What Are The Different Atomic Models? Dalton, Rutherford, Bohr and Heisenberg Models Explained
Summary
TLDRThis script takes viewers on a historical journey through the evolution of atomic theory, from Democritus' concept of atomos to Dalton's atomic model and beyond. It highlights key scientific milestones, such as the 'plum pudding' model by J.J. Thompson, Rutherford's discovery of the atomic nucleus, and Bohr's quantum theory. The narrative culminates with Schrödinger's quantum mechanical model, illustrating the profound transformation in our understanding of atomic structure and the relentless pursuit of knowledge.
Takeaways
- 🏀 The concept of 'basketball' often brings to mind an orange sphere or a favorite athlete's dunk.
- 🌐 Ancient Greek philosopher Democritus theorized that everything was made of 'atomos', meaning 'uncuttable', and that the properties of materials depended on the type of atomos they were composed of.
- 🔍 Aristotle's theory of four elements (earth, fire, water, air) largely discredited Democritus' theory.
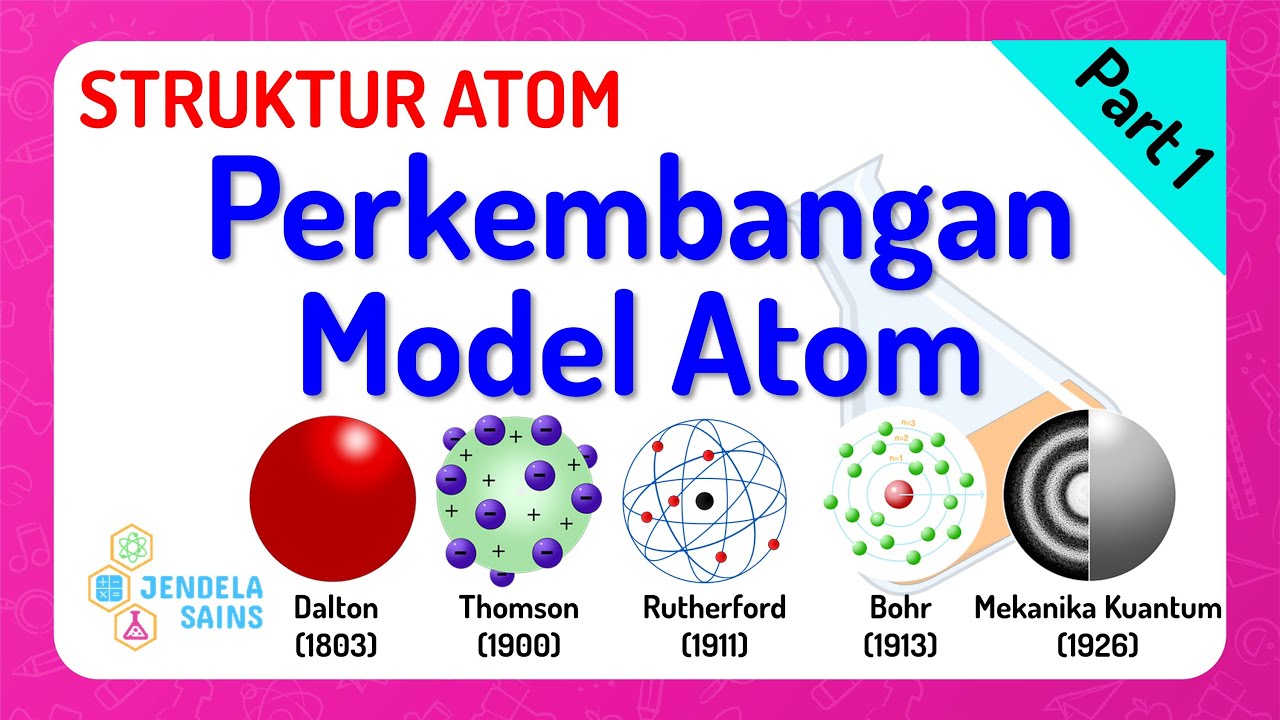
- 🧪 British chemist John Dalton proposed the law of multiple proportions and the theory of atomism, suggesting that everything is made up of unique atoms.
- 🔬 Dalton's atomic model described atoms as tiny, indestructible solid spheres, with different elements' atoms combining to form compounds.
- 🍮 J.J. Thompson's 'plum pudding' model depicted atoms as positively charged masses with tiny negative charges embedded, like plums in pudding.
- 🔳 Ernest Rutherford's gold-foil experiment led to a new atomic model, proposing a concentrated positively charged center (nucleus) with electrons orbiting around it.
- 🌐 Niels Bohr introduced the concept of quantized energy, suggesting electrons move in fixed orbits or shells around the nucleus.
- 🌌 Quantum mechanics, particularly the Heisenberg Uncertainty principle, challenged Bohr's model by stating it's impossible to know the exact position and trajectory of electrons.
- 🔬 Erwin Schrödinger's quantum mechanical model described electrons not in fixed orbits but as electron clouds in atomic orbitals, where the probability of finding an electron is highest.
Q & A
What was the first concept of atoms proposed by Democritus?
-Democritus proposed that everything in the world was made of tiny indestructible particles called 'atomos', which means 'uncuttable', and that the properties of materials depended on the type of atomos they were composed of.
How did Aristotle's view of the composition of the world differ from Democritus's theory?
-Aristotle believed that everything on the planet was made of four elements: earth, fire, water, and air, which was in contrast to Democritus's idea of 'atomos'.
What experiment led John Dalton to propose the law of multiple proportions and the theory of atomism?
-John Dalton conducted experiments where he mixed two gases and observed their behavior, particularly noting the fixed ratio in which gases reacted with each other.
What was the 'plum pudding' model of the atom proposed by J.J. Thompson?
-The 'plum pudding' model characterized an atom as a particle composed of a positively charged mass with tiny negative charges embedded in it, similar to plums in a pudding.
What experiment did Ernest Rutherford conduct to probe the structure of an atom?
-Rutherford conducted the gold-foil experiment, also known as the Geiger–Marsden experiment, which involved a thin sheet of gold foil and a screen coated with Zinc Sulphide to detect alpha particles.
What did Rutherford's observations of the gold-foil experiment lead to in terms of atomic structure?
-Rutherford proposed an atomic structure where most of the atom's mass was concentrated in a positively charged center, later named the nucleus, with electrons orbiting around it.
What discrepancy did Niels Bohr find in Rutherford's atomic model?
-Bohr found that if electrons were orbiting around a positively charged center, they would lose their energy and collapse into the nucleus, which contradicted the observed stability of atoms.
How did Niels Bohr's model of the atom address the issue of atomic stability?
-Bohr used the concept of quantized energy to propose that electrons moved in fixed orbits or shells around the nucleus, maintaining atomic stability by emitting or absorbing energy when jumping between these orbits.
What principle of quantum mechanics contradicts the idea of fixed electron orbits in Bohr's model?
-The Heisenberg Uncertainty principle states that it's impossible to know the exact position and trajectory of electrons in an atom, contradicting the fixed orbits in Bohr's model.
What is the significance of the quantum mechanical model of the atom proposed by Erwin Schrödinger?
-Schrödinger's model introduced the concept of electron clouds in atomic orbitals, where the probability of finding an electron is the highest, and formulated the Schrödinger-wave equations to calculate energy levels of electrons.
How does the evolution of atomic theory reflect the scientific pursuit of understanding the world?
-The evolution of atomic theory from Democritus to Schrödinger demonstrates a continuous scientific pursuit of deeper understanding, with each generation building upon and refining the ideas of their predecessors.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)