Aprende a construir una Tabla de frecuencia con datos agrupados
Summary
TLDRThis instructional video explains how to create a frequency distribution table using grouped data based on age collected from 50 individuals. It details the steps to determine the range, number of intervals, and interval width needed for the table. Viewers learn to categorize ages into specific intervals, calculate absolute and relative frequencies, and derive cumulative frequencies. The video also demonstrates how to use this table to answer statistical questions about the dataset, such as the percentage of individuals within certain age ranges, thus providing practical insights into data analysis.
Takeaways
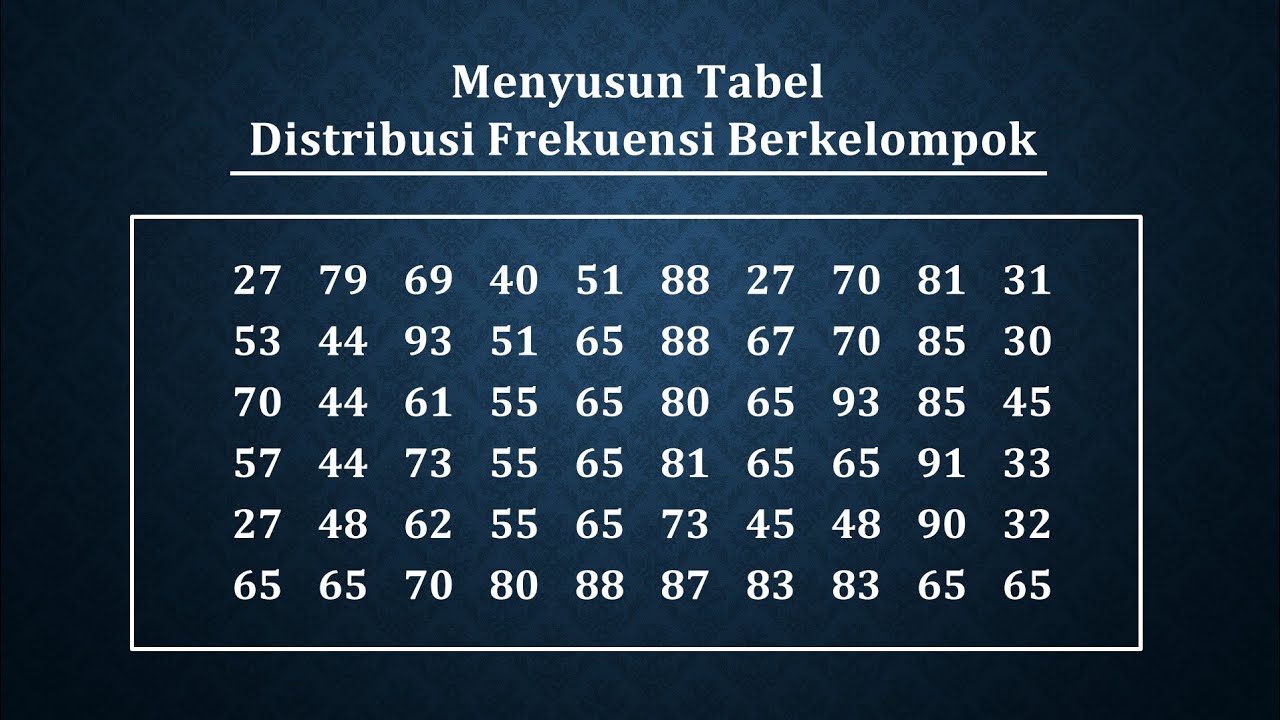
- 😀 The script discusses how to create a frequency distribution table using age data from a sample of 50 people.
- 😀 The range (R) is determined by subtracting the smallest value from the largest value in the dataset.
- 😀 The number of intervals (k) is calculated using Sturges' formula, which involves the logarithm of the number of data points.
- 😀 The amplitude of each interval is found by dividing the range by the number of intervals.
- 😀 The first interval starts with the minimum data point and is constructed based on the calculated amplitude.
- 😀 Class marks (midpoints) are computed as the average of the lower and upper boundaries of each interval.
- 😀 Absolute frequency is determined by counting the number of data points that fall within each interval.
- 😀 Relative frequency is calculated as the proportion of data points in each interval relative to the total number of data points.
- 😀 Cumulative frequency helps track the total number of observations up to a certain interval.
- 😀 The final table allows for various statistical analyses, such as calculating the percentage of people within specific age ranges.
