Incomplete Dominance and Codominance (Non- Mendelian Genetics)
Summary
TLDRThe Learning Science Channel's video delves into Mendelian inheritance patterns, focusing on incomplete dominance and co-dominance. In incomplete dominance, heterozygotes display an intermediate phenotype between homozygous parents, as exemplified by the red and white flowered goumamela plants producing pink offspring. Co-dominance, on the other hand, shows both parental traits in the offspring, like the red and white haired cattle resulting in a roan calf. The video uses Punnett squares to illustrate these concepts, emphasizing the importance of understanding non-Mendelian inheritance patterns in genetics.
Takeaways
- 🌟 Welcome to the Learning Science Channel, where educational videos on various scientific concepts are provided.
- 🎓 The channel covers topics in biology, chemistry, earth science, and physics, aiming to enhance understanding in these fields.
- 🔔 For new viewers, subscribing and enabling notifications is recommended to stay updated with the latest science lessons.
- 🧬 Today's lesson focuses on incomplete dominance and co-dominance, two patterns that deviate from Mendelian inheritance principles.
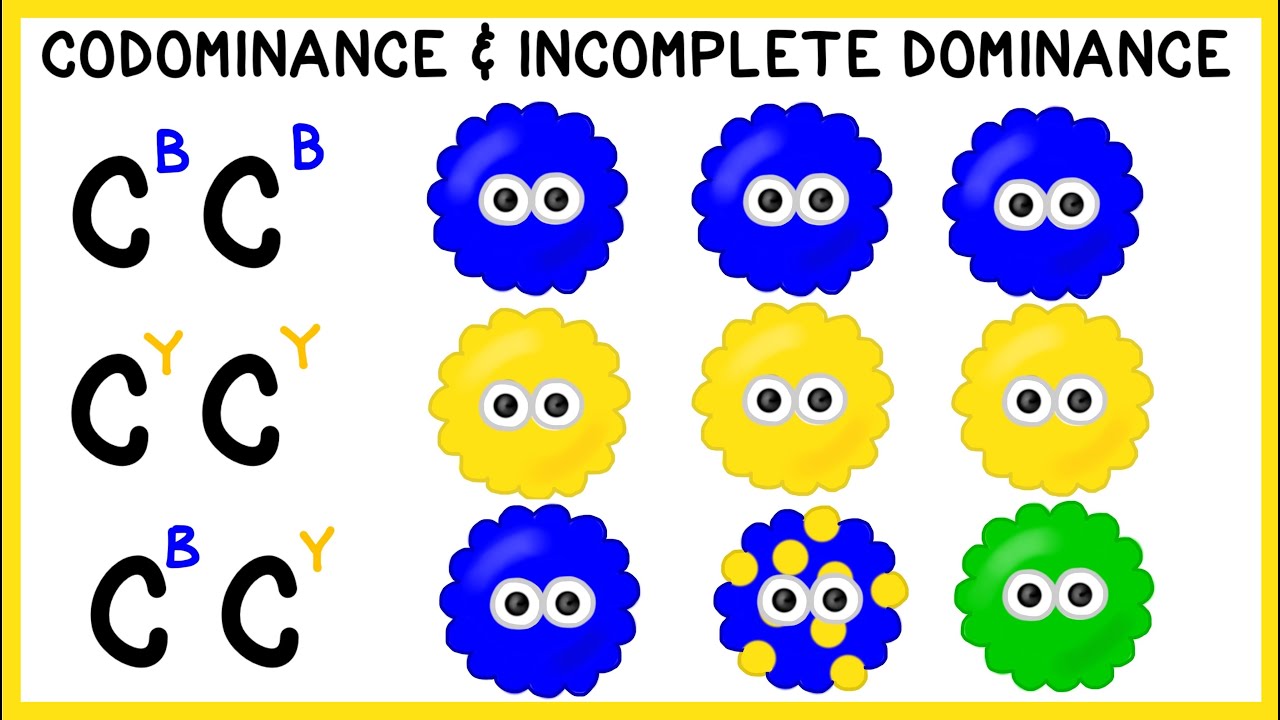
- 🌺 Incomplete dominance occurs when a heterozygote displays a phenotype intermediate between two homozygous phenotypes, with no allele being completely dominant.
- 🌸 An example of incomplete dominance is the cross between red and white flowered goumamela plants, resulting in pink-flowered offspring.
- 📊 Using a Punnett square, the genotypic and phenotypic ratios for incomplete dominance can be determined, often resulting in a 1:2:1 ratio.
- 🐄 Co-dominance is another non-Mendelian pattern where both alleles are expressed equally in the heterozygote, as seen in the red and white haired cattle cross.
- 🔍 The resulting offspring in co-dominance exhibits a phenotype that combines traits from both parents, such as a roan cattle with red and white hairs.
- 📚 Remember that in co-dominance, the phenotype of the heterozygote reflects both alleles, unlike typical dominance where one allele masks the other.
- 📝 The video concludes with a question to test the viewer's understanding of incomplete dominance in puppies, encouraging active participation and engagement.
Q & A
What is the main focus of the Learning Science Channel's video?
-The main focus of the video is to study incomplete dominance and co-dominance in the Mendelian patterns of inheritance.
What happens when the recessive gene is not observed in the presence of a dominant gene?
-The effects of the recessive gene are masked when the dominant gene is present, following Mendelian principles of heredity.
