13-7 - 4 Tahap Proses Audit
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the four key phases of the audit process: planning and approach, testing of controls and substantive tests, analytical procedures, and reporting. The first phase focuses on initial planning, understanding the client’s business, and risk assessment. The second phase involves testing controls and procedures to mitigate risks. The third phase reviews and analyzes potential misstatements, using detailed procedures to assess each account. The final phase focuses on compiling audit evidence, evaluating findings, and preparing the audit report. The video also covers the timing of tests and emphasizes the importance of these stages for a successful audit process.
Takeaways
- 😀 The audit process consists of four phases: planning and audit approach, test of controls (TOC) and substantive testing (ST), analytical procedures and risk assessment, and completion and audit reporting.
- 😀 The first phase involves planning the audit, assessing risks, and understanding the client's business and internal controls.
- 😀 Analytical procedures are conducted early on in the audit to assess trends and anomalies in financial data.
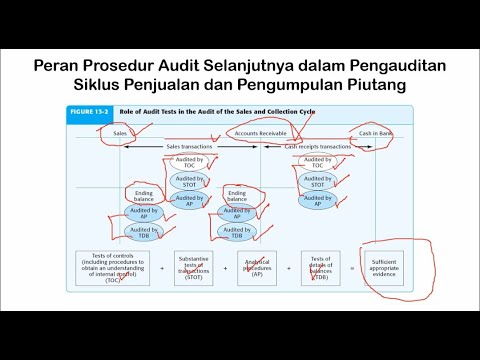
- 😀 In phase two, auditors perform tests of controls (TOC) to evaluate the effectiveness of internal controls, and substantive testing (ST) to verify transactions.
- 😀 Auditors must assess the possibility of material misstatements in the financial reports due to control risks and errors.
- 😀 Phase three focuses on further analytical procedures, identifying high-risk areas in the financial data, and determining any misstatements.
- 😀 The third phase also includes substantive testing to verify key account balances and the completeness of financial statements.
- 😀 In the final phase, the audit report is compiled after evaluating findings from tests, internal controls, and substantive procedures.
- 😀 The audit report includes a summary of key findings, such as any identified risks and misstatements, and is communicated with the audit committee and management.
- 😀 Timing of the audit is critical, with key procedures scheduled at specific points during the fiscal year, such as before and after the year-end closing.
- 😀 The entire audit process culminates in the preparation of the audit report, which communicates the auditor's findings and recommendations to management.
Q & A
What are the four phases of the audit process described in the transcript?
-The four phases of the audit process are: 1) Planning and Audit Approach, 2) Test of Controls (TOC) and Substantive Test (ST), 3) Analytical Procedures and Test Data (TDP), and 4) Audit Report Compilation and Final Procedures.
What is the purpose of the first phase in the audit process?
-The first phase involves planning and approaching the audit. Key steps include understanding the client's business, identifying risks, determining materiality, and evaluating internal controls before formulating an audit strategy.
What happens in the second phase involving Test of Controls and Substantive Test?
-In the second phase, auditors assess the effectiveness of internal controls (TOC) and perform substantive testing (ST) to gather evidence regarding the transactions and financial reports. This helps evaluate the possibility of misstatements in the financial statements.
How does Analytical Procedures play a role in phase 3?
-In phase 3, Analytical Procedures (AP) are used to identify unusual patterns or discrepancies in financial data, helping auditors assess areas where material misstatements could occur. It aids in determining risk levels and areas that require further scrutiny.
What does the final audit report include and when is it prepared?
-The final audit report, prepared in the fourth phase, includes the auditor's findings, such as internal control weaknesses and any discrepancies found in the financial statements. It also addresses the presentation and disclosure of financial data.
What is the significance of materiality in the audit process?
-Materiality refers to the threshold at which misstatements in financial statements could influence decision-making. During the planning phase, auditors determine the level of materiality to identify which areas need closer examination.
Why is understanding the client's business and industry important in the audit process?
-Understanding the client's business and industry helps auditors assess risks, identify key financial statement areas that could be prone to errors or fraud, and tailor the audit approach to the specific context of the client.
What role does the internal control evaluation play in the audit process?
-Evaluating internal controls helps auditors assess the reliability and effectiveness of processes in preventing or detecting errors or fraud. This step is essential for planning the audit approach and determining whether further testing is required.
How does the timing of tests impact the audit process?
-The timing of tests, as shown in the transcript, helps auditors plan when to perform different audit procedures. Certain tests, like substantive tests, are performed near the end of the fiscal year, while others, like confirmation procedures, happen earlier in the audit timeline.
What does the audit report communication with management entail?
-The audit report communication with management involves discussing the audit findings with the audit committee and management to ensure they understand the results and can address any issues or concerns raised by the audit.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)