Materiais e Processos de Fabricação para Engenharia de Produção: Usinagem não convencional
Summary
TLDRThis video covers unconventional machining processes, focusing on non-mechanical interactions between tools and materials, such as ultrasonic machining, water jet cutting, plasma cutting, and electrochemical methods. These techniques are used for specific, high-precision applications like glass, ceramics, and metals. Each process utilizes unique energy forms, from vibration and water pressure to electrical discharges and chemical reactions, ensuring efficient material removal with minimal waste. The video also touches on the equipment and parameters involved in these processes, showcasing their advantages in precision and automation.
Takeaways
- 😀 Non-conventional machining processes involve tool interactions that are not purely mechanical, including the use of electrical, chemical, and other energy sources.
- 😀 Ultrasonic machining involves a vibrating tool that oscillates at high frequency, using abrasive materials to erode the workpiece's surface.
- 😀 The abrasive particle size in ultrasonic machining affects dimensional precision and surface finish; smaller particles result in better results.
- 😀 Water jet machining uses high-pressure water (up to 400 MPa) to cut materials, with the ability to add abrasive particles for cutting harder materials.
- 😀 Water jet machining has advantages like minimal material loss, no surface burning, and environmental sustainability due to the ability to reuse water.
- 😀 Plasma cutting uses ionized gas (plasma) to cut materials, providing high energy levels and precise cuts for various applications.
- 😀 In electrochemical machining, the workpiece acts as the anode, where material is removed through oxidation and carried to the cathode, aided by an electrolyte flow.
- 😀 Electroerosion involves electric discharges between a tool and the workpiece, eroding material in the shape of the tool electrode.
- 😀 Electron beam machining uses a focused beam of high-energy electrons to vaporize or melt material from a workpiece, providing high-precision cuts.
- 😀 Laser machining uses highly focused light (laser) to remove material through ablation or vaporization, and it is effective for cutting fine materials and intricate shapes.
- 😀 Chemical machining uses chemical reactions, often with corrosive agents, to remove material in specific areas of a workpiece, often used for precise profiles or semiconductor fabrication.
Q & A
What are non-conventional machining processes?
-Non-conventional machining processes are those that involve interactions between tools and the workpiece that are not purely mechanical. These processes use different forms of energy, such as ultrasonic waves, electrical discharges, or chemical reactions, to remove material from the workpiece.
How does ultrasonic machining work?
-In ultrasonic machining, the tool vibrates at high frequencies with a very small amplitude. This vibration helps to propel abrasive particles against the workpiece, eroding it in the shape of the vibrating tool. The process is suitable for hard, brittle materials like ceramics and glass.
What is the importance of the abrasive grain size in ultrasonic machining?
-The grain size of the abrasive used in ultrasonic machining affects the precision and surface finish. Smaller grains result in better dimensional accuracy and surface finish, while larger grains may lead to a coarser finish and reduced precision.
What materials are commonly used in ultrasonic machining tools and abrasives?
-Common materials for ultrasonic machining tools include carbon steel and stainless steel. Abrasives used in this process can include silicon carbide, aluminum oxide, and diamond, depending on the material being machined.
What is water jet machining, and what are its applications?
-Water jet machining uses high-pressure water to cut through materials, sometimes with the addition of abrasives for tougher materials. It is ideal for cutting ceramics, glass, metals, and other materials with complex shapes and small tolerances, without generating heat.
What are the advantages of water jet machining?
-The main advantages of water jet machining include minimal material waste, no heat-affected zones, the ability to cut intricate shapes, and environmentally friendly processes due to the recyclability of the water used.
What is plasma cutting, and how does it work?
-Plasma cutting involves using a high-temperature ionized gas (plasma) to melt and blow away material. The gas is ionized by passing an electrical arc through it, which creates a high-energy state capable of cutting metals, especially those with a high melting point.
How does electrochemical machining work?
-In electrochemical machining, the workpiece acts as the anode and undergoes oxidation, which removes material through a chemical reaction. The tool, acting as the cathode, receives electrons, and the material is removed by electrolysis with the help of an electrolyte solution.
What is electrodischarge machining, and how is it different from traditional machining?
-Electrodischarge machining (EDM) uses electrical discharges to erode material from the workpiece. Unlike traditional machining, EDM does not involve direct contact between the tool and workpiece, making it ideal for precision machining of hard metals or complex geometries.
What is laser machining, and what makes it effective for certain materials?
-Laser machining uses a highly concentrated beam of light (laser) to vaporize or ablate material. It is effective for materials with high absorption rates of light, and its precision makes it ideal for cutting small holes, fine profiles, and thin materials.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Materiais e Processos de Fabricação para Engenharia de Produção - Usinagem não convencional...

