Tutorial VLAN : Konsep Dasar Virtual Local Area Network :
Summary
TLDRThis video provides a detailed explanation of VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks) and their importance in network management. It covers the concept of separating networks within the same physical segment using VLANs, improving security, bandwidth management, and access control. The video also explores how VLANs work on Layer 2, utilizing protocols like 802.1Q. Key concepts such as VLAN IDs, switch configurations, trunking, and access modes are discussed, highlighting the efficiency of VLANs in larger networks. Additionally, the video covers practical scenarios involving multiple floors or networks, emphasizing the role of VLANs in network isolation.
Takeaways
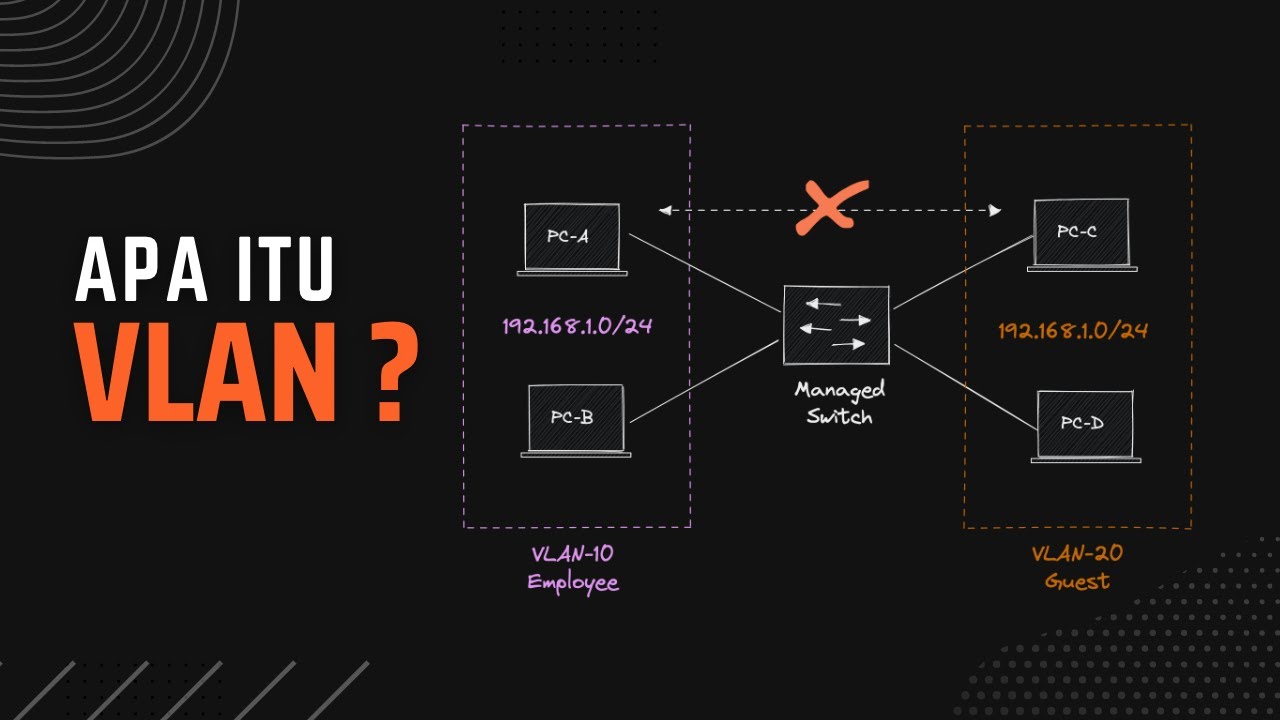
- 😀 VLAN is a protocol that allows the creation of multiple networks within the same physical network segment, effectively separating them for better network management.
- 😀 VLANs are used to manage network resources like bandwidth and security by logically separating networks that might otherwise share the same physical infrastructure.
- 😀 Managed switches are necessary for configuring VLANs, allowing for specific port configurations, such as access and trunking modes, to ensure proper data flow between VLANs.
- 😀 The IEEE 802.1Q protocol is used in VLANs to insert VLAN IDs into Ethernet frames, enabling identification and separation of data from different VLANs.
- 😀 VLANs allow for isolated communication between networks, meaning that devices in different VLANs cannot communicate unless explicitly configured to do so.
- 😀 VLAN IDs range from 1 to 4094, with IDs from 1 to 1005 being the normal range, IDs from 1006 to 4094 reserved for extended VLANs, and some IDs reserved for internal device use.
- 😀 In a typical VLAN setup, different devices (e.g., departments, staff, and management) can be assigned unique VLAN IDs, ensuring network traffic remains segregated.
- 😀 When expanding across multiple floors or buildings, VLANs can be maintained by connecting switches with the same VLAN ID configuration, preventing network mixing.
- 😀 Access ports are configured to carry only one VLAN ID, while trunk ports can carry multiple VLAN IDs, reducing the need for multiple cables between switches.
- 😀 The efficiency of network wiring can be improved by using trunking mode, where a single cable can carry data for multiple VLANs, simplifying network management.
Q & A
What is a VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network)?
-A VLAN is a protocol that allows the creation of multiple networks within the same physical network segment. It is used to segment networks for better management, such as for bandwidth control, access control, and security.
Why would you use VLANs in a network?
-VLANs are used to separate networks for reasons such as better network management, controlling bandwidth, improving security, and reducing network congestion.
How does VLAN segmentation work within a network?
-VLAN segmentation works by assigning different VLAN IDs to different groups in the network. This ensures that devices within each VLAN cannot communicate with those in other VLANs unless explicitly routed or bridged.
What is the difference between a switch with VLAN support and a regular switch?
-A switch with VLAN support, also known as a manageable switch, can be configured to create and manage VLANs, whereas a regular, unmanaged switch forwards data across all connected devices without segmentation.
What is the role of the IEEE 802.1Q protocol in VLANs?
-IEEE 802.1Q is the standard protocol used to tag Ethernet frames with VLAN IDs. This allows VLANs to be differentiated and ensures that only devices within the same VLAN can communicate with each other.
How does VLAN communication occur between switches?
-When VLANs are implemented, switches use VLAN IDs to tag packets. Only devices with matching VLAN IDs can communicate. If a packet's VLAN ID doesn't match, the switch won't forward the data to the other VLANs.
What are the two modes of ports in VLANs, and how do they differ?
-The two modes of ports in VLANs are 'Access' and 'Trunking.' Access mode ports are configured to carry traffic for a single VLAN, while Trunking mode ports can carry multiple VLANs' traffic, allowing for more efficient communication across multiple networks.
What is the issue with using multiple cables to connect VLANs across floors?
-Using multiple cables to connect VLANs across floors can become inefficient as the number of VLANs increases, leading to a lot of physical cables, which can be difficult to manage and not scalable.
How can you overcome the challenge of connecting multiple VLANs across several floors?
-To overcome this challenge, you can use Trunking mode on switches. Trunking allows multiple VLANs to be transmitted over a single cable, significantly simplifying the network configuration.
What are the different ranges of VLAN IDs, and how are they used?
-VLAN IDs range from 1 to 4094. VLAN IDs from 1 to 1005 are normal VLANs that can be configured, used, and modified. VLANs 1006 to 4094 are extended VLANs used for specific purposes, and certain VLAN IDs like 3968, 4047, and 4094 are reserved for internal device use.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)