VLANs Explained | Cisco CCNA 200-301
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the CertBros team explains the concept of VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks), highlighting their importance in managing network traffic. VLANs help reduce broadcast overhead and improve scalability without the need for extra hardware or re-cabling. The video covers how VLANs function, the differences between access and trunk ports, the use of 802.1q tagging for traffic identification, and the role of native VLANs. The tutorial also addresses potential configuration issues, such as native VLAN mismatches. Overall, it provides a clear and accessible guide to understanding VLANs and their practical applications in networking.
Takeaways
- 😀 VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks) allow you to divide a single LAN into smaller, more manageable segments.
- 😀 One major advantage of VLANs is that they help control broadcast traffic, reducing network congestion.
- 😀 Without VLANs, broadcast traffic can slow down networks, especially in environments where multiple departments exist.
- 😀 VLANs are a virtual solution to physically separating networks, eliminating the need for additional hardware or cabling.
- 😀 You can assign VLANs to specific interfaces on a switch, allowing better control over which devices can communicate with each other.
- 😀 VLANs are scalable and flexible, allowing the addition of new departments or devices without needing new physical equipment.
- 😀 Cisco switches and others have a default VLAN (VLAN 1) where all interfaces are initially assigned.
- 😀 VLANs are not limited to a single switch and can be spread across multiple switches, making them highly versatile.
- 😀 A trunk port is used to carry traffic from multiple VLANs between switches, and it uses tags to identify which VLAN the traffic belongs to.
- 😀 The 802.1q tag is used in trunking to identify which VLAN a particular frame belongs to, allowing switches to correctly route traffic.
- 😀 The concept of native VLANs allows frames from a specific VLAN to be sent untagged across a trunk, typically using VLAN 1 by default.
- 😀 A mismatch in native VLAN settings between two switches can lead to traffic being incorrectly routed, but modern switches alert you to such issues.
Q & A
What is a VLAN and why is it used?
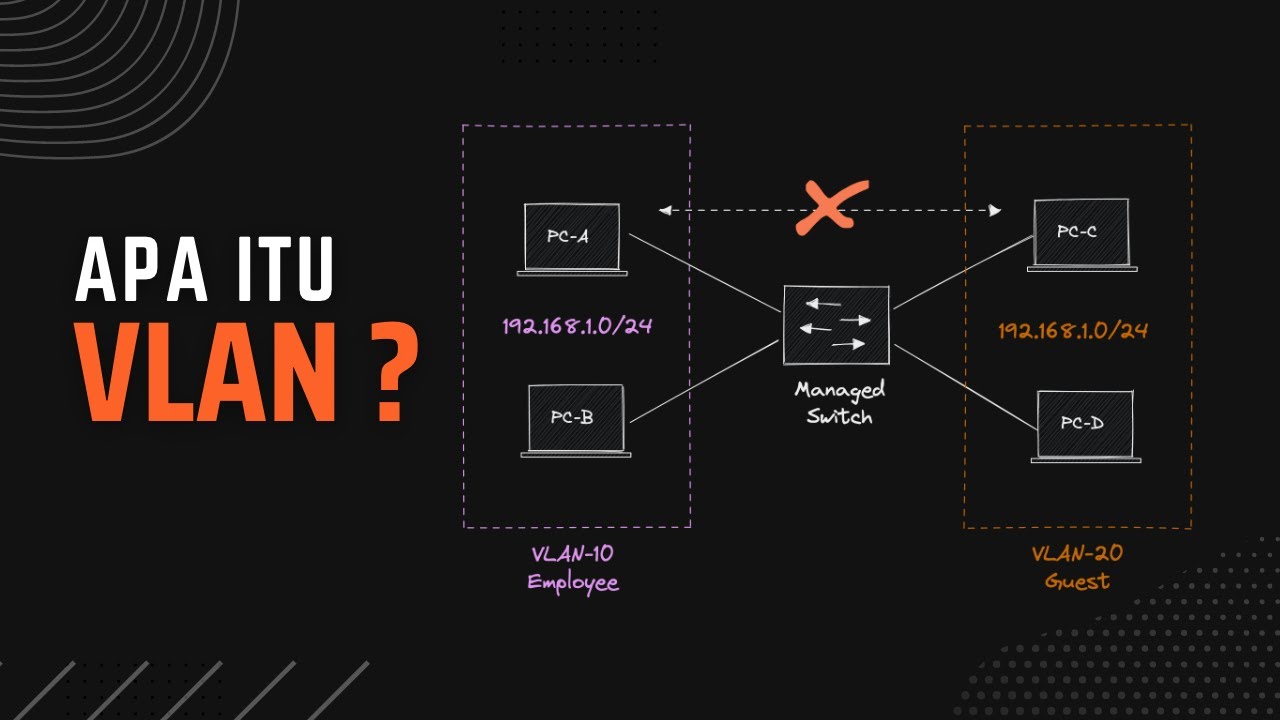
-A VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) is a way to segment a physical LAN into smaller, isolated logical networks. It is used to reduce broadcast traffic, improve network efficiency, and manage traffic more effectively.
How does a VLAN help manage broadcast traffic?
-In a VLAN, broadcast traffic is confined to specific segments of the network. By splitting the network into smaller broadcast domains, VLANs prevent broadcasts from affecting the entire network, thereby reducing congestion and improving performance.
What is the difference between a router and a VLAN for managing broadcast traffic?
-A router can create separate broadcast domains by assigning different interfaces to different networks, but VLANs allow you to segment your network virtually without the need for additional hardware. VLANs are more cost-effective and scalable compared to routers.
What are the benefits of VLANs over physically splitting a network?
-VLANs provide the same benefits of physical separation of networks, such as reduced broadcast traffic, but without the need for new equipment, cabling, or physical reconfiguration. VLANs are scalable and flexible.
How are VLANs implemented in a switch?
-By default, all interfaces on a switch are assigned to VLAN 1. You can create additional VLANs and assign specific interfaces to each VLAN. This allows the switch to isolate traffic between different VLANs, ensuring that only devices within the same VLAN can communicate.
What is a trunk port and why is it needed?
-A trunk port is used to carry traffic from multiple VLANs between switches or other networking devices. Unlike an access port, which is assigned to a single VLAN, a trunk port can handle traffic from several VLANs simultaneously.
What is an 802.1q tag and why is it important?
-An 802.1q tag is a 4-byte tag added to frames to identify which VLAN the frame belongs to when it is sent across a trunk port. This ensures that VLAN information is preserved as the frame travels between switches and devices.
What is a native VLAN and how does it function?
-A native VLAN is the VLAN that a switch assumes a frame belongs to if it arrives untagged on a trunk port. By default, VLAN 1 is the native VLAN, but it can be configured to a different VLAN if necessary.
What problems can occur if the native VLAN is mismatched between switches?
-If switches have different native VLANs configured, untagged frames sent from one switch may be incorrectly assumed to belong to the wrong VLAN by the other switch. This can prevent frames from reaching their intended destination, leading to network connectivity issues.
What is the role of VLAN tagging in a network with multiple switches?
-VLAN tagging allows switches to correctly identify and route traffic from multiple VLANs over a trunk link. When a frame is sent from one switch to another, the VLAN tag ensures that the traffic is delivered to the correct VLAN on the receiving switch.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)