Proses Pemesinan Non Tradisional part 1

WATER JET MACHINE PROCESS : Working of abrasive water Jet machining process (animation).

Introduction: Advanced Machining Processes

Materiais e Processos de Fabricação para Engenharia de Produção - Usinagem convencional: Exercícios
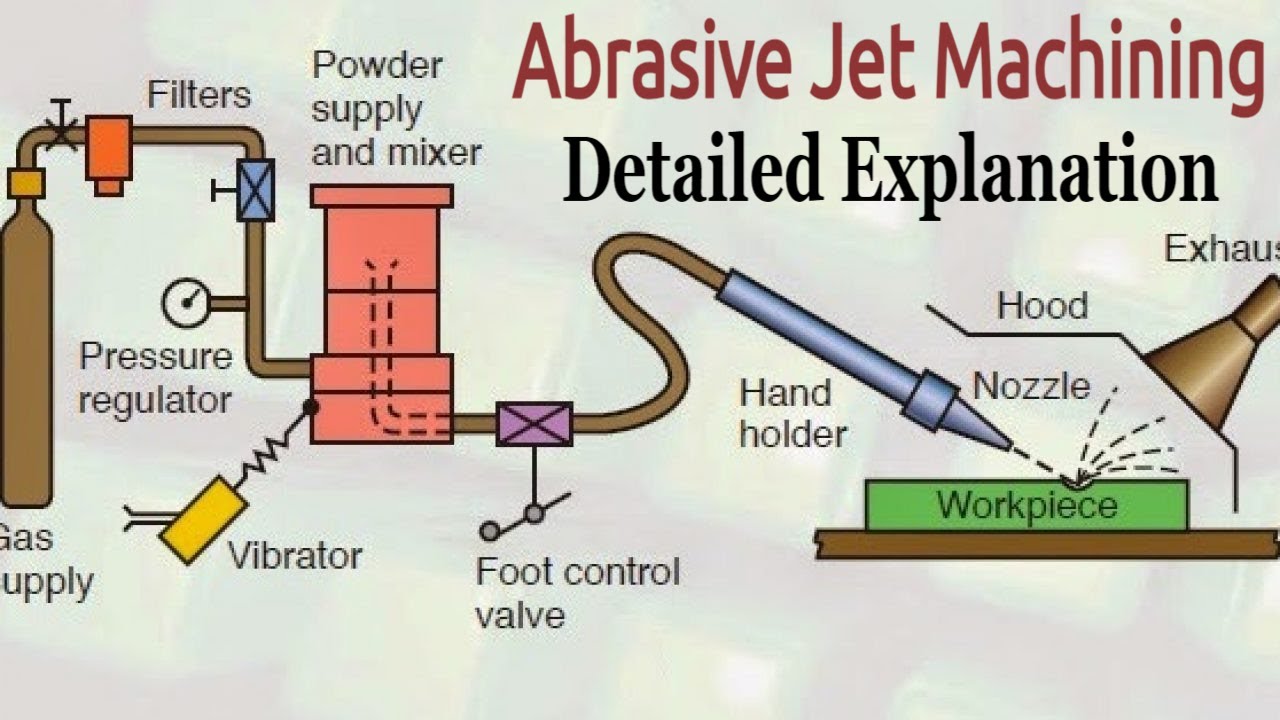
How an Abrasive Jet Machining Works?
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)