What is incomplete dominance and how does it differ from the Mendelian pattern of inheritance?
-Incomplete dominance is a non-Mendelian pattern of inheritance where a heterozygote shows a phenotype intermediate between the two homozygous phenotypes, with neither allele being completely dominant over the other.
Can you provide an example of incomplete dominance from the video?
-An example of incomplete dominance is the cross between a red-flowered and a white-flowered goumamela plant, resulting in a pink-flowered goumamela plant.
How is the phenotype of the offspring from a cross between two pink goumamela plants described in the video?
-The phenotypes of the offspring are red, pink, and white flowered goumamela plants, with a phenotypic ratio of 1:2:1 and a genotypic ratio of 1:2:1.
What is co-dominance and how does it manifest in inheritance?
-Co-dominance is a non-Mendelian pattern of inheritance where both alleles are expressed equally in the phenotype of the heterozygote, resulting in offspring that exhibit traits of both parents.
Give an example of co-dominance mentioned in the video.
-An example of co-dominance is when a red-haired cattle is crossed with a white-haired cattle, resulting in a roan cattle with red and white hairs.
How are the phenotypic and genotypic percentages calculated in the case of co-dominance with the roan cattle example?
-In the case of co-dominance with the roan cattle, the phenotypic percentage is 100% roan cattle, and the genotypic percentage is 100% RW.
What is the phenotypic ratio when a roan cattle is mated with a white cattle, as per the video?
-The phenotypic ratio when a roan cattle is mated with a white cattle is 2 roan cattle to 2 white cattle.
What is the significance of the Punnett square in understanding incomplete dominance and co-dominance?
-The Punnett square is used to predict the genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring in crosses involving incomplete dominance and co-dominance, helping to visualize the inheritance patterns.
How does the video conclude in terms of learning outcomes?
-The video concludes by encouraging viewers to apply their understanding of incomplete dominance and co-dominance to answer a question about puppy inheritance patterns.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

S9Q1W4-5 | Non-Mendelian Inheritance
Non-Mendelian Inheritance | Grade 9 Science Quarter 1 Week 4-5 | Maestrang Techy
Codominance and Incomplete Dominance: Non-Mendelian Genetics

NON-MENDELIAN GENETICS: INCOMPLETE DOMINANCE || GRADE 9 SCIENCE _ BIOLOGY

Non-Mendelian Genetics (Co-dominance): Knowledge Catalog Grade 9 Biology #8

Non-Mendelian Inheritance I FULL VIDEO
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)