Merasionalkan Penyebut Pecahan Bentuk Akar (1) - Matematika Kelas 9
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video from Angeles channel, the focus is on rationalizing the denominator of radical expressions, specifically the form \( \sqrt{a} \) and \( \sqrt{b} \). The method involves multiplying both the numerator and denominator by the conjugate of the denominator. The video explains three types of radicals and provides a step-by-step guide to simplify expressions like \( \frac{a+b}{\sqrt{c}} \). Examples are worked through, demonstrating how to simplify radical expressions by multiplying with conjugates and aiming for a square root in the denominator. The host encourages viewers to watch the entire video, subscribe, and engage with the content for a comprehensive understanding of rationalizing radical denominators.
Takeaways
- 📚 The video discusses the process of rationalizing the denominator of a radical fraction.
- 🔢 Rationalization involves multiplying both the numerator and the denominator by the conjugate of the denominator.
- 📐 There are three types of radical expressions: \( \sqrt{a} \), \( \sqrt{b} \), and \( \sqrt{a+b} \), and \( \sqrt{a-b} \).
- 📝 The conjugate of the denominator is crucial for the rationalization process, and it is formed by pairing the radical with its corresponding root.
- 📖 The video provides a step-by-step guide to understanding and performing the rationalization of radicals.
- 📐 The script includes examples to illustrate the process, such as rationalizing \( \frac{4\sqrt{5}}{\sqrt{5}+4\sqrt{5}} \) and \( \frac{\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{6}} \).
- 🔑 The video emphasizes the importance of simplifying the result by looking for perfect square factors within the radicals.
- 🎯 The video aims to be educational, particularly for those interested in learning mathematics.
- 💡 The presenter encourages viewers to watch the entire video for a complete understanding and not to skip any part.
- 🌐 The video is part of a series, with the next installment focusing on rationalizing the denominator of the form \( \sqrt{a+b} \) and \( \sqrt{a-b} \).
Q & A
What is the main topic discussed in the video?
-The main topic discussed in the video is rationalizing the denominator of radical expressions, specifically focusing on the form 'a per square root of b'.
What is the method used to rationalize the denominator of a radical expression?
-The method used to rationalize the denominator of a radical expression is to multiply both the numerator and the denominator by the conjugate of the denominator.
What are the three types of radical expressions mentioned in the video?
-The three types of radical expressions mentioned are 'a per square root of b', 'c per square root of a plus minus square root of b', and 'a plus minus square root of b'.
What does the term 'conjugate' refer to in the context of rationalizing denominators?
-In the context of rationalizing denominators, 'conjugate' refers to the expression that is formed by changing the sign of the radical part of the denominator.
How does the video suggest simplifying the expression 'a square root of b per square root of d'?
-The video suggests simplifying the expression 'a square root of b per square root of d' by multiplying it with the conjugate of the denominator, which is 'square root of b', resulting in 'a square root of b times square root of d'.
What is the purpose of multiplying by the conjugate in the rationalization process?
-The purpose of multiplying by the conjugate in the rationalization process is to eliminate the radical from the denominator, making the expression easier to work with.
Can you provide an example of rationalizing a denominator from the video?
-An example from the video is rationalizing the expression '4 per square root of 5'. The conjugate of the denominator 'square root of 5' is 'square root of 5', and multiplying the numerator and denominator by this conjugate results in '4 square root of 5 per square root of 25', which simplifies to '5'.
What is the significance of having a perfect square in the rationalization process?
-Having a perfect square in the rationalization process is significant because it allows for the radical to be simplified, making the expression more manageable.
How does the video handle the simplification of radicals in the denominator?
-The video handles the simplification of radicals in the denominator by multiplying the numerator and denominator by the conjugate and then simplifying by combining like terms and reducing the radicals to their simplest form.
What is the final step in rationalizing the denominator according to the video?
-The final step in rationalizing the denominator, as per the video, is to simplify the resulting expression by reducing any radicals that are perfect squares and combining like terms.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
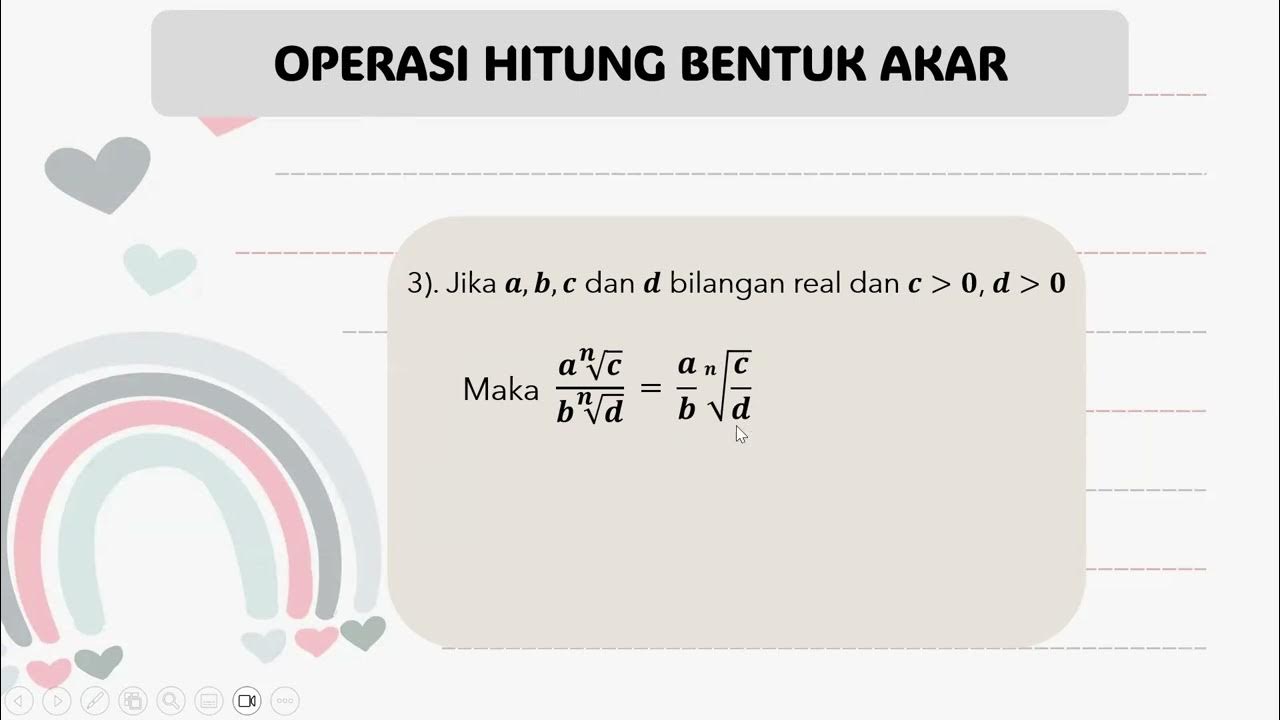
Asinkronus Topik Bentuk Akar W 2

Solving Quadratic Equations using Quadratic Formula

RACIONALIZAÇÃO DE DENOMINADORES RESUMÃO

Kurikulum Merdeka Matematika Kelas 8 Bab 1 Bilangan Berpangkat

Complete Integration and Derivative Formulae List | Easy Trick to Learn| Engineering Mathematics 2
Simplifying Radicals With Variables, Exponents, Fractions, Cube Roots - Algebra
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)