Basic Theory of Magnetism | Magnetic Force Concept | Earth Magnetism Theory - Magnetism | IPA Class9
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the fascinating world of magnetism, beginning with the concept of magnetic force and the Earth's magnetism. It covers the discovery of magnets, the types of magnetic materials, and how magnets are made through rubbing, induction, and electromagnetism. The video highlights everyday applications of electromagnets, such as in electric bells and telephones. It also explains the Earth's magnetic field, its protective role against cosmic radiation, and how it contributes to phenomena like the aurora. Overall, it offers a comprehensive introduction to the principles and uses of magnetism.
Takeaways
- 😀 The term 'magnet' originates from 'magnitis lithos', meaning 'magnesia stone', named after the region of Manisa in ancient Greece where magnetic stones were first discovered.
- 😀 Magnets have two poles, a north pole and a south pole. These poles always exist together, and similar poles repel while opposite poles attract.
- 😀 Magnets are made from materials like iron and steel, which can be magnetized by rubbing them in a fixed direction or by induction.
- 😀 The Earth's magnetic field is similar to that of a giant magnet with magnetic north and south poles, and this magnetic field plays a crucial role in protecting life on Earth.
- 😀 Materials are classified into three groups based on their magnetic properties: ferromagnetic (strong attraction to magnets), paramagnetic (weak attraction), and diamagnetic (no attraction).
- 😀 Magnets can be created by rubbing iron with a magnet or by using a coil of wire and DC current, which induces magnetism in the material.
- 😀 Electromagnets are created by wrapping iron or steel with a conducting wire, and the direction of the current determines the magnetic poles of the material.
- 😀 Everyday applications of electromagnets include electric bells, switches, and landline telephones, where the current causes an iron core to act as an electromagnet and perform specific functions.
- 😀 The Earth's magnetic field causes phenomena such as auroras when charged particles from the Sun are trapped near the magnetic poles and ionize the atmosphere.
- 😀 The Earth's magnetic field protects us from harmful cosmic radiation and solar particles, which would otherwise be dangerous to life on Earth.
Q & A
What is the origin of the word 'magnet'?
-The word 'magnet' comes from the Greek term 'magnitis lithos', which means 'magnesia stone'. Magnesia was an ancient region in Greece, now part of Turkey, where magnetic stones were first discovered.
How can you determine the poles of a bar magnet?
-You can determine the poles of a bar magnet by placing it on a cork and floating it in water. The tip pointing towards the north is the north pole, and the tip pointing towards the south is the south pole.
What happens when like magnetic poles are brought together?
-Like magnetic poles will repel each other. For example, a north pole will repel another north pole, and a south pole will repel another south pole.
What is the difference between ferromagnetic, paramagnetic, and diamagnetic materials?
-Ferromagnetic materials, such as iron and steel, are strongly attracted to magnets. Paramagnetic materials, like magnesium, are weakly attracted to magnets. Diamagnetic materials, such as gold and copper, are not attracted to magnets at all.
How is magnetism induced in a material like iron?
-Magnetism can be induced in a material like iron by rubbing it in one direction with a magnetic pole. This aligns the elementary magnets (tiny magnetic regions) inside the material, making it behave like a magnet.
What is an electromagnet and how is it created?
-An electromagnet is created by wrapping a coil of wire around a piece of iron or steel and passing a direct current (DC) through the wire. This creates a magnetic field, turning the iron or steel into a magnet. The direction of the current determines the polarity of the poles.
Give an example of how electromagnets are used in everyday life.
-Electromagnets are used in electric bells. When the bell button is pressed, current flows through a coil, turning an iron core into an electromagnet that moves a striker to hit the bell, causing it to ring.
What happens when a material is heated or hammered to demagnetize it?
-When a material is heated or hammered, the elementary magnets inside become misaligned, causing the material to lose its magnetic properties.
How does Earth's magnetic field protect life on Earth?
-Earth's magnetic field protects life by deflecting cosmic radiation and electric particles from the Sun and other celestial bodies. These particles are drawn toward the magnetic poles, where they ionize and create auroras, preventing harmful radiation from reaching the surface.
What is meant by the term 'declination' in relation to Earth's magnetic field?
-Declination refers to the difference between the geographic poles and the magnetic poles of the Earth. The Earth's magnetic poles are not perfectly aligned with the geographic poles, which causes this misalignment.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
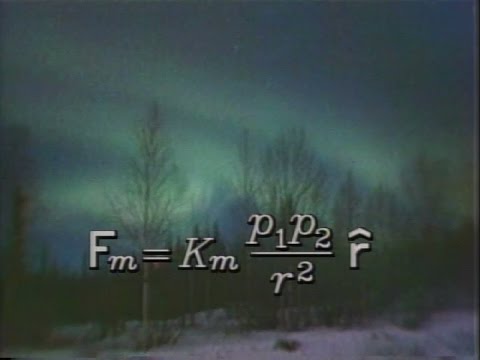
Episode 34: Magnetism - The Mechanical Universe

