what are tissues in human body, what are tissues made of, what are tissues class 9, Human tissues,
Summary
TLDRThis video script explores the fundamental role of tissues in the human body, detailing four main types: epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous tissues. Epithelial tissues protect and secrete, while connective tissues provide support and elasticity. Muscle tissues enable movement and maintain posture, with three subtypes each serving specific functions. Nervous tissue, composed of neurons and neuroglia, transmits signals crucial for sensory perception and motor control. Together, these tissues form organs and systems essential for the body's proper functioning.
Takeaways
- 🧱 Tissues are the building blocks of our bodies, composed of specialized cells that perform specific tasks for the proper functioning of our body.
- 🔍 There are four main types of tissues in the human body: epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous tissues, each with unique functions.
- 🌐 Epithelial tissue is vital for protection, secretion, absorption, excretion, filtration, and sensory reception, and comes in simple and stratified forms.
- 👥 Connective tissue provides support and elasticity, includes loose and dense connective tissue, and specialized forms like cartilage, bone, and blood.
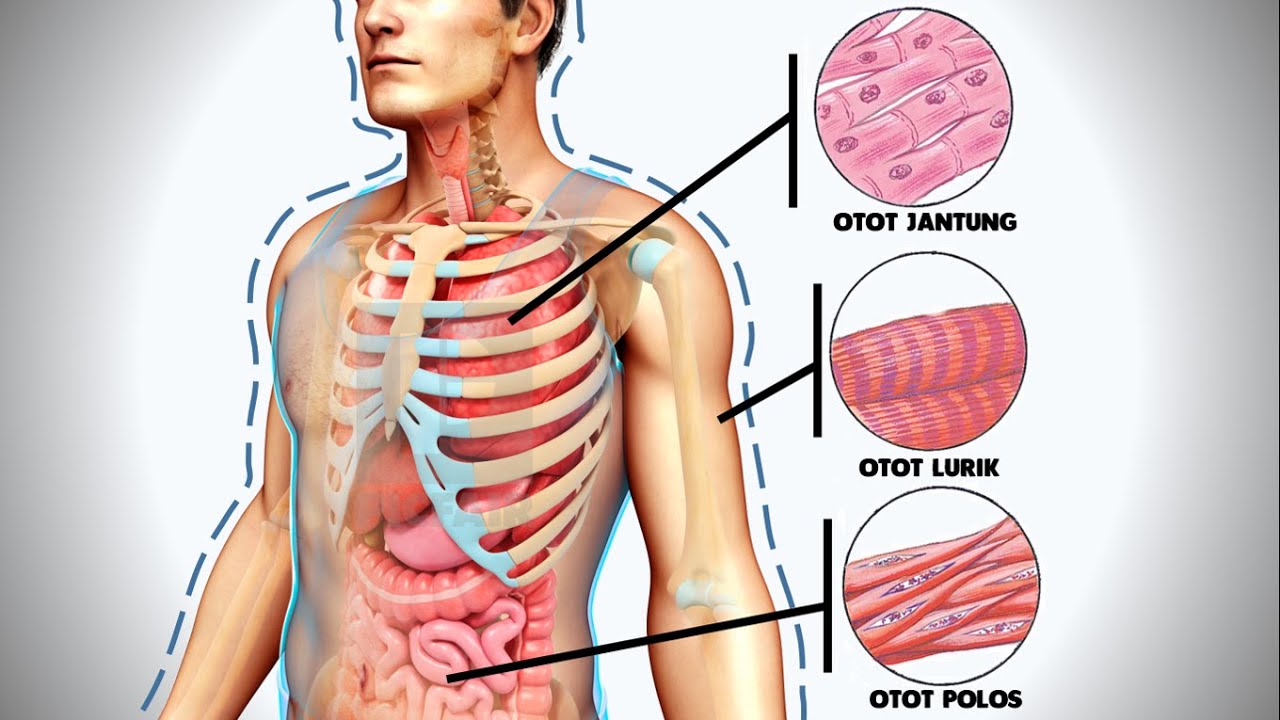
- 💪 Muscle tissue allows for movement, posture maintenance, and various functions, with three main types: skeletal, smooth, and cardiac.
- 🚀 Skeletal muscle is striated, under voluntary control, and responsible for physical activities like walking and lifting.
- 🌀 Smooth muscle is found in internal organs, lacks striations, and is regulated by the autonomic nervous system for processes like digestion.
- 💓 Cardiac muscle is found in the heart, striated with a branching pattern, and has its own electrical conduction system for heartbeat regulation.
- 🧠 Nervous tissue is composed of neurons and neuroglia, responsible for transmitting electrical impulses for sensory perception, motor control, and cognition.
- 🌿 Neurons have cell bodies, dendrites, and axons for signal reception and transmission, with myelin sheaths for increased speed.
- 🧬 The nervous system is divided into the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and the peripheral nervous system (all other nerves and ganglia).
Q & A
What are tissues and why are they important for the human body?
-Tissues are the building blocks of our bodies, consisting of groups of specialized cells that work together to perform specific tasks vital for the proper functioning of our body.
How many main types of tissues are there in the human body?
-There are four main types of tissues in the human body: epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous tissues.
What is the origin of the term 'epithelium' and what does it do?
-The term 'epithelium' comes from the Greek words 'epi' and 'theal', and it refers to the thin tissue forming the outer layer of a body's surface and lining the elementary canal and other hollow structures.
What are the two main types of epithelial tissue and where are they found?
-The two main types of epithelial tissue are simple epithelium, which is found in areas requiring rapid diffusion, and stratified epithelium, which is found in areas requiring protection.
What are some common subtypes of epithelial tissue and their functions?
-Common subtypes include squamous epithelium for protection or absorption, cuboidal epithelium for secretion or absorption, columna epithelium for secretion, and pseudostratified epithelium for both protection and secretion.
What are the functions of epithelial tissue?
-Epithelial tissue functions include protection, secretion, absorption, excretion, filtration, and sensory reception.
What are the main types of connective tissues and their functions?
-Main types of connective tissues include connective tissue proper (loose and dense), cartilage, bone, and blood. They provide structural support, protection, connection, storage, and transport of vital substances.
What are the three main types of muscle tissue and their primary functions?
-The three main types of muscle tissue are skeletal, smooth, and cardiac. Skeletal muscles are for voluntary movement, smooth muscles are for involuntary processes like digestion, and cardiac muscles are for the heartbeat.
How do the characteristics of nervous tissue contribute to its function?
-Nervous tissue is composed of neurons and neuroglia, allowing it to transmit electrical impulses for sensory perception, motor control, coordination, and communication.
What are the two main components of nervous tissue and their roles?
-The two main components of nervous tissue are neurons, which transmit nerve signals, and neuroglia, which provide support and protection to neurons.
How is the nervous system organized and what are its two main parts?
-The nervous system is organized into circuits and networks of neurons and is divided into the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and the peripheral nervous system (all other nerves and ganglia).
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)