Kemagnetan : Medan Magnet dan Kemagnetan Bumi
Summary
TLDRThis educational video delves into the fascinating world of magnetism, explaining concepts such as magnetic fields, the Earth's magnetic field, and the phenomena of auroras. It covers the basics of how magnets attract objects, how the Earth's magnetic field protects us from harmful solar winds, and introduces the idea of magnetic declination and inclination. The video also emphasizes the importance of these concepts for navigators and explains how the Earth's magnetic poles differ from its geographic poles. A comprehensive guide to understanding the invisible forces shaping our planet and its environment.
Takeaways
- 😀 Magnetic fields are created by magnets and they attract certain materials, as shown by iron filings.
- 😀 Magnetic field lines always move from the north pole of the magnet to the south pole, and they never intersect.
- 😀 The strength of the magnetic field is greater where the magnetic field lines are closer together.
- 😀 Earth's magnetic field acts as a giant magnet, protecting the planet from harmful solar winds and solar flares.
- 😀 The compass needle points to the Earth's magnetic south pole, not the geographic north pole, due to the Earth's magnetism.
- 😀 The Earth's magnetic field protects us from the dangers of solar storms, as seen in phenomena like auroras.
- 😀 Magnetic declination is the angle between the geographic north and the magnetic north indicated by a compass, which varies by location.
- 😀 Magnetic inclination is the angle of the magnetic field relative to the Earth's surface, which changes as you get closer to the poles.
- 😀 Navigators must account for both magnetic declination and inclination when using a compass, especially near the magnetic poles.
- 😀 The magnetic field's protective function is essential in shielding us from solar storms, demonstrated by auroras at the poles.
- 😀 Understanding the differences between geographic and magnetic poles is crucial for accurate navigation using a compass.
Q & A
What is magnetism and what is discussed in the video?
-The video discusses the concept of magnetism, specifically the magnetic field and how it works around magnets. It explains that a magnet has the property of attracting other objects, and around it, there are magnetic field lines that guide this attraction.
What is the direction of the magnetic field lines around a magnet?
-Magnetic field lines move from the north pole of the magnet to the south pole. The field lines never intersect, and their density indicates the strength of the magnetic field.
How does the strength of a magnetic field vary in different areas of a magnet?
-The strength of the magnetic field is stronger where the magnetic field lines are closer together. Conversely, where the lines are more spread out, the field strength is weaker.
What is the relationship between Earth's magnetic field and the compass needle?
-The compass needle points toward the Earth's magnetic poles, which are not aligned perfectly with the geographical poles. The needle points toward the magnetic south pole of Earth, which is located near the Earth's geographic north pole.
What role does Earth's magnetic field play in protecting the planet?
-Earth's magnetic field protects us from harmful solar wind and solar flares. These phenomena can cause disruptions in electronic devices, but the magnetic field shields the Earth from their full effects.
What is Aurora Borealis and how does it relate to Earth's magnetic field?
-Aurora Borealis (Northern Lights) is a phenomenon caused by the interaction of the Earth's magnetic field with charged particles from the sun. The magnetic field deflects these particles, and when they collide with the atmosphere, they create beautiful light displays.
What is magnetic declination and how does it affect compass readings?
-Magnetic declination is the angle of deviation between the geographic north and the magnetic north. The compass needle does not always point directly to the geographic north because of this difference, which can vary by location.
What is magnetic inclination and why is it important for navigational tools like compasses?
-Magnetic inclination refers to the angle at which the magnetic field lines enter or leave the Earth's surface. This angle changes based on the location on Earth and affects how the compass needle behaves, especially near the poles.
How do the magnetic poles of the Earth differ from the geographic poles?
-The Earth's magnetic poles are different from its geographic poles. The magnetic north pole is located near the geographic south pole, and the magnetic south pole is near the geographic north pole. This misalignment causes variations in compass readings.
Why do sailors need to be cautious when navigating near the magnetic poles?
-Sailors need to be cautious near the magnetic poles because the compass readings can become unreliable due to the steep magnetic inclination. The compass needle can behave unpredictably, and readings can change rapidly as they get closer to the poles.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео

