.
What is an important property of fluids?
-Density is an important property of fluids, defined as a material's intrinsic property that depends on how atoms are structured within the material.
How is density calculated?
-Density is calculated as the ratio of a material's mass to its volume, expressed mathematically as density equals mass divided by volume.
What is specific gravity?
-Specific gravity is the ratio of a material's density to the density of water at 4 degrees Celsius, and it is a dimensionless number.
What is pressure in a fluid?
-Pressure in a fluid is the force that acts perpendicular to a surface, and it is defined as the magnitude of force per unit area.
What is the relationship between pressure, density, and height in a fluid column?
-The pressure exerted by a fluid column is equal to the product of the fluid's density, gravitational acceleration, and height of the column.
Who was Torricelli and what is his contribution to understanding atmospheric pressure?
-Torricelli was an Italian physicist who conducted an experiment that allowed for the measurement of atmospheric pressure. His experiment showed that atmospheric pressure could be measured by the height of a mercury column.
What is absolute pressure?
-Absolute pressure is the sum of the pressure exerted by the surrounding medium on the top of a fluid and the pressure due to the fluid column between the ground and the object.
What is Pascal's principle?
-Pascal's principle states that the pressure applied to a fluid at rest is transmitted equally and undiminished to all portions of the fluid and the walls of the containing vessel.
How does the principle of Archimedes relate to buoyancy?
-The principle of Archimedes states that a body submerged in a fluid experiences an upward force equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the body, which is the basis for the phenomenon of buoyancy.
What determines whether an object will float or sink in a fluid?
-An object will float if its average density is less than the fluid's density, and it will sink if its average density is greater than the fluid's density.
How can the distance traveled by pistons in a hydraulic system be calculated?
-In an ideal system without energy loss, the work input is equal to the work output. Therefore, the distance traveled by pistons can be calculated based on the work done and the forces applied.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)