NON-MENDELIAN GENETICS: INCOMPLETE DOMINANCE || GRADE 9 SCIENCE _ BIOLOGY
Summary
TLDRThis video lesson delves into non-Mendelian inheritance, focusing on incomplete dominance. It explains how, unlike Mendel's laws, certain traits in organisms, such as flower colors and human hair, blend due to the equal contribution of both alleles. The lesson showcases Gregor Mendel’s foundational work and introduces Carl Correns' experiment with four o'clock flowers, which led to the discovery of incomplete dominance. Examples across plants, animals, and humans highlight this genetic phenomenon, where offspring show intermediate traits, offering a deeper understanding of inheritance beyond Mendelian patterns.
Takeaways
- 😀 Gregor Mendel is known as the father of genetics, and he formulated the laws of heredity based on experiments with garden plants.
- 😀 Traits can be dominant (visible) or recessive (hidden), and these physical features are passed from one generation to the next through genes.
- 😀 Mendel's experiments showed complete dominance, where one allele (dominant) overpowers the other (recessive).
- 😀 Incomplete dominance is a non-Mendelian pattern of inheritance where neither allele is completely dominant, resulting in an intermediate phenotype.
- 😀 Carl Correns proposed the term incomplete dominance after experimenting with four o'clock flowers, where crossing red (dominant) and white (recessive) flowers resulted in pink offspring.
- 😀 The Punnett Square is used to predict the genetic outcomes of offspring, illustrating the combination of alleles from both parents.
- 😀 In incomplete dominance, the resulting phenotype is a blend of the parental traits, as seen in the pink four o'clock flowers.
- 😀 The F2 generation of incomplete dominance shows a 1:2:1 phenotypic ratio: 25% red, 50% pink, and 25% white flowers.
- 😀 Incomplete dominance does not involve complete blending but an intermediate expression of both alleles, which can still be distinguished in the genotype.
- 😀 Incomplete dominance is not limited to plants but also occurs in animals and humans, affecting traits like hair type, height, and skin color.
- 😀 Examples of incomplete dominance in animals include the blue-feathered chicken (cross of black and white parents) and varying fur lengths in rabbits and dogs.
Q & A
Who is considered the father of genetics, and why?
-Gregor Mendel is considered the father of genetics because he formulated the laws of heredity based on his experiments with garden plants. His work laid the foundation for understanding genetic inheritance.
What are the two types of traits Mendel identified?
-Mendel identified two types of traits: dominant traits, which are expressed and visible in an organism, and recessive traits, which are hidden or not expressed.
What is the main concept behind Mendel's experiments?
-Mendel's experiments showed that dominant traits are expressed over recessive traits, and that genes are passed from one generation to the next according to predictable patterns.
What is the focus of the video in terms of inheritance patterns?
-The video focuses on non-Mendelian inheritance patterns, specifically incomplete dominance, which occurs when the phenotype is an intermediate between two alleles.
Who proposed the term 'incomplete dominance' and what was the basis for this concept?
-The term 'incomplete dominance' was proposed by German botanist Carl Correns. He based his concept on experiments with four o'clock flowers, where the offspring displayed an intermediate pink color, showing neither red nor white dominance.
How does incomplete dominance differ from Mendel’s laws of inheritance?
-Incomplete dominance differs from Mendel's laws because in Mendel's patterns, one allele is completely dominant over the other, while in incomplete dominance, neither allele is completely dominant, resulting in a blended or intermediate phenotype.
What is the role of the Punnett Square in studying incomplete dominance?
-The Punnett Square is used to visually represent and predict the possible genotypes and phenotypes of offspring from a specific cross. It helps to understand how incomplete dominance works by showing the blending of alleles.
What was the result of the F1 generation in Carl Correns' experiment with four o'clock flowers?
-The result of the F1 generation in Carl Correns' experiment was that the offspring had pink-colored flowers, showing an intermediate phenotype between the red and white parent flowers.
What ratio of phenotypes was observed in the F2 generation of the four o'clock flowers?
-In the F2 generation, the phenotypes followed a 1:2:1 ratio: 25% red flowers, 50% pink flowers, and 25% white flowers.
What real-life examples of incomplete dominance are mentioned in the video?
-Real-life examples of incomplete dominance mentioned in the video include human hair and eye color, human height, skin color, and examples in animals like rabbits, chickens, and dogs.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

