Tahapan Audit
Summary
TLDRThis video delves into the key stages of the audit process, focusing on the first two critical steps: client acceptance and audit planning. It explains how auditors assess client integrity, identify risks, and ensure independence before deciding to take on the audit. The planning phase covers understanding the client's business, performing analytical procedures, and creating a comprehensive audit plan. The video emphasizes the importance of thorough preparation to address potential risks and ensure the audit is conducted efficiently and effectively. This foundational approach sets the stage for successful audit execution and reporting.
Takeaways
- 😀 Acceptance of audit engagement begins with evaluating the integrity of the management, checking past audits, and reviewing external sources like news or legal reports.
- 😀 The auditor must assess the risk factors associated with the client’s business environment, such as legal challenges or extraordinary risks.
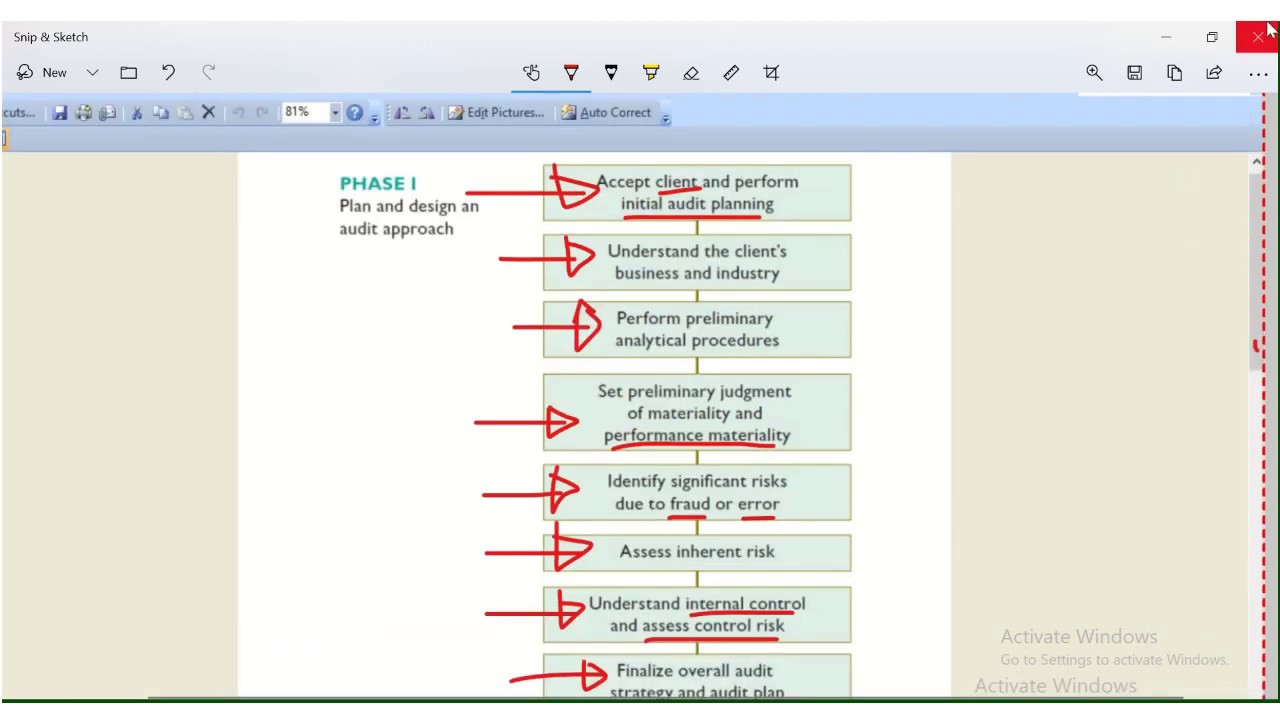
- 😀 Understanding the client’s business and industry is crucial before starting the audit process to ensure a solid audit plan.
- 😀 Analytical procedures are used to compare financial data from previous years and against industry standards to identify unusual trends.
- 😀 The auditor must evaluate the materiality of financial data and the risks involved in the audit, focusing on key areas of financial statements.
- 😀 Control risk assessment and understanding the client's internal controls are important before deciding on further audit procedures like testing or substantive testing.
- 😀 The auditor should ensure independence and address any conflicts of interest before accepting an audit engagement.
- 😀 When preparing the audit plan, auditors must determine what specialists, like appraisers or actuaries, may be needed for specific tasks.
- 😀 If the client has failed to revise misstatements or take corrective actions for fraud, the auditor may decide to reject the engagement.
- 😀 After accepting the engagement, the auditor drafts the engagement letter, outlining the scope, objectives, responsibilities, and expectations from both the auditor and the client.
Q & A
What are the key stages in the audit process discussed in the script?
-The key stages in the audit process discussed in the script are: 1) Acceptance of Engagement, 2) Planning, 3) Execution of Audit Procedures, and 4) Reporting.
What factors should be considered when deciding to accept or decline an audit engagement?
-Factors to consider include evaluating the integrity of management, assessing the client’s business risks, reviewing past audit experience, evaluating the legal and financial environment of the client, and determining if the audit firm has the capacity to handle the engagement.
What is the role of 'materiality' in the audit process?