Q & A
What is the purpose of creating a frequency distribution table?
-The purpose is to organize and summarize data, making it easier to analyze the distribution of values, such as ages in this case.
How is the range (R) of the data calculated?
-The range is calculated by subtracting the minimum value from the maximum value in the dataset.
What formula is used to determine the number of intervals (k)?
-The formula is k = 1 + 3.322 * log10(n), where n is the total number of data points.
How do you calculate the amplitude (h) of each interval?
-The amplitude is calculated by dividing the range (R) by the number of intervals (k).
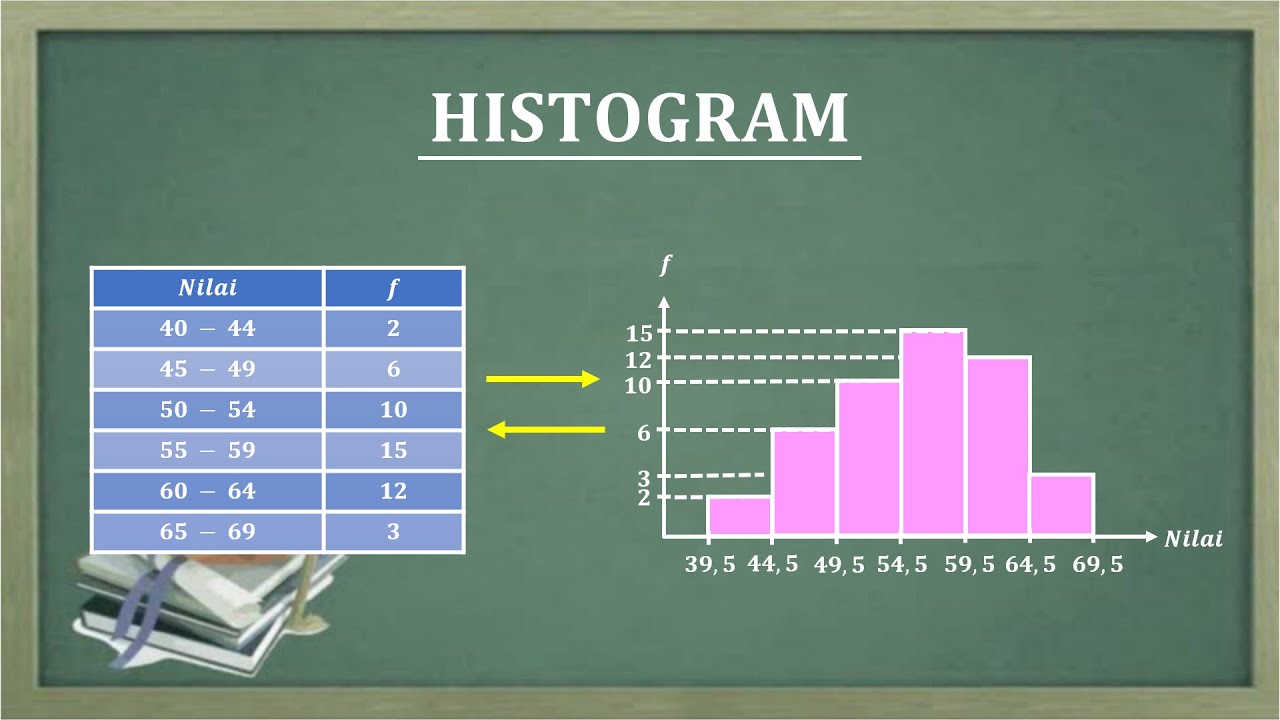
What are the components of the frequency distribution table?
-The components include class intervals, class marks, absolute frequency, relative frequency, absolute cumulative frequency, and relative cumulative frequency.
How is the class mark (x') determined?
-The class mark is determined by averaging the lower and upper limits of each interval.
What is the process for calculating absolute frequency?
-Absolute frequency is calculated by counting the number of data points that fall within each defined interval.
How do you calculate relative frequency from absolute frequency?
-Relative frequency is calculated by dividing the absolute frequency of each interval by the total number of data points.
What does cumulative frequency represent in the context of this analysis?
-Cumulative frequency represents the running total of frequencies up to a certain interval, helping to show the accumulation of data points.
What type of statistical questions can be answered using the frequency distribution table?
-Questions such as the percentage of individuals within specific age ranges or the number of individuals above or below a certain age can be answered using this table.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)