S9Q1W4-5 | Non-Mendelian Inheritance
Non-Mendelian Inheritance | Grade 9 Science Quarter 1 Week 4-5 | Maestrang Techy

Incomplete Dominance and Codominance (Non- Mendelian Genetics)
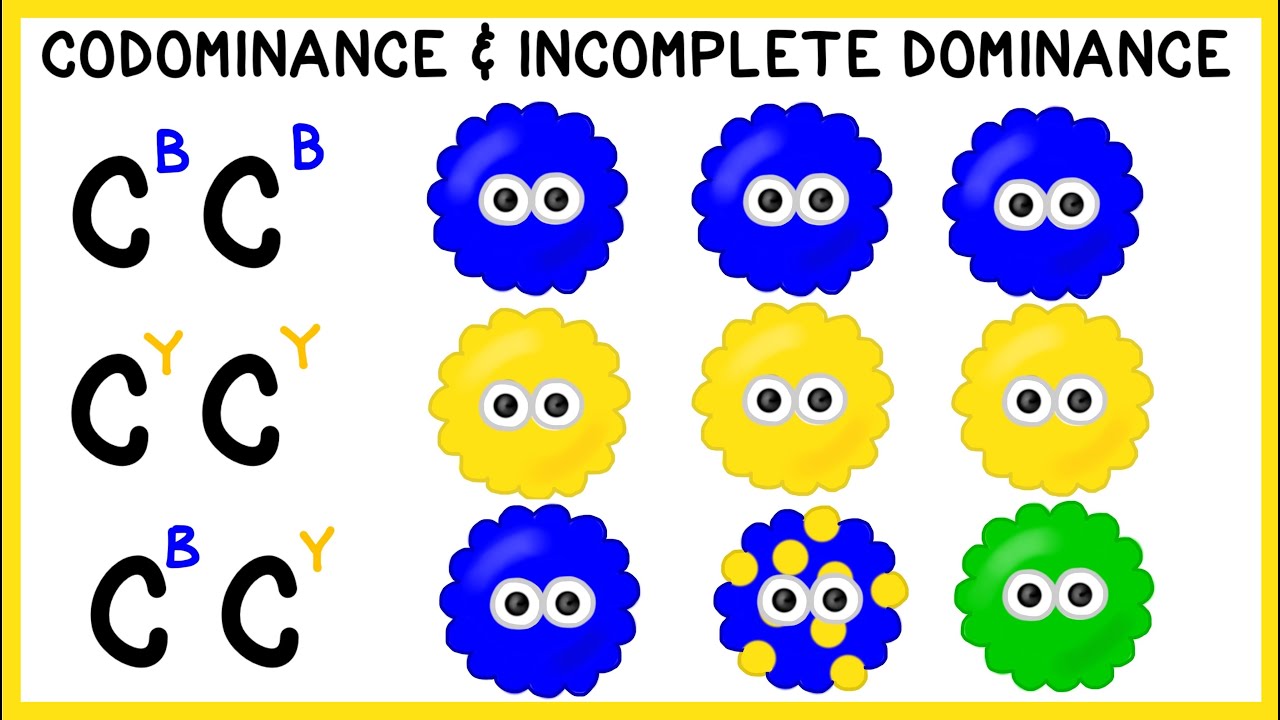
Codominance and Incomplete Dominance: Non-Mendelian Genetics

Non-Mendelian Genetics (Co-dominance): Knowledge Catalog Grade 9 Biology #8

The DNA and Non-Mendelian Genetics (Incomplete Dominance): Knowledge Catalog Grade 9 Biology #7
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)