How an Abrasive Jet Machining Works?
Summary
TLDRThis video lecture explains the process of Abrasive Jet Machining (AJM), a non-contact, non-conventional method used for machining hard and brittle materials. It covers the working principle, where high-velocity abrasive particles are propelled by compressed air to remove material from the workpiece. The video discusses the necessary equipment, including compressors, filters, and nozzles, as well as applications such as cutting, drilling, cleaning, and etching. Advantages include low heat production, flexibility, and smooth finishes, while disadvantages involve slow material removal rates and poor precision. The video provides a clear overview of AJM’s practical uses, benefits, and limitations.
Takeaways
- 😀 Abrasive Jet Machining (AJM) is a non-contact, non-conventional machining process that uses high-velocity abrasive particles propelled by compressed air to remove material from the workpiece.
- 😀 AJM works based on the principle of abrasive erosion, where abrasive particles impact the workpiece surface causing brittle fracture and material removal.
- 😀 Common abrasives used in AJM include aluminum oxide, silicon carbide, sodium bicarbonate, crushed glass, and glass beads.
- 😀 The abrasive jet used in AJM typically has a velocity of around 200 meters per second, impacting the workpiece surface to create cavities or other features.
- 😀 AJM is particularly suitable for machining hard and brittle materials, making it ideal for materials like glass and ceramics.
- 😀 The AJM setup includes a gas propulsion system, air compressor, filter, pressure regulator, abrasive mixing system, and a nozzle through which the abrasive jet is directed.
- 😀 The process starts with clean and dry compressed air mixed with abrasive particles, which are then expelled through a nozzle with a small diameter (0.18 to 0.8 mm).
- 😀 Applications of AJM include cutting thin sections, contouring, drilling, producing shallow cavities, deburring, and marking on materials like glass and super alloys.
- 😀 AJM is also used for cleaning and polishing plastic components like nylon and Teflon, as well as frosting glass surfaces.
- 😀 Advantages of AJM include flexibility, low heat production, smooth surface finish, and low equipment costs, as it uses compressed air and simple abrasive materials.
- 😀 Disadvantages of AJM include low material removal rate, poor machining accuracy, nozzle wear, and challenges in machining soft metals due to abrasive particle sticking.
Q & A
What is Abrasive Jet Machining (AJM)?
-Abrasive Jet Machining (AJM) is a non-contact, non-conventional machining process that uses a high-velocity stream of abrasive particles propelled by compressed air to remove material from a workpiece's surface.
What is the basic working principle of AJM?
-The working principle of AJM is based on abrasive erosion. A high-velocity jet of abrasive particles impacts the workpiece, causing material removal through impact and brittle fracture.
What types of abrasives are commonly used in AJM?
-Common abrasives used in AJM include aluminum oxide, silicon carbide, sodium bicarbonate, crushed glass, and glass beads.
What equipment is used in the AJM process?
-The equipment used in AJM includes a gas propulsion system (typically compressed air), a filter to clean the air, a pressure regulator, an abrasive mixture, and a nozzle to direct the abrasive stream onto the workpiece.
How does the nozzle function in AJM?
-The nozzle in AJM has a small diameter (ranging from 0.18 to 0.8 mm) through which the mixed abrasive particles and compressed air are directed at the workpiece. This nozzle helps to focus the stream for efficient material removal.
What are the key applications of Abrasive Jet Machining?
-Key applications of AJM include cutting slots, thin sections, contouring, drilling operations, deburring, polishing and frosting plastic or nylon components, etching or marking glass cylinders, and processing super alloys and refractory materials.
What are the main advantages of using AJM?
-Advantages of AJM include flexibility for machining complex shapes, low heat generation (making it ideal for heat-sensitive materials), smooth surface finishes, low equipment cost due to the use of compressed air, and the ability to machine brittle and hard materials without thermal damage.
What are the disadvantages of Abrasive Jet Machining?
-Disadvantages of AJM include a low material removal rate, poor machining accuracy, high nozzle wear, and difficulty machining soft metals due to abrasive particles sticking to the surface, requiring additional cleaning.
Why is AJM considered a non-contact machining process?
-AJM is considered a non-contact process because the abrasive particles never physically touch the workpiece. Instead, they are propelled by air and impact the surface, removing material through erosion without any direct contact.
How is the speed of the abrasive jet in AJM controlled?
-The speed of the abrasive jet is controlled by regulating the pressure of the compressed air. The abrasive particles are propelled at speeds of around 200 meters per second towards the workpiece.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

WATER JET MACHINE PROCESS : Working of abrasive water Jet machining process (animation).

