4 Fase Audit (AKSK)
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the key phases of an audit, focusing on how auditors plan, assess risks, and evaluate financial statements. The process is structured into phases, from client acceptance and understanding the business environment to testing controls, analyzing financial data, and determining materiality. Auditors conduct substantive tests, assess inherent and control risks, and finalize their report, ensuring the financial statements are accurate and reliable. The audit concludes with a formal report and communication of any findings to the audit committee, ensuring transparency and accountability.
Takeaways
- 😀 The audit process consists of structured phases to help auditors carry out their tasks efficiently and achieve audit objectives.
- 😀 The first phase involves planning and designing an audit approach based on risk assessment procedures, including deciding on client acceptance and understanding their needs for an audit.
- 😀 The second phase focuses on understanding the client's business and industry, which helps assess the risk of material misstatement in the financial statements.
- 😀 Analytical procedures are used in the third phase to compare financial ratios and detect unusual changes in financial statements, helping the auditor focus attention on specific areas.
- 😀 The fourth phase requires determining materiality levels, considering factors like relativity and qualitative aspects that impact the audit process.
- 😀 Significant risks, including those arising from fraud or error, must be identified to decide on the necessary audit procedures.
- 😀 Inherent risk assessment helps the auditor understand the risk of misstatement before considering internal controls.
- 😀 Understanding internal control and assessing control risk are essential to determine the reliability of financial statements and to guide further audit procedures.
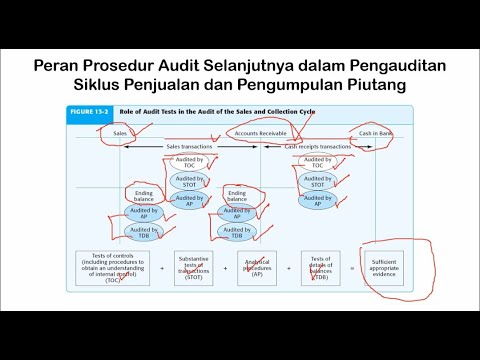
- 😀 Phase 2 involves tests of controls and substantive tests of transactions to detect material misstatements and assess the effectiveness of internal controls.
- 😀 Phase 4 focuses on completing the audit, gathering final evidence, and issuing the audit report, which provides an opinion on the financial statements based on collected evidence.
Q & A
What is the first phase of the audit process?
-The first phase is planning and designing an audit approach based on risk assessment procedures. This phase is crucial to ensure the audit is carried out in a structured and organized way, helping auditors achieve their audit objectives.
Why must auditors conduct a risk assessment during the planning phase?
-Auditors must conduct a risk assessment to identify potential risks that could affect the financial statements. This helps auditors decide on appropriate audit procedures and allocate resources effectively.
What is the purpose of accepting clients and conducting initial planning?
-In this phase, the auditor must decide whether to accept a new client or maintain the relationship with an existing client. They also evaluate whether the client is worthy of being audited and communicate with the previous auditor, if applicable.
How does understanding the client's business and industry impact the audit process?
-Understanding the client's business and industry is essential for auditors to assess the risk of material misstatement. Each industry has its unique characteristics and potential risks, so auditors need to be aware of these factors to ensure accurate financial reporting.
What are analytical procedures, and when are they performed in the audit process?
-Analytical procedures are tests that involve comparing financial data, such as financial ratios, with benchmarks. They are conducted during the planning phase to identify unusual changes and during the third phase to gain deeper insights into financial performance.
What is materiality in the audit process, and why is it important?
-Materiality refers to the significance of an error in the financial statements that could influence the decisions of financial statement users. It is important because it helps auditors determine which misstatements are large enough to affect the audit’s conclusions.
What is the purpose of conducting tests of controls in the audit?
-Tests of controls are performed to evaluate the effectiveness of a company’s internal control system in preventing or detecting material misstatements. These tests are critical for assessing control risk and deciding whether further audit procedures are necessary.
What is the difference between substantive tests and tests of controls?
-Substantive tests focus on detecting material misstatements directly in the financial statements, while tests of controls assess the effectiveness of internal controls in preventing misstatements. Both are used to determine the overall risk of the audit.
Why must auditors assess inherent risk during the audit?
-Inherent risk is the risk that material misstatements exist in the financial statements before considering internal controls. Assessing inherent risk helps auditors determine the level of scrutiny and testing required for different areas of the financial statements.
What actions does an auditor take in the completion phase of an audit?
-In the completion phase, the auditor conducts final testing for presentation and disclosure objectives, gathers additional evidence, evaluates the going concern assumption, and issues the audit report. The auditor also communicates with the audit committee and management about any significant findings.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)