Jaringan Hewan
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, the speaker explores the four main types of animal tissues: epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous tissue. Each type is examined for its unique structures and essential functions, including protection, support, and signal transmission within the body. The session emphasizes the characteristics of epithelial layers, the diverse roles of connective tissues, and the different muscle types, concluding with a brief on nervous tissue. The speaker encourages student interaction and understanding, setting the stage for more in-depth discussions in future lessons.
Takeaways
- 😀 The lesson focuses on animal tissues, following a previous discussion on plant tissues.
- 📚 There are four main types of animal tissues: epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous tissues.
- 🔍 Epithelial tissue serves functions such as protection, secretion, and diffusion, with various shapes like squamous, cuboidal, and columnar.
- 🧩 Connective tissue supports and binds other tissues, including types such as blood, bone, and adipose tissue.
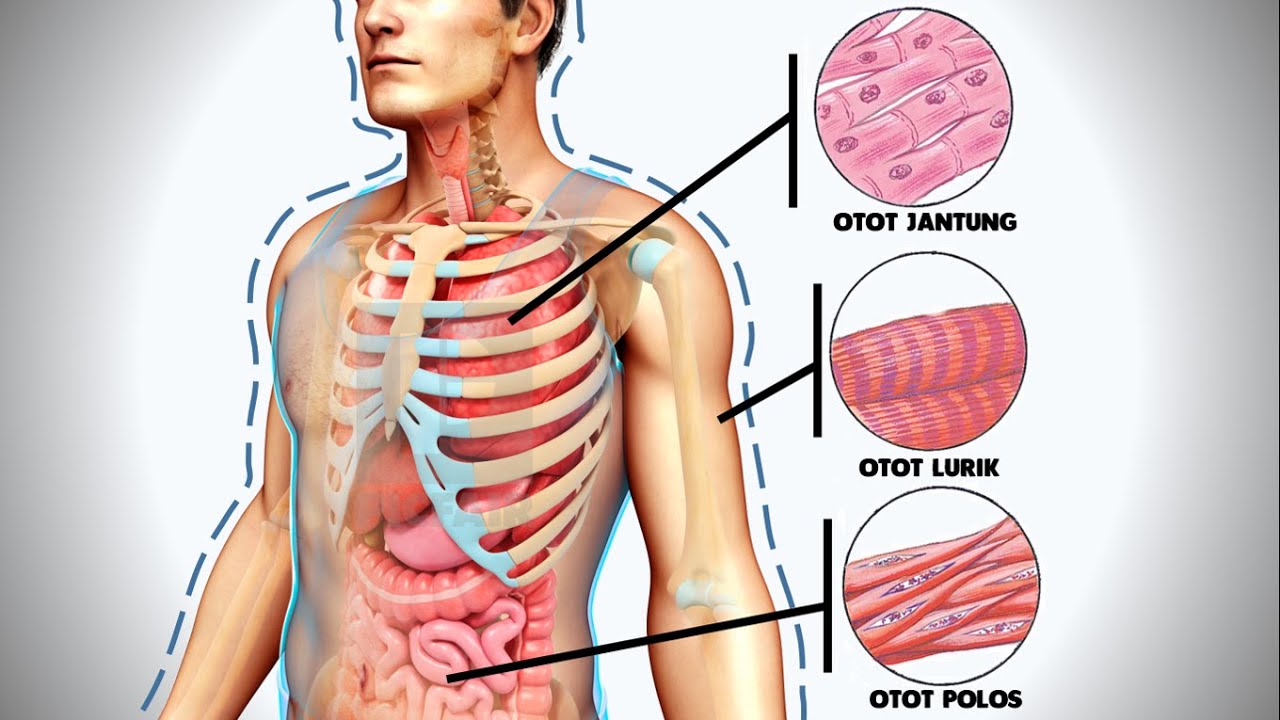
- 💪 Muscle tissue is categorized into three types: smooth (involuntary), skeletal (voluntary), and cardiac (heart).
- 🧠 Nervous tissue is essential for transmitting signals and consists of sensory, motor, and connecting neurons.
- 📊 Visual aids and diagrams are emphasized for better understanding of the different tissue types.
- 🤔 Students are encouraged to ask questions and engage with the material for clarity.
- 📝 Reviewing the lesson material and preparing for follow-up discussions is recommended for students.
- 🌟 The speaker motivates students to stay enthusiastic and focused on their learning journey.
Q & A
What are the main components of animal tissue discussed in the video?
-The video discusses four main components of animal tissue: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue.
What functions does epithelial tissue serve?
-Epithelial tissue protects underlying structures, facilitates absorption, secretion, and diffusion, and can produce enzymes.
How is connective tissue characterized in the script?
-Connective tissue is described as a type of tissue that binds and supports other tissues, containing fibers such as collagen, elastin, and reticular fibers.
What are the three types of muscle tissue mentioned?
-The video mentions three types of muscle tissue: smooth muscle, striated (skeletal) muscle, and cardiac muscle.
What are the components of blood as discussed in the video?
-Blood consists of red blood cells (erythrocytes), white blood cells (leukocytes), and platelets (thrombocytes), which have roles in oxygen transport, immune response, and clotting.
What does the video say about the role of epithelial tissue in the body?
-Epithelial tissue lines surfaces, cavities, and organs, providing protection, absorption, and secretion functions throughout the body.
How many types of connective tissue are listed, and what are they?
-The video lists seven types of connective tissue: loose connective tissue, dense connective tissue, adipose tissue, cartilage, bone, blood, and lymphatic tissue.
What is the significance of muscle tissue in living organisms?
-Muscle tissue is crucial for movement in living organisms, with each type of muscle tissue serving specific functions related to movement and support.
How does the video illustrate the functions of the nervous tissue?
-Nervous tissue is responsible for transmitting signals throughout the body, coordinating responses, and processing information from the environment.
What are the visual aids mentioned in the video, and how do they support learning?
-The video refers to various diagrams and illustrations of different tissues to enhance understanding and facilitate visual learning of the concepts discussed.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

jaringan hewan (bahasa indonesia)
Media Pembelajaran Jaringan Hewan - Kelas Daring Biologi SMA Kelas XI

Animal Tissues

MATERI MARTIKULASI | JARINGAN TUBUH MANUSIA

what are tissues in human body, what are tissues made of, what are tissues class 9, Human tissues,

IMAT Biology Lesson 6.1 | Anatomy and Physiology | Animal Tissues Part I
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)