ACCOUNTING BASICS: a Guide to (Almost) Everything
Summary
TLDRThis script introduces financial accounting as a process that involves identifying, recording, summarizing, and analyzing financial transactions to report them in financial statements. It uses the metaphor of a tree with various branches to describe the different types of accounting. The video follows the journey of Ruff Times, a tabloid newspaper, to explain key concepts such as double-entry accounting, the accounting equation, and the importance of adhering to the accrual method. It outlines the steps from journal entries to creating financial statements, including the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement, and concludes with the accounting cycle's role in reflecting a business's financial health.
Takeaways
- 🌳 Accounting is an ancient practice with various branches, including financial, managerial, tax, audit, and bookkeeping.
- 📈 Financial accounting involves identifying, recording, summarizing, and analyzing an entity's financial transactions for reporting purposes.
- 👋 James explains financial accounting in a simplified manner over a 10-minute video, aiming to provide a clear understanding of the topic.
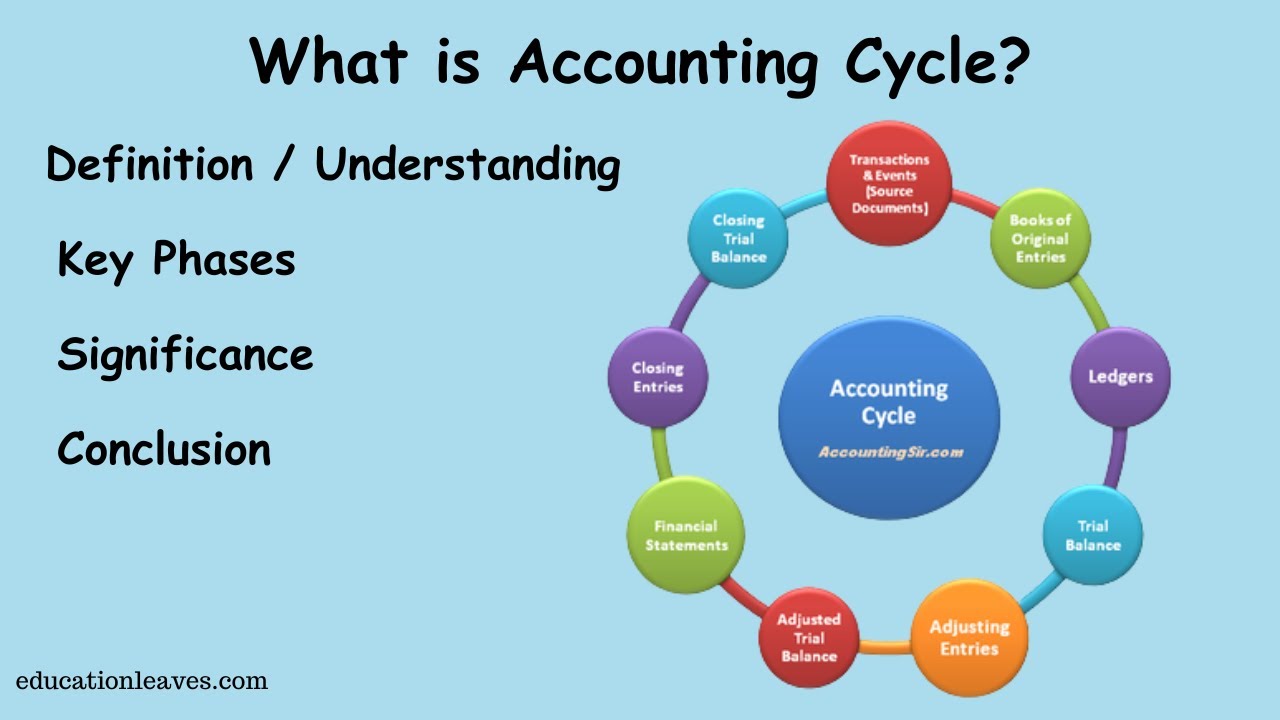
- 📚 The accounting equation (Assets = Liabilities + Equity) is the foundation of double-entry accounting and ensures that transactions always balance.
- 📝 Journal entries are the first step in recording financial transactions, consisting of a journal number, date, description, and debits/credits.
- 💼 Double-entry accounting requires that every transaction affects at least two accounts, with equal total debits and credits.
- 📋 The general ledger is a central database that stores all financial data, including accounts and journal entries, often managed through accounting software.
- 🔄 Adjusting entries are made at the end of a financial year to align financial records with the accrual method of accounting.
- 📊 Financial statements, including the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement, summarize a business's financial activities and health.
- 🔄 The accounting cycle is a series of steps that include identifying transactions, recording them, and preparing financial statements for the next accounting period.
Q & A
What is the primary purpose of financial accounting?
-The primary purpose of financial accounting is to identify, record, summarize, and analyze an entity's financial transactions and report them in financial statements.
What are the main branches of accounting mentioned in the script?
-The main branches of accounting mentioned are financial accounting, managerial accounting, tax accounting, audit, and bookkeeping.
What is the accounting equation?
-The accounting equation is Assets = Liabilities + Equity, which represents the fundamental principle that a business's assets are equal to its liabilities and equity.
How does double-entry accounting work?
-Double-entry accounting works on the principle that every transaction affects at least two accounts, with total debits equaling total credits, ensuring the accounting equation always balances.
What is the difference between cash accounting and accrual accounting?
-Cash accounting recognizes revenue when cash is received and expenses when they are paid out. Accrual accounting recognizes revenue as it is earned and records expenses as they are incurred, providing a more accurate reflection of a business's financial performance.
What is an adjusting entry in accounting?
-An adjusting entry is a journal entry made at the end of a financial period to ensure that revenues and expenses are recorded in the correct period, in accordance with the accrual method of accounting.
What are the three main financial statements?
-The three main financial statements are the balance sheet, the income statement, and the cash flow statement.
What is a trial balance in accounting?
-A trial balance is an internal report that summarizes the closing balances of all general ledger accounts, used to check for errors and ensure that debits and credits are in balance.
What is the purpose of closing entries in the accounting cycle?
-Closing entries are used to clear out temporary accounts like revenues, expenses, and dividends, resetting them to zero and preparing the books for the next financial period.
Why is it important for businesses to follow the accrual method of accounting?
-The accrual method of accounting is important because it provides a true and fair view of a business's financial health by recognizing revenues as they are earned and expenses as they are incurred, which is more accurate than cash accounting for financial reporting purposes.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)