Auditing 101 | Part 1: Starting the Audit: A Guide for CPAs & Aspiring Auditors | Maxwell CPA Review
Summary
TLDRIn this YouTube series on the audit process, the speaker guides viewers through each phase, from client acceptance to post-audit tasks. Aimed primarily at CPA exam candidates and auditing interns, the series emphasizes understanding the rationale behind audit procedures. Key topics include the importance of audits for financial statement reliability, the client's responsibilities, the engagement letter, audit documentation, and planning. The speaker also discusses the roles of internal auditors, specialists, and component auditors, providing a comprehensive foundation for mastering auditing concepts.
Takeaways
- 😀 Audits are essential for validating the accuracy of financial statements provided by companies to stakeholders like investors and creditors.
- 😀 Client acceptance is a critical phase where auditors must assess the integrity of potential clients before agreeing to perform an audit.
- 😀 Management of the client company holds primary responsibility for the preparation and fair presentation of financial statements and internal controls.
- 😀 An engagement letter serves as a contract between auditors and management, outlining responsibilities and expected deliverables.
- 😀 Audit documentation, or working papers, must support the auditor's opinion and demonstrate adherence to auditing standards.
- 😀 The quality of audit evidence is influenced by the nature, extent, and timing of the audit procedures performed.
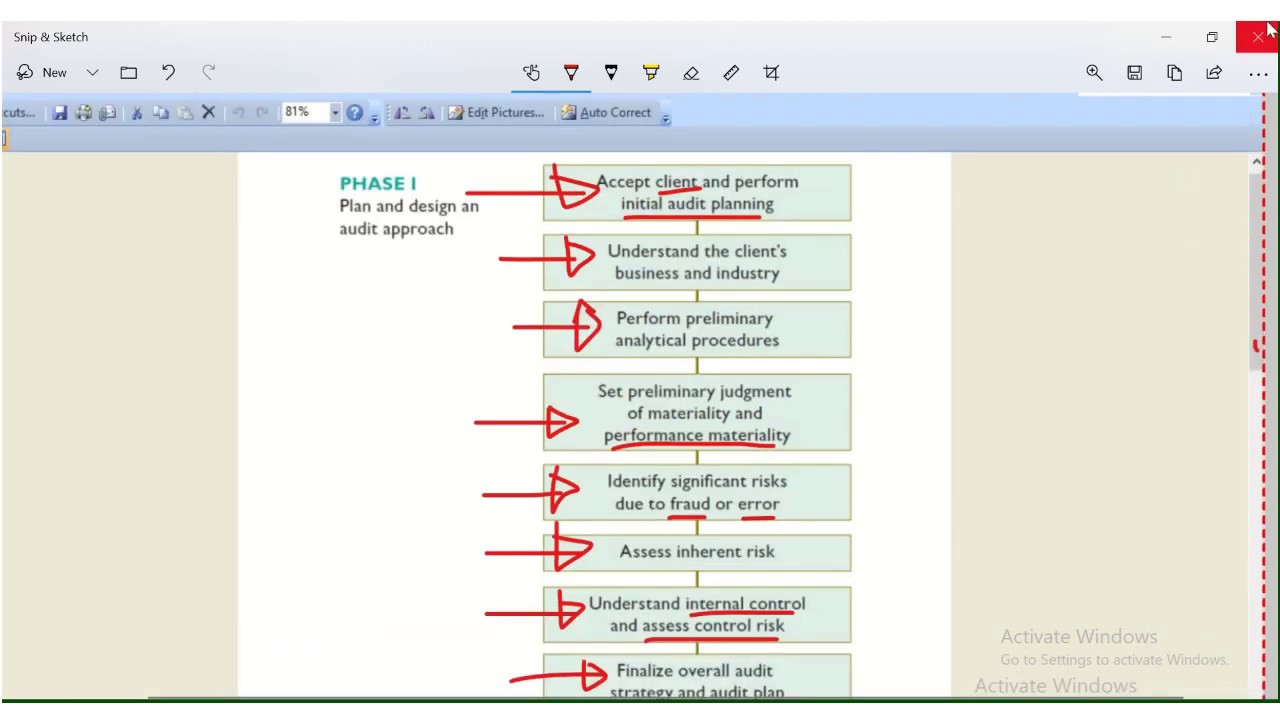
- 😀 During the planning phase, auditors must develop an audit strategy and plan that outline overall objectives and specific procedures.
- 😀 Analytical procedures are required in both the planning phase and overall review phase to assess risks and understand the client's business.
- 😀 Internal auditors can assist in the audit process, but their lack of independence requires careful consideration in low-complexity areas.
- 😀 Group audits involve component auditors for different subsidiaries, while the group auditor maintains overall responsibility for the consolidated financial statements.
Q & A
What is the primary purpose of an audit?
-The primary purpose of an audit is to provide assurance to users of financial statements, such as investors and creditors, that the financial statements are fairly presented and legitimate.
Why is client acceptance important in the audit process?
-Client acceptance is crucial because auditors need to avoid working with clients who lack integrity, as this could compromise the reliability of the financial information they provide.
What responsibilities does management have during an audit?
-Management is responsible for the preparation and fair presentation of financial statements, designing and implementing internal controls, and providing auditors access to necessary documentation and employees.
What is included in the engagement letter?
-The engagement letter outlines the responsibilities of both the auditor and management, the expected reports, the company's method of accounting, and audit fees. It does not include specific information that could enable management to manipulate the audit.
What are working papers in auditing?
-Working papers are documents used by auditors to record their test work and findings. They are owned by the auditors and serve to support the auditor's opinion and demonstrate compliance with auditing standards.
How does the auditor determine the quality of audit evidence?
-The quality of audit evidence is determined by the nature, extent, and timing of audit procedures. The nature refers to the type of tests performed, the extent refers to the amount of testing, and timing refers to when the tests are conducted.
What is the difference between the audit strategy and the audit plan?
-The audit strategy is a high-level document that outlines overall objectives and resource needs, while the audit plan provides detailed procedures that auditors will perform during the audit.
Why is it necessary to perform analytical procedures during the planning phase?
-Analytical procedures are performed to analyze trends and ratios, which helps auditors identify areas of higher risk and gain a better understanding of the client's business.
What should auditors consider when reviewing the predecessor auditor?
-Auditors should communicate with the predecessor auditor to understand the reasons for the change in auditors, particularly any concerns about the integrity of the client.
What are the roles of internal auditors and specialists in the audit process?
-Internal auditors assist with lower-complexity tasks but are not independent. Specialists are hired for their expertise in complex areas, and while they perform specific tasks, the overall responsibility remains with the external auditor.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)