KEMAGNETAN KELAS 9 part 2 - MEDAN MAGNET DAN MAGNET BUMI
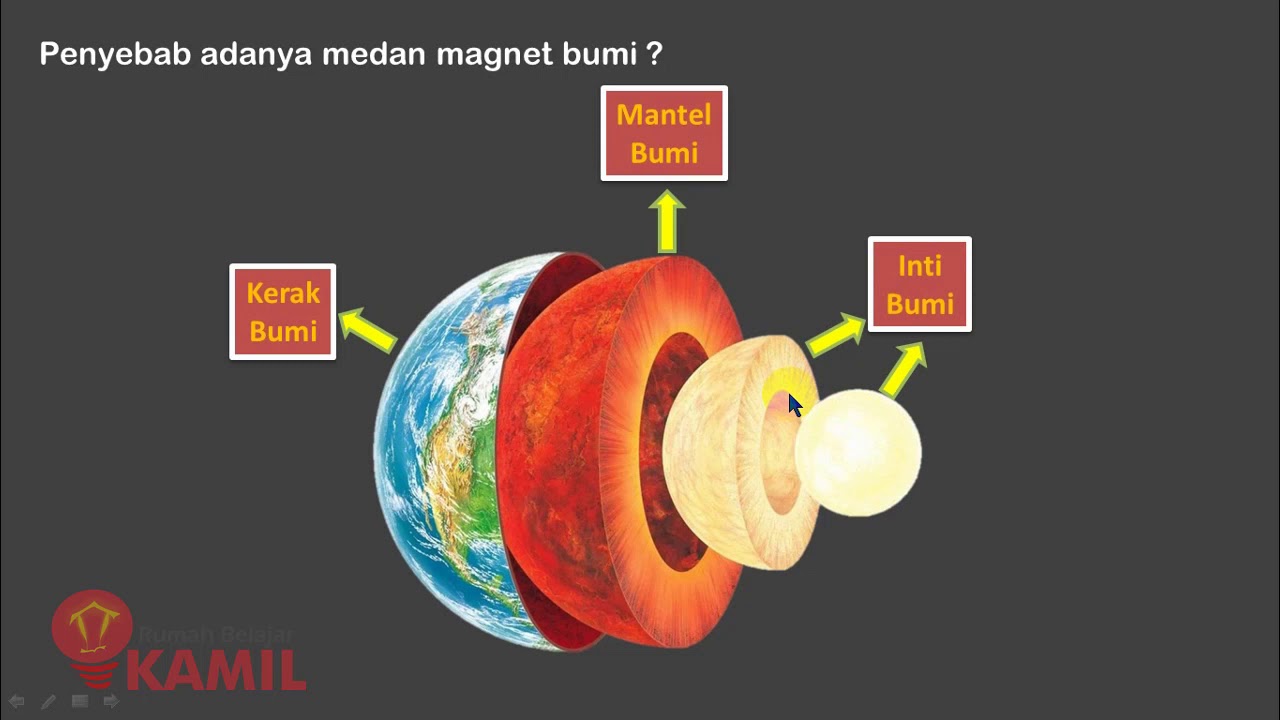
IPA Kelas 9 Semester 2 : Kemagnetan (Part 2 : Medan Magnet dan Magnet pada Bumi)

Magnetostatika bagian 1

Teori Kemagnetan Bumi Kelas 9 Semester Genap

Basic Theory of Magnetism | Magnetic Force Concept | Earth Magnetism Theory - Magnetism | IPA Class9
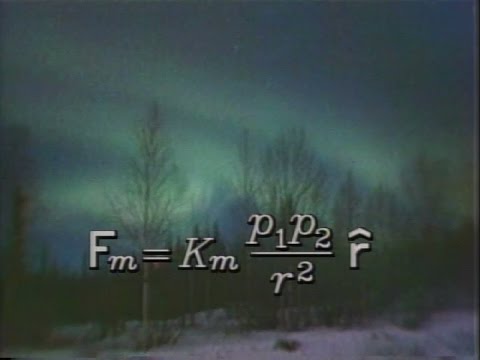
Episode 34: Magnetism - The Mechanical Universe
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