Magnetism | The Dr. Binocs Show | Educational Videos For Kids

KEMAGNETAN KELAS 9 part 2 - MEDAN MAGNET DAN MAGNET BUMI

Física - Magnetismo: imãs e campo magnético

El magnetismo terrestre Carl Friedrich Gauss Física Geofísica
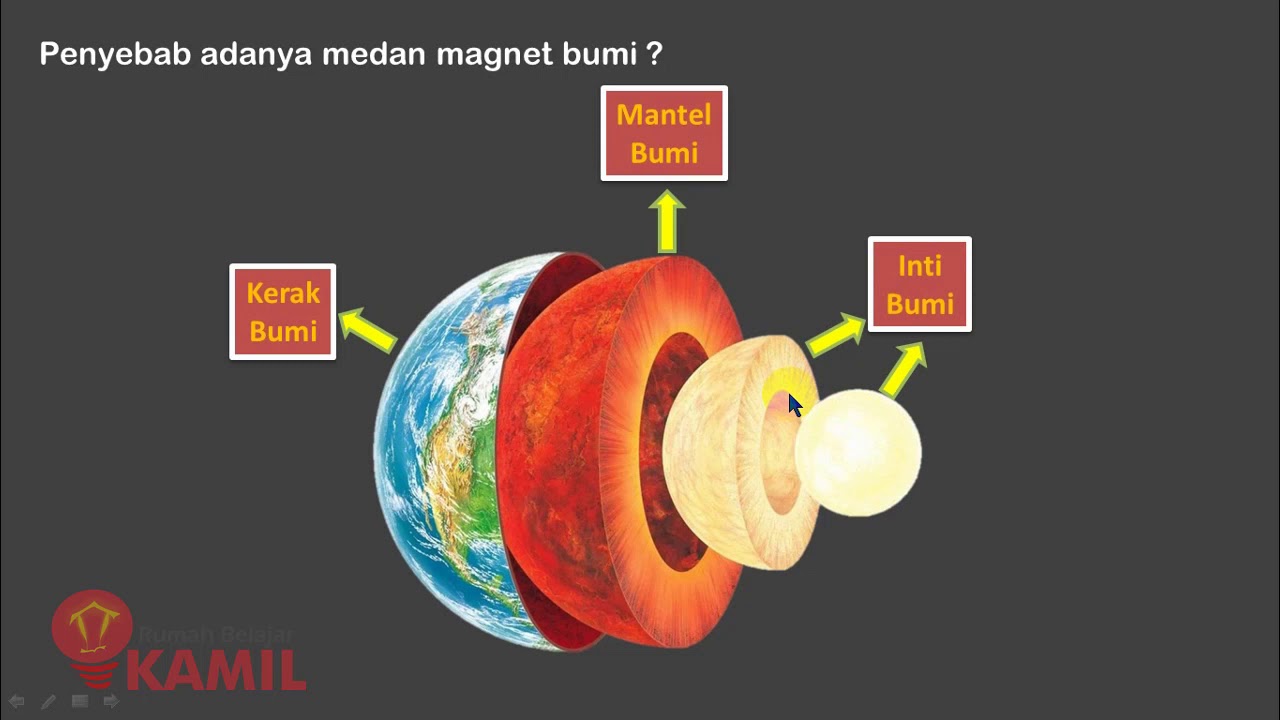
IPA Kelas 9 Semester 2 : Kemagnetan (Part 2 : Medan Magnet dan Magnet pada Bumi)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)