Proses Pemesinan Non Tradisional part 1
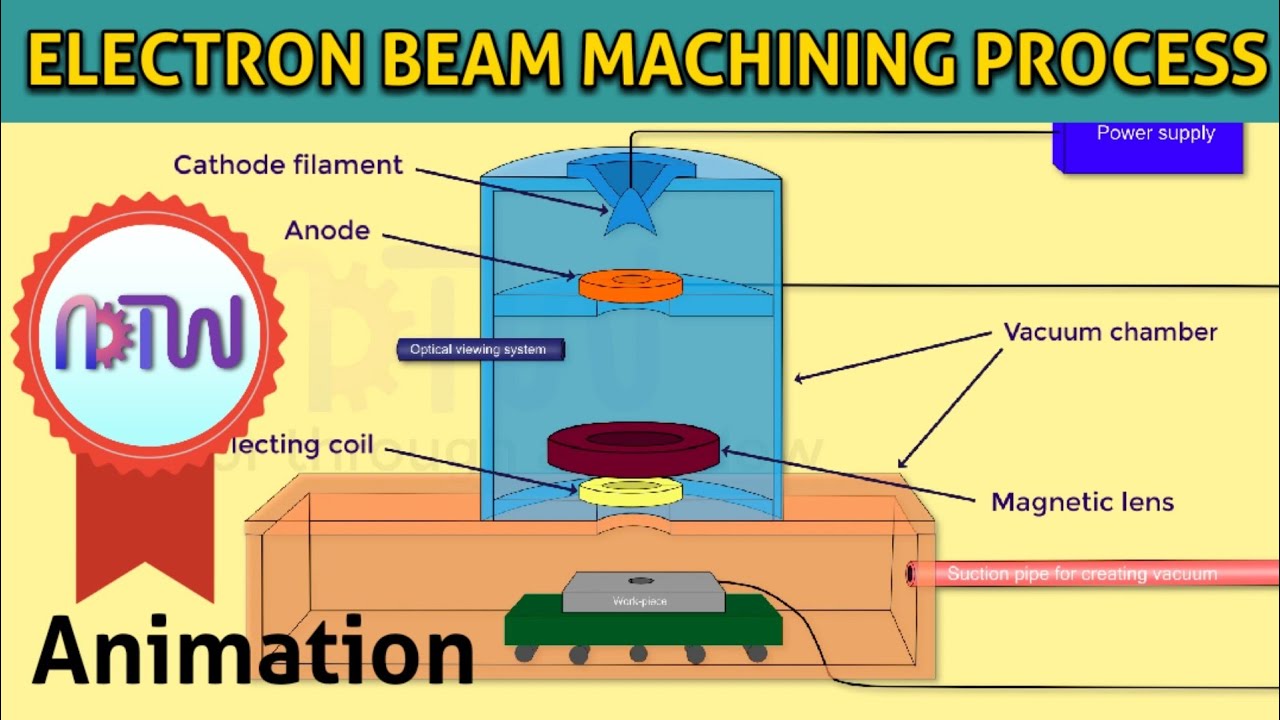
ELECTRON BEAM MACHINING PROCESS (EBM): Construction and Working of electron beam machining process.

Introduction: Advanced Machining Processes
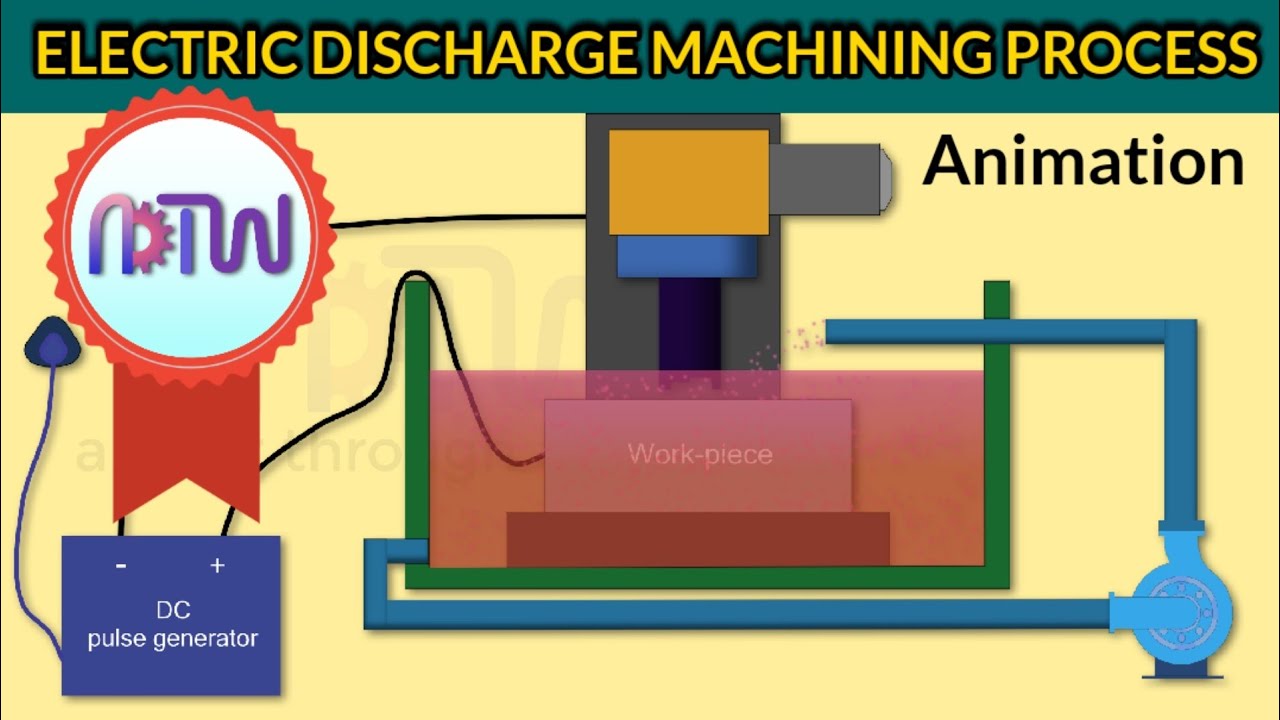
ELECTRIC DISCHARGE MACHINING PROCESS (Animation): How electric discharge maching works

Materiais e Processos de Fabricação para Engenharia de Produção: Usinagem não convencional
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)