-Materiality in the audit process refers to setting a threshold for what is considered a significant error or discrepancy in financial statements. It helps auditors focus on areas that could affect the overall financial accuracy.
How do auditors assess the risks associated with a client’s business during the audit planning phase?
-Auditors assess business risks by reviewing the client's industry, financial reports, and historical performance. They may also analyze external factors, such as legal risks, market conditions, and financial health.
What are 'analytical procedures' and why are they important during an audit?
-Analytical procedures involve comparing financial data across periods, industries, or similar companies to identify inconsistencies or anomalies. These procedures help auditors detect potential errors or areas needing further investigation.
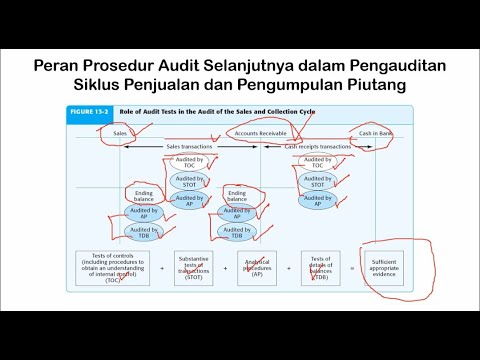
What is the purpose of a test of controls in the audit process?
-The purpose of a test of controls is to evaluate whether the internal controls within a company are effective in preventing or detecting errors and fraud in the financial reporting process.
Why do auditors perform 'substantive tests' during an audit?
-Substantive tests are performed to verify the accuracy and completeness of financial statements. These tests directly assess financial records, such as reviewing transaction logs or checking balances, to ensure they are correctly reported.
What is the significance of the engagement letter in the audit process?
-The engagement letter formally outlines the terms of the audit, including the scope, objectives, responsibilities of both the auditor and the client, the applicable standards, and other relevant details. It ensures clear understanding and agreement between both parties.
What should auditors do if they identify significant discrepancies during their analysis?
-If auditors identify significant discrepancies, they should investigate further, discuss the findings with management, and consider the potential impact on the audit. The discrepancies may require adjustments or additional audit procedures.
What are the specific tasks involved in audit planning according to the script?
-Tasks involved in audit planning include gaining an understanding of the client’s business and industry, conducting analytical procedures, assessing materiality and risks, developing an audit plan and program, and determining the necessary resources and expertise.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
PERENCANAAN AUDIT - Strategi Audit Keseluruhan dan Program Audit

Auditing 101 | Part 1: Starting the Audit: A Guide for CPAs & Aspiring Auditors | Maxwell CPA Review
13-7 - 4 Tahap Proses Audit

4 Fase Audit (AKSK)

تدقيق 101 - (1) - مفهوم التدقيق وقبول العميل

How to Conduct Internal Audit Step by Step Process
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)