jaringan hewan (bahasa indonesia)
Summary
TLDRThe video provides an educational overview of animal tissues, explaining the four main types: epithelial, nervous, muscle, and connective tissues. It details the structure, function, and classification of each, such as how epithelial tissue covers surfaces, muscle tissue enables movement, nervous tissue transmits signals, and connective tissue supports and binds the body. Key examples include the skin, kidneys, intestines, and bones. The video concludes by summarizing the classifications and roles of these tissues, offering a clear understanding of how animal bodies are structured and function.
Takeaways
- 🧬 Animal tissues are groups of cells that work together to perform specific functions.
- 🧫 There are four basic types of animal tissues: epithelial, nervous, muscle, and connective tissues.
- 🏥 Epithelial tissue covers and protects the outer and inner surfaces of the body, and it comes in various forms such as simple squamous, stratified squamous, columnar, and cuboidal epithelium.
- 💨 Simple squamous epithelium, found in the alveoli, allows for the transport of small molecules across membranes.
- 🛡️ Stratified squamous epithelium, found in the skin, protects organs from external friction.
- 🧠 Nervous tissue is made up of neurons, which transmit signals throughout the body, allowing us to respond to stimuli like touching sharp objects.
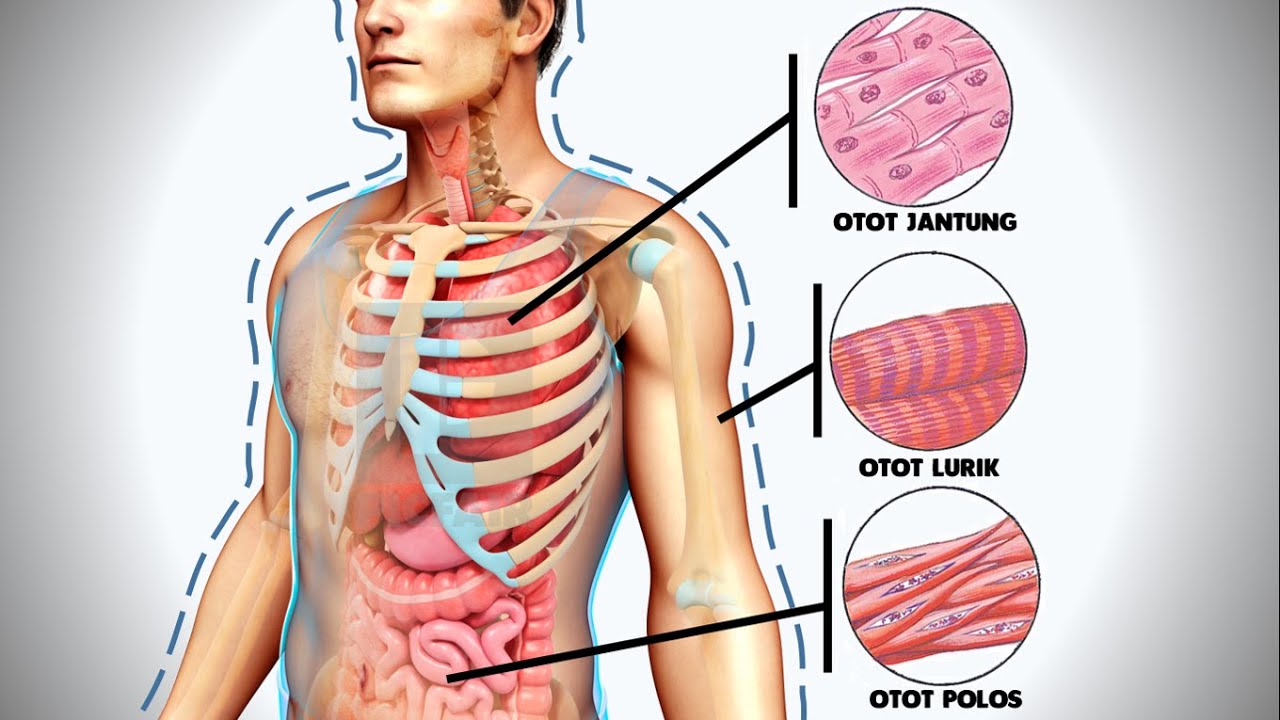
- 💪 Muscle tissue enables movement, with skeletal muscles responsible for voluntary movement, smooth muscles for involuntary actions, and cardiac muscles for heart function.
- 🩸 Connective tissue includes blood, bones, dense connective tissue, cartilage, loose connective tissue, and adipose tissue, all of which support and connect body parts.
- 🔄 Blood is composed of red and white blood cells and platelets, which transport gases and other materials throughout the body.
- 🧱 Cartilage and bones protect and support organs, while ligaments and tendons connect bones and ensure flexibility.
Q & A
What is a tissue in animals?
-A tissue in animals is a group of cells with similar structures that work together to perform a specific function.
What are the four basic types of animal tissues?
-The four basic types of animal tissues are epithelial tissue, nervous tissue, muscle tissue, and connective tissue.
What is the role of epithelial tissue in animals?
-Epithelial tissue covers and protects the outer and inner surfaces of the animal's body. It functions in absorption, secretion, and protection against friction.
How is epithelial tissue classified based on shape and layers?
-Epithelial tissue is classified into simple squamous, stratified squamous, simple columnar, and simple cuboidal. Simple squamous is found in areas like alveoli, and stratified squamous is found in skin, providing protection.
What are neurons, and what role do they play in the body?
-Neurons are nerve cells that transmit electrical impulses. They help communicate signals within the body, allowing actions like reflexes and movement.
How do neurons transmit signals?
-Neurons transmit signals through dendrites that receive information, and axons that send information to other neurons, enabling the movement of muscles or reflex actions.
What are the three types of muscle tissues, and what are their functions?
-The three types of muscle tissues are skeletal muscles (voluntary movement), smooth muscles (involuntary movements in organs like intestines), and cardiac muscles (involuntary contractions of the heart).
What distinguishes skeletal muscle from smooth muscle?
-Skeletal muscle is striated and controls voluntary movements, while smooth muscle is non-striated and controls involuntary movements, such as the contraction of the intestines.
What is connective tissue, and what are its types?
-Connective tissue supports and binds different parts of the body. Types include blood, bone, dense connective tissue, cartilage, loose connective tissue, and adipose tissue.
What is the function of blood as a connective tissue?
-Blood, as a connective tissue, transports gases, nutrients, and waste materials throughout the body, using its components like red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)