BAB 2 PETA, PENGINDRAAN JAUH, DAN SISTEM INFORMASI GEOGRAFIS | GEOGRAFI X SMA/MA | KURIKULUM MERDEKA
Summary
TLDRThe video discusses the concept of maps, defined as flat representations of the Earth's surface, incorporating both natural and human-made elements. It categorizes maps based on content (general vs. thematic) and scale (large, medium, small, and geographic). The video explains different types of maps, such as topographic and cadastral maps, and their functions, including showing locations and representing phenomena. It also covers map projection methods, cartographic principles, and essential components like titles, legends, and scales. Finally, the importance of maps in agriculture, disaster management, and spatial planning is highlighted.
Takeaways
- 🗺️ A map is a representation of the Earth's surface on a flat plane, created through a projection system according to Indonesian Government Regulation No. 8 of 2013.
- 📊 Maps are categorized into two types based on content: general maps (such as topographic maps and world maps) and thematic maps, which focus on specific phenomena.
- 🔍 General maps display the Earth's surface broadly, showing both natural and cultural features, while thematic maps provide detailed information on specific topics, such as population distribution.
- 📏 Maps are also classified by scale, including cadastral maps (1:100 to 1:5,000), large scale (1:5,000 to 1:250,000), medium scale (1:250,000 to 1:500,000), small scale (1:500,000 to 1:1,000,000), and geographic scale (over 1:1,000,000).
- 📌 The functions of maps include showing positions or locations, illustrating phenomena and features of the Earth, and providing information in a spatial context.
- 📐 Map projections can be categorized by projection type (azimuthal, conical, and cylindrical) and their geometric criteria, affecting how the Earth's surface is represented.
- 🧭 Projections are classified based on the axis of symmetry (normal, oblique, and transverse), influencing how accurately different regions are depicted.
- 🔄 Key components of maps include the main map, title, orientation, legend, scale, insets, coordinate lines (latitude and longitude), source data, and lettering.
- 🎨 Colors in maps represent various features, such as green for land areas, blue for water bodies, and red or black for transportation networks.
- 🌍 Maps have practical applications in fields like agriculture, disaster mitigation, and urban planning, aiding in decision-making and spatial analysis.
Q & A
What is the definition of a map (peta) according to Indonesian regulations?
-A map is a representation of the Earth's surface on a flat plane with a certain scale, depicting both natural and human-made elements above and below the surface.
What are the two main categories of maps based on their content?
-Maps are categorized into general maps and thematic maps.
How are maps classified based on scale?
-Maps can be classified as cadastral maps, large scale maps, medium scale maps, small scale maps, and geographic scale maps.
What distinguishes a thematic map from a general map?
-Thematic maps focus on specific phenomena or themes, providing detailed information about a particular subject, while general maps give an overall depiction of the Earth's surface.
What is the purpose of contour lines on a topographic map?
-Contour lines represent the relief of the Earth's surface; closer lines indicate steep terrain, while wider spacing shows gentler slopes.
Can you give examples of thematic maps mentioned in the transcript?
-Examples of thematic maps include population density maps and maps showing the distribution of ethnic groups in Indonesia.
What are the four types of map projections based on projection surface?
-The four types are azimuthal projection, conic projection, cylindrical projection, and tangent or secant projections.
What is the significance of map scale?
-The scale of a map indicates the relationship between distance on the map and actual distance on the ground, helping users understand size and distance.
What are some essential components that must be included in a well-designed map?
-Essential components include the main map, title, orientation (north arrow), legend, scale, inset maps, and coordinates (longitude and latitude).
How does toponymy relate to cartography?
-Toponymy is the study of place names and their significance in cartography, ensuring proper labeling of geographical features according to their location and context.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

PENGERTIAN PETA DAN SYARAT PETA #geography #education #kurikulummerdeka

Mengenal Fungsi, Jenis, dan Unsur-unsur Peta | IPS | SayaBisa

Sistem Proyeksi Peta

IPS kelas 7 bab 1a - Apa itu peta
Pengetahuan Dasar Peta , Peta dan Pemetaan - Materi Pembelajaran Geografi
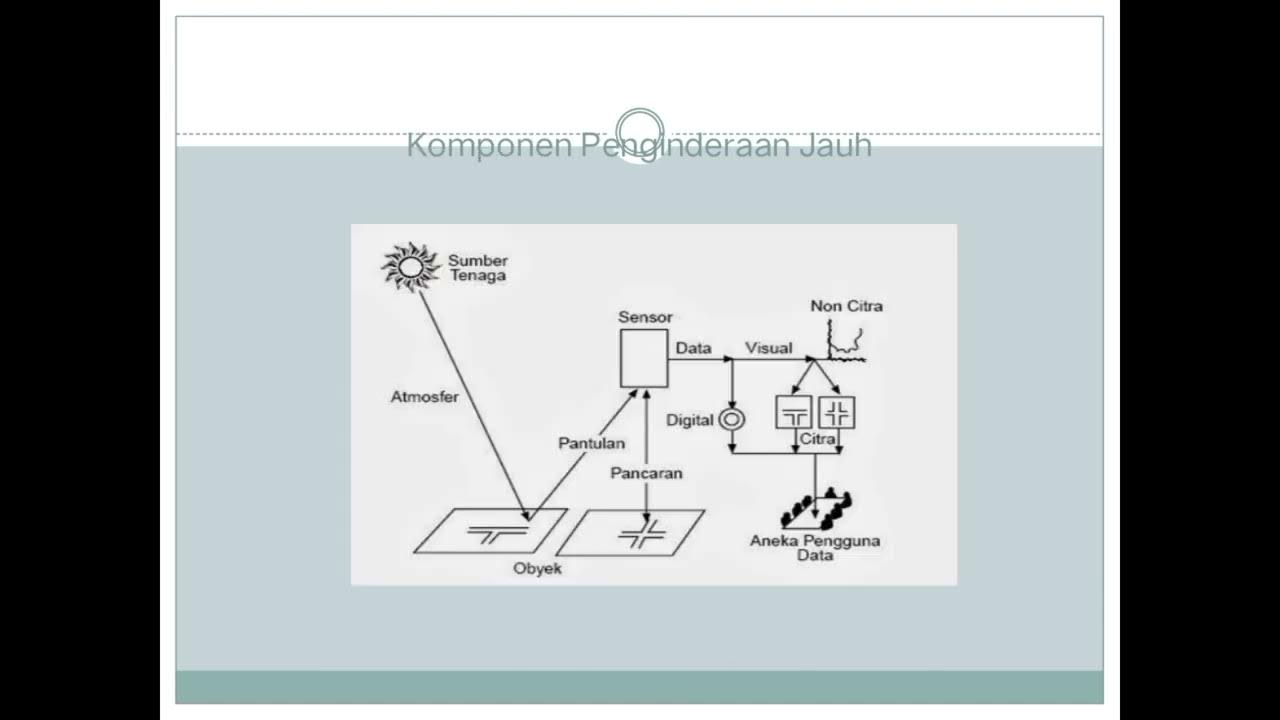
Popy X 1 Dasar Pemetaan Indera SIG Geo X Regulasi Diri
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)